(Press-News.org) A strange thing about black holes: they shine.
The current issue of Science Express features a paper by the Event Horizon telescope team – a collaboration that includes Avery Broderick, Associate Faculty at Perimeter Institute – that may shed light on the origin of the bright jets given off by some black holes. In a world first, the team has been able to look at a distant black hole and find out where its jets are launched from: the "launchpad".
Many galaxies, including our own Milky Way, have a huge black hole lurking at their cores. In about 10 percent of such galaxies, the hole gives off huge, tight streams of electrons and other sub-atomic particles traveling at nearly the speed of light. They can be so bright that they outshine the rest of the galaxy combined.
With the new data coming in, theorists like Perimeter's Avery Broderick can start to tell the difference between these models of hole-driven jets and accretion-driven jets. "We are now beginning to see that spin is playing a role in jet production," says Broderick. "That is, not only can we say that the jets originate near the black hole, but because the emission region is so small, it must be coming from a rotating black hole."
"The black hole is really the engine that drives the jet," he adds. "It's an extraordinary thing."
INFORMATION:
Read more on Perimeter's website and download a graphic of the black hole "launchpad": http://www.perimeterinstitute.ca/News/In_The_Media/World%27s_First_Glimpse_of_Black_Hole_Launchpad/
For more information:
RJ Taylor
Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics
519-569-7600 ext. 5371
rtaylor@perimeterinstitute.ca
About Perimeter Institute:
Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics is an independent, non-profit, scientific research organization working to advance our understanding of physical laws and develop new ideas about the very essence of space, time, matter, and information. Located in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada, Perimeter also provides a wide array of research training and educational outreach activities to nurture scientific talent and share the importance of discovery and innovation among students, teachers, and the general public. In partnership with the Governments of Ontario and Canada, Perimeter is a successful example of public-private collaboration in scientific research, training, and outreach. http://www.perimeterinstitute.ca
World's first glimpse of a black hole 'launchpad'
2012-09-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Newspaper sales suffer due to lack of stimulating content
2012-09-28
Los Angeles, CA (September 27, 2012) – Since the newspaper industry started to experience a major decrease in readership in recent years, many people have deemed the internet and other forms of new media as the culprits. However, a recent study published in the Journalism & Mass Communication Quarterly, a SAGE Journal, finds that sales are down because readers need more engaging and stimulating content.
Study authors Rachel Davis Mersey, Edward C. Malthouse, and Bobby J. Calder suggested that it is crucial for journalists and practitioners to focus their efforts on creating ...
Researchers investigate aggression among kindergartners
2012-09-28
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Not all aggressive children are aggressive for the same reasons, according to Penn State researchers, who found that some kindergartners who are aggressive show low verbal abilities while others are more easily physiologically aroused. The findings suggest that different types of treatments may be needed to help kids with different underlying causes for problem behavior.
"Aggressive responses to being frustrated are a normal part of early childhood, but children are increasingly expected to manage their emotions and control their behavior when ...
Liver cells, insulin-producing cells, thymus can be grown in lymph nodes, Pitt team finds
2012-09-28
PITTSBURGH, Sept. 27, 2012 – Lymph nodes can provide a suitable home for a variety of cells and tissues from other organs, suggesting that a cell-based alternative to whole organ transplantation might one day be feasible, according to researchers at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine and its McGowan Institute for Regenerative Medicine. In a report recently published online in Nature Biotechnology, the research team showed for the first time that liver cells, thymus tissue and insulin-producing pancreatic islet cells, in an animal model, can thrive in lymph ...
Genetic sleuthing uncovers deadly new virus in Africa
2012-09-28
An isolated outbreak of a deadly disease known as acute hemorrhagic fever, which killed two people and left one gravely ill in the Democratic Republic of Congo in the summer of 2009, was probably caused by a novel virus scientists have never seen before.
Described this week in the open-access journal PLoS Pathogens, the new microbe has been named Bas-Congo virus (BASV) after the province in the southwest corner of the Congo where the three people lived.
It was discovered by an international research consortium that included the University of California, San Francisco ...
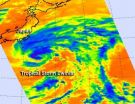
NASA sees light rainfall in Tropical Storm Nadine
2012-09-28
NASA's TRMM satellite noticed that the intensity of rainfall in Tropical Storm Nadine has diminished today, Sept. 27.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite passed over Tropical Storm Nadine on Sept. 27 at 0739 UTC (4:39 a.m. EDT) and at 0917 UTC (5:17 a.m. EDT). At NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., several TRMM instruments were used to create a full picture of Nadine's weakened rainfall. The image was created with an enhanced infrared image from TRMM's Visible and InfraRed Scanner (VIRS) overlaid with rainfall data derived from ...
Simulations uncover 'flashy' secrets of merging black holes
2012-09-28
VIDEO:
Supercomputer models of merging black holes reveal properties that are crucial to understanding future detections of gravitational waves. This movie follows two orbiting black holes and their accretion disk during...
Click here for more information.
According to Einstein, whenever massive objects interact, they produce gravitational waves -- distortions in the very fabric of space and time -- that ripple outward across the universe at the speed of light. While astronomers ...
Landsat satellites find the 'sweet spot' for crops
2012-09-28
Farmers are using maps created with free data from NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey's Landsat satellites that show locations that are good and not good for growing crops.
Farmer Gary Wagner walks into his field where the summer leaves on the sugar beet plants are a rich emerald hue -- not necessarily a good color when it comes to sugar beets, either for the environment or the farmer. That hue tells Wagner that he's leaving money in the field in unused nitrogen fertilizer, which if left in the soil can act as a pollutant when washed into waterways, and in unproduced ...
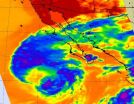
NASA sees a western weakness in Tropical Storm Miriam
2012-09-28
NASA infrared satellite imagery showed Tropical Storm Miriam had strong convection and thunderstorm activity in all quadrants of the storm on Sept. 26, except the western quadrant. That activity waned dramatically in 24 hours because of strong wind shear and cooler sea surface temperatures.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured infrared data on Tropical Storm Miriam on Sept. 26 at 2047 UTC, when it was off the coast of Baja California. Strongest thunderstorms with very cold cloud top temperatures appear to ...
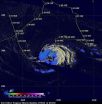
NASA sees a wide-eyed Super Typhoon Jelawat
2012-09-28
One day ago, Super Typhoon Jelawat's eye was about 25 nautical miles in diameter, today, Sept. 27, NASA satellite data indicated that eye has grown to 36 nautical miles!
The latest infrared image from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies on NASA's Aqua satellite shows a clear eye in Typhoon Jelawat on Sept. 25. The cloud top temperatures of the thunderstorms surrounding the eye exceed -63 Fahrenheit (-52 Celsius) indicating that they are very powerful and heavy rainmakers.. Jelawat also has a rounded shape indicating that circulation is strong ...
NASA sees Tropical Storm Ewiniar embedded in low pressure
2012-09-28
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Ewiniar and noticed strong convection still persists in the storm, despite now being embedded in a subtropical area of low pressure off the coast of Japan.
As Tropical Storm Ewiniar continues to move northward it wound up in an elongated area of low pressure (called a trough) off Japan's east coast. The trough is bringing a strong westerly flow of air into Ewiniar. Despite being battered by those winds, infrared data from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite is showing ...