(Press-News.org) Certain medical students may be more likely to stay in their own countries or work in rural areas of their own countries when they qualify as doctors, suggests a study published on bmj.com today.
Given that many low income countries have insufficient doctors to meet their needs, particularly in rural areas, the authors suggest that policy makers could use this evidence to adjust entrance criteria for medical schools that favour subsequent practice in less well served areas of their country.
Previous studies have shown that, in high income countries, doctors with rural backgrounds are more likely to work in rural locations of their own countries. So could certain characteristics of medical students in low income countries be associated with graduate doctors staying to practice in that country or in its rural areas?
A team of researchers based in Nepal set out to test this theory. They tracked 710 graduate doctors from the first 22 classes (1983-2004) of Nepal's first medical college, the Institute of Medicine, to their current practice locations.
To determine which characteristics predicted working in underserved areas, they analysed seven factors including sex, age entering medical school, place of birth, place of high school, type of pre-medical education, and academic rank.
A total of 193 (27%) doctors were working in Nepal's rural districts, 261 (37%) were working in the capital Kathmandu, and 256 (36%) were working abroad.
Of those working abroad, 188 (73%) were in the United States and later graduating classes were more likely to be working in foreign countries.
Those with pre-medical education as paramedics (a common route into medicine in Nepal) were twice as likely to be working in Nepal and 3.5 times as likely to be in rural Nepal, compared with students with a college science background.
Students who were academically in the lower third of their medical school class were twice as likely to be working in rural Nepal as those from the upper third.
After adjusting for all variables, a paramedical background was independently associated with a doctor remaining in Nepal, while rural birthplace and older age entering medical school were each independently associated with a doctor working in rural Nepal.
The authors say that their findings need to be validated in other settings, but they suggest that policy makers in medical education who are committed to producing doctors for underserved areas of their country could use this evidence to revise entrance criteria for medical school. This may result in more of the graduating class "staying home," they conclude.
INFORMATION: END
A paper published on bmj.com today suggests that over 1000 people have committed suicide due to the 2008-2010 economic recession in the UK (846 men and 155 women).
Suicides began to rise in the UK in 2008 following 20 years of decline - suicides rose 8% among men and 9% among women in 2008, compared to 2007. And even though suicides did begin to fall in 2010 figures were still above the 2007 averages.
Previous studies have concluded that unemployment does increase the risk of suicide and non-fatal self-harm but while suicides tend to increase during economic downturns, ...
In a cautionary editorial alongside a related article in today's issue of the British medical journal BMJ, leading experts in health policy and behavioral economics argue that pay-for-performance (P4P) schemes – which financially reward doctors and hospitals for hitting specific, numerical targets in such matters as preventing hospital readmissions or prescribing certain drugs – are likely to do more harm than good.
Such schemes are being adopted as a key component of the Accountable Care Organization strategy mandated by the 2010 health reform and are now part of the ...
In a major breakthrough, an international team of scientists has proven that addiction to morphine and heroin can be blocked, while at the same time increasing pain relief.
The team from the University of Adelaide and University of Colorado has discovered the key mechanism in the body's immune system that amplifies addiction to opioid drugs.
Laboratory studies have shown that the drug (+)-naloxone (pronounced: PLUS nal-OX-own) will selectively block the immune-addiction response.
The results – which could eventually lead to new co-formulated drugs that assist patients ...
When a carnivore becomes extinct, other predatory species could soon follow, according to new research. Scientists have previously put forward this theory, but a University of Exeter team has now carried out the first experiment to prove it.
Published today (15 August 2012) in the Royal Society journal Biology Letters, the study shows how the demise of one carnivore species can indirectly cause another to become extinct. The University of Exeter team believes any extinction can create a ripple effect across a food web, with far-reaching consequences for many other animals. ...
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- From an engineer's perspective, plants such as palm trees, bamboo, maples and even potatoes are examples of precise engineering on a microscopic scale. Like wooden beams reinforcing a house, cell walls make up the structural supports of all plants. Depending on how the cell walls are arranged, and what they are made of, a plant can be as flimsy as a reed, or as sturdy as an oak.
An MIT researcher has compiled data on the microstructures of a number of different plants, from apples and potatoes to willow and spruce trees, and has found that plants exhibit ...
It's become a sport of sorts, predicting the low point of Arctic sea ice each year. Expert scientists with decades of experience do it but so do enthusiasts, whose guesses are gamely included in a monthly predictions roundup collected by Sea Ice Outlook, an effort supported by the U.S. government.
When averaged, the predictions have come in remarkably close to the mark in the past two years. But the low and high predictions are off by hundreds of thousands of square kilometers.
Researchers are working hard to improve their ability to more accurately predict how much ...
Girls with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) – and their families – often look forward to the likely decline in visible symptoms such as fidgety or disruptive behavior as they mature into young women.
However, new findings from UC Berkeley caution that, as they enter adulthood, girls with histories of ADHD are more prone to internalize their struggles and feelings of failure – a development that can manifest itself in self-injury and even attempted suicide.
"Like boys with ADHD, girls continue to have problems with academic achievement and relationships, ...
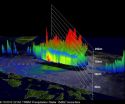
An intensifying Tropical storm called Kai-Tak (locally known as Helen) is causing more rain in the Philippines as it passes over northern Luzon. The Philippines have had a very wet month with the capital of Manila experiencing massive flooding earlier this month. NASA's TRMM satellite identified where the heavy rain was falling.
Kai-tak has caused another day of warnings in the Philippines. On August 14, Public storm warning signal #1 is in effect for these provinces in Luzon: La Union, Nueva Ecija, Pangasinan, Rest of Aurora, and Tarlac.
In addition, Public storm warning ...
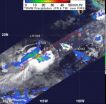
Tropical Storm Hector is battling wind shear over the open waters of the Eastern Pacific Ocean, and NASA satellite data shows that has been affecting its organization and rainfall rates.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite known as TRMM is managed by both NASA and the Japanese Space Agency. From its orbit in space, TRMM's instruments can estimate rainfall from tropical cyclones.
The TRMM satellite captured rainfall rates from Tropical Storm Hector on August 14, 2012 1:28 a.m. EDT. TRMM data showed that Hector had a small area of moderate to heavy rainfall ...
VIDEO:
Filmed at 10,000 frames per second by Japan's NHK television, movies like this of electromagnetic bursts called "sprites " will help scientists better understand how weather high in the atmosphere relates...
Click here for more information.
High above the clouds during thunderstorms, some 50 miles above Earth a different kind of lightning dances. Bursts of red and blue light, known as "sprites," flash for a scant one thousandth of a second. They are often ...