(Press-News.org) RICHLAND, Wash. -- Anyone who owns an electronic device knows that lithium ion batteries could work better and last longer. Now, scientists examining battery materials on the nano-scale reveal how nickel forms a physical barrier that impedes the shuttling of lithium ions in the electrode, reducing how fast the materials charge and discharge. Published last week in Nano Letters, the research also suggests a way to improve the materials.
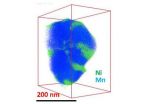
The researchers, led by the Department of Energy's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory's Chongmin Wang, created high-resolution 3D images of electrode materials made from lithium-nickel-manganese oxide layered nanoparticles, mapping the individual elements. These maps showed that nickel formed clumps at certain spots in the nanoparticles. A higher magnification view showed the nickel blocking the channels through which lithium ions normally travel when batteries are charged and discharged.
"We were surprised to see the nickel selectively segregate like it did. When the moving lithium ions hit the segregated nickel rich layer, they essentially encounter a barrier that appears to slow them down," said Wang, a materials scientist based at EMSL, the Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory, a DOE user facility on PNNL's campus. "The block forms in the manufacturing process, and we'd like to find a way to prevent it."
Lithium ions are positively charged atoms that move between negative and positive electrodes when a battery is being charged or is in use. They essentially catch or release the negatively charged electrons, whose movement through a device such as a laptop forms the electric current.
In lithium-manganese oxide electrodes, the manganese and oxygen atoms form rows like a field of cornstalks. In the channels between the stalks, lithium ions zip towards the electrodes on either end, the direction depending on whether the battery is being used or being charged.
Researchers have known for a long time that adding nickel improves how much energy the electrode can hold, battery qualities known as capacity and voltage. But scientists haven't understood why the capacity falls after repeated usage -- a situation consumers experience when a dying battery holds its charge for less and less time.
To find out, Wang, materials scientist Meng Gu and their collaborators used electron microscopy at EMSL and the National Center for Electron Microscopy at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory to view how the different atoms are arranged in the electrode materials produced by Argonne National Laboratory researchers. The electrodes were based on nanoparticles made with lithium, nickel, and manganese oxides.
First, the team took high-resolution images that clearly showed rows of atoms separated by channels filled with lithium ions. On the surface, they saw the accumulation of nickel at the ends of the rows, essentially blocking lithium from moving in and out.
To find out how the surface layer is distributed on and within the whole nanoparticle, the team used a technique called three-dimensional composition mapping. Using a nanoparticle about 200 nanometers in size, they took 50 images of the individual elements as they tilted the nanoparticle at various angles. The team reconstructed a three-dimensional map from the individual elemental maps, revealing spots of nickel on a background of lithium-manganese oxide.
The three-dimensional distribution of manganese, oxygen and lithium atoms along the surface and within the particle was relatively even. The nickel, however, parked itself in small areas on the surface. Internally, the nickel clumped on the edges of smaller regions called grains.
To explore why nickel aggregates on certain surfaces, the team calculated how easily nickel and lithium traveled through the channels. Nickel moved more easily up and down the channels than lithium. While nickel normally resides within the manganese oxide cornrows, sometimes it slips out into the channels. And when it does, this analysis showed that it flows much easier through the channels to the end of the field, where it accumulates and forms a block.
The researchers used a variety of methods to make the nanoparticles. Wang said that the longer the nanoparticles stayed at high temperature during fabrication, the more nickel segregated and the poorer the particles performed in charging and discharging tests. They plan on doing more closely controlled experiments to determine if a particular manufacturing method produces a better electrode.
This work was supported by PNNL's Chemical Imaging Initiative.
INFORMATION:
Reference: Meng Gu, Ilias Belharouak, Arda Genc, Zhiguo Wang, Dapeng Wang, Khalil Amine, Fei Gao, Guangwen Zhou, Suntharampillai Thevuthasan, Donald R. Baer, Ji-Guang Zhang, Nigel D. Browning, Jun Liu, and Chongmin Wang. Conflicting Roles of Ni in Controlling Cathode Performance in Li-ion Batteries, NanoLetters Sept. 17, 2012, doi: dx.doi.org/10.1021/nl302249v. (http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/nl302249v)
EMSL, the Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory, is a national scientific user facility sponsored by the Department of Energy's Office of Science. Located at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory in Richland, Wash., EMSL offers an open, collaborative environment for scientific discovery to researchers around the world. Its integrated computational and experimental resources enable researchers to realize important scientific insights and create new technologies. Follow EMSL on Facebook, LinkedIn and Twitter.
Interdisciplinary teams at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory address many of America's most pressing issues in energy, the environment and national security through advances in basic and applied science. PNNL employs 4,700 staff, has an annual budget of nearly $1.1 billion, and has been managed for the U.S. Department of Energy by Ohio-based Battelle since the laboratory's inception in 1965. For more, visit the PNNL's News Center, or follow PNNL on Facebook, LinkedIn and Twitter.
Nickelblock: An element's love-hate relationship with battery electrodes
Images show how nickel, which enhances battery capacity, also appears to hinder charging rates
2012-09-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Measuring the universe's 'exit door'
2012-09-28
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- The point of no return: In astronomy, it's known as a black hole — a region in space where the pull of gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape. Black holes that can be billions of times more massive than our sun may reside at the heart of most galaxies. Such supermassive black holes are so powerful that activity at their boundaries can ripple throughout their host galaxies.
Now, an international team, led by researchers at MIT's Haystack Observatory, has for the first time measured the radius of a black hole at the center of a distant ...
World's first glimpse of a black hole 'launchpad'
2012-09-28
A strange thing about black holes: they shine.
The current issue of Science Express features a paper by the Event Horizon telescope team – a collaboration that includes Avery Broderick, Associate Faculty at Perimeter Institute – that may shed light on the origin of the bright jets given off by some black holes. In a world first, the team has been able to look at a distant black hole and find out where its jets are launched from: the "launchpad".
Many galaxies, including our own Milky Way, have a huge black hole lurking at their cores. In about 10 percent of such galaxies, ...
Newspaper sales suffer due to lack of stimulating content
2012-09-28
Los Angeles, CA (September 27, 2012) – Since the newspaper industry started to experience a major decrease in readership in recent years, many people have deemed the internet and other forms of new media as the culprits. However, a recent study published in the Journalism & Mass Communication Quarterly, a SAGE Journal, finds that sales are down because readers need more engaging and stimulating content.
Study authors Rachel Davis Mersey, Edward C. Malthouse, and Bobby J. Calder suggested that it is crucial for journalists and practitioners to focus their efforts on creating ...
Researchers investigate aggression among kindergartners
2012-09-28
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Not all aggressive children are aggressive for the same reasons, according to Penn State researchers, who found that some kindergartners who are aggressive show low verbal abilities while others are more easily physiologically aroused. The findings suggest that different types of treatments may be needed to help kids with different underlying causes for problem behavior.
"Aggressive responses to being frustrated are a normal part of early childhood, but children are increasingly expected to manage their emotions and control their behavior when ...
Liver cells, insulin-producing cells, thymus can be grown in lymph nodes, Pitt team finds
2012-09-28
PITTSBURGH, Sept. 27, 2012 – Lymph nodes can provide a suitable home for a variety of cells and tissues from other organs, suggesting that a cell-based alternative to whole organ transplantation might one day be feasible, according to researchers at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine and its McGowan Institute for Regenerative Medicine. In a report recently published online in Nature Biotechnology, the research team showed for the first time that liver cells, thymus tissue and insulin-producing pancreatic islet cells, in an animal model, can thrive in lymph ...
Genetic sleuthing uncovers deadly new virus in Africa
2012-09-28
An isolated outbreak of a deadly disease known as acute hemorrhagic fever, which killed two people and left one gravely ill in the Democratic Republic of Congo in the summer of 2009, was probably caused by a novel virus scientists have never seen before.
Described this week in the open-access journal PLoS Pathogens, the new microbe has been named Bas-Congo virus (BASV) after the province in the southwest corner of the Congo where the three people lived.
It was discovered by an international research consortium that included the University of California, San Francisco ...
NASA sees light rainfall in Tropical Storm Nadine
2012-09-28
NASA's TRMM satellite noticed that the intensity of rainfall in Tropical Storm Nadine has diminished today, Sept. 27.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite passed over Tropical Storm Nadine on Sept. 27 at 0739 UTC (4:39 a.m. EDT) and at 0917 UTC (5:17 a.m. EDT). At NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., several TRMM instruments were used to create a full picture of Nadine's weakened rainfall. The image was created with an enhanced infrared image from TRMM's Visible and InfraRed Scanner (VIRS) overlaid with rainfall data derived from ...
Simulations uncover 'flashy' secrets of merging black holes
2012-09-28
VIDEO:
Supercomputer models of merging black holes reveal properties that are crucial to understanding future detections of gravitational waves. This movie follows two orbiting black holes and their accretion disk during...
Click here for more information.
According to Einstein, whenever massive objects interact, they produce gravitational waves -- distortions in the very fabric of space and time -- that ripple outward across the universe at the speed of light. While astronomers ...
Landsat satellites find the 'sweet spot' for crops
2012-09-28
Farmers are using maps created with free data from NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey's Landsat satellites that show locations that are good and not good for growing crops.
Farmer Gary Wagner walks into his field where the summer leaves on the sugar beet plants are a rich emerald hue -- not necessarily a good color when it comes to sugar beets, either for the environment or the farmer. That hue tells Wagner that he's leaving money in the field in unused nitrogen fertilizer, which if left in the soil can act as a pollutant when washed into waterways, and in unproduced ...
NASA sees a western weakness in Tropical Storm Miriam
2012-09-28
NASA infrared satellite imagery showed Tropical Storm Miriam had strong convection and thunderstorm activity in all quadrants of the storm on Sept. 26, except the western quadrant. That activity waned dramatically in 24 hours because of strong wind shear and cooler sea surface temperatures.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured infrared data on Tropical Storm Miriam on Sept. 26 at 2047 UTC, when it was off the coast of Baja California. Strongest thunderstorms with very cold cloud top temperatures appear to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
[Press-News.org] Nickelblock: An element's love-hate relationship with battery electrodesImages show how nickel, which enhances battery capacity, also appears to hinder charging rates