(Press-News.org) Munich, Germany – August 28 2012: Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation (Afib) is safe and suppresses arrhythmia recurrences in 74% of patients after a single procedure, according to results from the one-year follow-up of the Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Pilot Study, the first European registry to evaluate the real-life epidemiology of catheter ablation for AFib. The survey also showed that arrhythmia-related symptoms such as palpitations, shortness of breath, fatigue or dizziness - present in 86% of patients before the ablation - were significantly reduced.
The findings were presented today at ESC Congress 2012 by Dr Elena Arbelo from Hospital Clínic de Barcelona, Spain, a co-investigator of the study.
"Atrial fibrillation is the most frequent heart rhythm disorder and it represents a highly significant burden of disease and expenditure throughout the world," explained Dr Arbelo. "The currently available pharmacological therapies are not 100% effective, and they have secondary effects."
While symptoms remain the major reason for Afib ablation, patients also welcome a drug-free life-style. The principal ablation strategy is the isolation of the pulmonary veins with additional linear and/or fragmented electrogram ablation in 10-20% of patients.
The AFib Ablation Pilot Study, the first registry to evaluate the day-to-day diagnostic and therapeutic processes of AFib ablation in Europe, is a prospective, multicentre, 12-month observational study which recruited 1410 patients from 10 different European countries (Belgium, Czech Republic, Denmark, France, Germany, Greece, Italy, Netherlands, Poland, Spain).
Results from the in-hospital phase of the study were presented ESC Congress 2011 and showed that two-thirds of patients having catheter ablation have paroxysmal AFib, and up to 40% have no apparent underlying cardiac disorder.(1)
Now, results from the 12-month follow-up visit period provide further details of real-life outcomes:
Over the study period 77% of patients visited the clinic in person for review; however, at the 12-month follow-up 42% of the evaluations were by telephone.
Over half of the study population became asymptomatic after the ablation procedure (symptoms were present in 90% of patients at baseline).
76% of patients had a periodical ECG to document arrhythmia recurrence, and only 50% of patients had Holter monitoring.
One-third of patients had a transthoracic echocardiogram during follow-up. Other tests such as cardiac CT or MRI were rare.
Almost 20% of patients had a second ablation procedure.
At 12 months around half of the study population were taking anticoagulants and 43% antiarrhythmic drugs. At discharge, 97% of patients had been prescribed anticoagulants and 67% antiarrhythmic medication.
The procedure was considered successful in 74% of patients, meaning no documented arrhythmias after a 3-month blanking period. However, just over 50% of patients were still taking antiarrhythmic drugs.
Complications during the first year after the ablation were infrequent (2.6%), and mainly related to cerebrovascular events (0.54%) or vascular injuries (0.71%). There were four deaths: one secondary to hemorrhagic stroke, one for a non-cardiovascular cause and two of unknown origin.
"The information obtained by the registry reflects everyday practice across Europe," said Dr Arbelo. "It is remarkable to see how most hospitals are evaluating the results of catheter ablation in a much more practical way than what is recommended for clinical trials, basing it mainly on periodical electrocardiograms and occasional Holter monitoring." She added that the results offer no clear definition how a successful procedure is defined - by abolition of symptoms or the absence of arrhythmias without antiarrhythmic drugs.
Commenting on the first-year information derived from the pilot registry, Dr Arbelo said: "Atrial fibrillation is a major cardiovascular challenge in modern society and its medical and socioeconomic impact is expected to rise over the coming years. The AFib Ablation Registry provides an exceptional insight into the impact which catheter ablation may have in the management of patients with this arrhythmia."
###
Notes to editors
Please note that the author's photo and CV as well as the spokesperson's CV can be found here
1. Arbelo E, Brugada J, Hindricks G, et al. ESC-EURObservational Research Programme: The Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Pilot Study, conducted by the European Heart Rhythm Association. Europace 2012; 14: 1094-1103.
About the European Society of Cardiology www.escardio.org
The European Society of Cardiology (ESC) represents more than 75,000 cardiology professionals across Europe and the Mediterranean. Its mission is to reduce the burden of cardiovascular disease in Europe.
About ESC Congress 2012
The ESC Congress is currently the world's premier conference on the science, management and prevention of cardiovascular disease. ESC Congress 2012 takes place 25-29 August at the Messe München in Munich. The scientific programme is available at: http://spo.escardio.org/Welcome.aspx?eevtid=54
More information is available from the ESC Press Office at press@escardio.org.
Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation: Results from the first European registry
2012-08-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
CT angiography and perfusion to assess coronary artery disease: The CORE320 study
2012-08-28
Munich, Germany – August 28 2012: A non-invasive imaging strategy which integrates non-invasive CT angiography (CTA) and CT myocardial perfusion imaging (CTP) has robust diagnostic accuracy for identifying patients with flow-limiting coronary artery disease in need of myocardial revascularisation, according to results of the CORE320 study presented here today by Dr Joao AC Lima from Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, USA.
The CORE320 study is a prospective multicentre international trial which evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of combined non-invasive CTA and CTP as compared ...
Chinese scientists successfully crack the genome of diploid cotton
2012-08-28
August 28, 2012, Shenzhen, China – The international research team led by Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences and BGI have completed the genome sequence and analysis of a diploid cotton-- Gossypium raimondii. The cotton genome provides an invaluable resource for the study and genetic improvement of cotton quality and output, and sheds new lights on understanding the genetic characteristics and evolutionary mechanism underlying cotton and its close relatives. The study was published online in Nature Genetics. (http://www.nature.com/ng/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/ng.2371.html).
Cotton, ...
The FAME 2 trial
2012-08-28
Munich, Germany – August 28 2012: Patients with stable coronary artery disease (CAD) had a lower need for urgent revascularisation when receiving fractional flow reserve (FFR)-guided PCI plus the best available medical therapy (MT) than when receiving MT alone. The results, from a final analysis of the FAME 2 trial, were presented today during a Hot Line session of ESC Congress 2012 in Munich. Treatment guided by fractional flow reserve assessment helped reduce the risk of urgent revascularisation by a factor of eight.
The FAME 2 (FFR-Guided Percutaneous Coronary Intervention ...
Zebrafish study explains why the circadian rhythm affects your health
2012-08-28
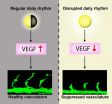
Disruptions to the circadian rhythm can affect the growth of blood vessels in the body, thus causing illnesses such as diabetes, obesity, and cancer, according to a new study from Linköping University and Karolinska Institutet in Sweden.
The circadian rhythm is regulated by a "clock" that reacts to both incoming light and genetic factors.
In an article now being published in the scientific journal Cell Reports, it is demonstrated for the first time that disruption of the circadian rhythm immediately inhibit blood vessel growth in zebra fish embryos.
Professor Yihai Cao ...
Global platelet reactivity and high risk ACS patients
2012-08-28
Global platelet reactivity is more effective than responsiveness to clopidogrel in identifying acute coronary syndrome (ACS) patients at high risk of ischemic events, according to research presented at ESC Congress 2012.
The results from the RECLOSE 2-ACS study were presented by Dr Rossella Marcucci from the University of Florence.
The Responsiveness to Clopidogrel and Stent thrombosis 2 – ACS (RECLOSE 2-ACS) study is a prospective, observational, referral centre cohort study of 1,789 patients with acute coronary syndromes undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention ...
Botany student proves 'New England Banksia' a distinct species
2012-08-28
The New England Banksia is largely restricted to the eastern edge of the New England Tableland, and is common in places along Waterfall Way. Ms Stimpson's research has raised this flowering plant, until now classified as a variety of the Hairpin Banksia (B. spinulosa), to the taxonomic level of a distinct species. The study was published in the open access journal PhytoKeys.
"I love the Proteaceae – the family of flowering plants that includes the Banksia and Grevillea genera in Australia and Protea in South Africa," Ms Stimpson said. "Surprisingly, molecular evidence ...
Women 40% less likely to die after TAVI than men
2012-08-28
Munich, Germany – August 27 2012: Women with severe aortic stenosis are 40% less likely to die after transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) than men, reveals the latest data from the largest study to date of gender differences in outcomes after TAVI. The findings were presented at ESC Congress 2012 by Professor Karin Humphries from St. Paul's Hospital.
More than 1.5 million people in the US suffer from aortic stenosis, a progressive disease where the aortic valve becomes obstructed, leading to life-threatening heart problems. If left untreated, half of all patients ...
TAVI improves quality of life in patients with severe aortic stenosis for at least 1 year
2012-08-28
Munich, Germany – August 28 2012: Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) leads to meaningful improvements in health-related quality of life in patients with severe aortic stenosis that are maintained for at least 1 year, according to a study presented at ESC Congress 2012. The results from the German transcatheter aortic valve interventions registry were presented by Professor Till Neumann, MD, from Essen, Germany.
Aortic stenosis is the most common valvular heart disease with increasing incidence especially with regard to the ageing of the population. Today, ...
Lifestyle changes could prevent 400 cardiac events and 200 deaths in Swedish PCI patients
2012-08-28
Munich, Germany – August 27 2012: Up to 400 cardiac events and 200 deaths in Swedish PCI patients could be avoided by following a heart healthy lifestyle, according to research from the SPICI study presented at ESC Congress 2012. The results were presented at ESC press conference by Professor Joep Perk from Linnaeus University and at the scientific session by Dr Roland CARLSSON.
The benefits of adherence to a heart healthy lifestyle in combination with drug treatment after an acute myocardial infarction treated with coronary artery balloon intervention (PCI) have recently ...
Smoking after stroke increases death risk by 3-fold
2012-08-28
Munich, Germany – August 28 2012: Patients who resume smoking after a stroke increase their risk of death by three-fold, according to research presented at ESC Congress 2012 by Professor Furio Colivicchi from San Filippo Neri Hospital. The researchers also found that the earlier patients resume smoking, the greater their risk of death with one year.
"It is well established that smoking increases the risk of having a stroke," said Professor Colivicchi. "Quitting smoking after an acute ischemic stroke may be more effective than any medication in reducing the risk of further ...