(Press-News.org) Studying leukemia in mice, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have reduced a life-threatening complication of stem cell transplants, the only curative treatment when leukemia returns.
About 50 percent of leukemia patients who receive stem cells from another person develop graft-versus-host disease, a condition where donor immune cells attack the patient's own body. The main organs affected are the skin, liver and gut. Now, the scientists have shown they can redirect donor immune cells away from these vital organs. Steering immune cells away from healthy tissue also leaves more of them available for their intended purpose – killing cancer cells.
"This is the first example of reducing graft-versus-host disease not by killing the T- cells, but simply by altering how they circulate and traffic," says John F. DiPersio, MD, PhD, the Virginia E. and Sam J. Golman Professor of Medicine. "Donor T-cells do good things in terms of eliminating the recipient's leukemia, but they can also attack normal tissues leading to death in a number of patients. The goal is to minimize graft-versus-host disease, while maintaining the therapeutic graft-versus-leukemia effect."
The study is now available online in Blood.
Working with mice, Jaebok Choi, PhD, research assistant professor of medicine, showed that eliminating or blocking a particular protein – the interferon gamma receptor – on donor T-cells makes them unable to migrate to critical organs such as the intestines but still leaves them completely capable of killing leukemia cells.
"The fact that blocking the interferon gamma receptor can redirect donor T-cells away from the gastrointestinal tract, at least in mice, is very exciting because graft-versus-host disease in the gut results in most of the deaths after stem cell transplant," DiPersio says. "People can tolerate graft-versus-host disease of the skin. But in the GI tract, it causes relentless diarrhea and severe infections due to gut bacteria leaking into the blood, which can result in severe toxicity, reduction in the quality of life or even death in some patients."
Long known to be involved in inflammation, the roles of interferon gamma, its receptor and their downstream signaling molecules are just beginning to be described in the context of graft-versus-host disease, says DiPersio, who treats patients at Siteman Cancer Center at Barnes-Jewish Hospital and Washington University School of Medicine.
The cascade begins when interferon gamma activates its receptor. The interferon gamma receptor then activates molecules known as JAK kinases, followed by STAT, and finally CXCR3. CXCR3 mediates the trafficking of donor T-cells to the GI tract and other target organs.
Since deleting the interferon gamma receptor from donor T-cells directs them away from target organs, the researchers asked whether they could produce the same beneficial effects by inhibiting some of the receptor's downstream signaling molecules. Indeed, Choi also found that knocking out CXCR3 reduces graft-versus- host disease, but not completely.
"There are probably additional downstream targets of interferon gamma receptor signaling other than JAKs, STATs and CXCR3 that are responsible for T-cell trafficking to the GI tract and other target organs," DiPersio says. "We're trying to figure out what those are."
To move their findings closer to possible use in humans, Choi and DiPersio also showed that they could mimic the protective effect of deleting the interferon gamma receptor with existing drugs that block JAK kinases. In this case, they tested two JAK inhibitors, one of which is currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat myelofibrosis, a pre-leukemic condition in which the bone marrow is replaced with fibrous tissue.
While they showed that JAK inhibitors are effective in redirecting donor T-cells away from target organs and reducing graft-versus-host disease in mice with leukemia, they have not yet tested whether these drugs also preserve the desired anti-leukemia effect.
"The proof-of-principle behind these experiments is the exciting part," DiPersio says. "If you can change where the T-cells go as opposed to killing them, you prevent the life-threatening complications and maintain the clinical benefit of the transplant."
###
Choi J, Ziga ED, Ritchey J, Collins L, Prior JL, Cooper ML, Piwnica-Worms D, DiPersio JF. INF gamma receptor signaling mediates alloreactive T cell trafficking and GvHD. Blood. Online Sept. 12, 2012.
This work was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute (R01 CA83845 and R21 grants CA110489, CA132269, CA141523 P01 CA101937, P50 CA94056, the Bryan Thomas Campbell Foundation, the Molecular Imaging Center Pilot Research Project 2010 Awards (P50 CA94056), the Translational Oncology Group at the Washington University School of Medicine, the Siteman Cancer Center Research Development Awards in Developmental Therapeutics, and the American Cancer Society Institutional Research Grant (IRG-58-010-53).
Washington University School of Medicine's 2,100 employed and volunteer faculty physicians also are the medical staff of Barnes-Jewish and St. Louis Children's hospitals. The School of Medicine is one of the leading medical research, teaching and patient care institutions in the nation, currently ranked sixth in the nation by U.S. News & World Report. Through its affiliations with Barnes-Jewish and St. Louis Children's hospitals, the School of Medicine is linked to BJC HealthCare.
Deadly complication of stem cell transplants reduced in mice
2012-09-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
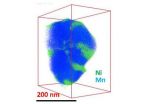
Nickelblock: An element's love-hate relationship with battery electrodes
2012-09-28
RICHLAND, Wash. -- Anyone who owns an electronic device knows that lithium ion batteries could work better and last longer. Now, scientists examining battery materials on the nano-scale reveal how nickel forms a physical barrier that impedes the shuttling of lithium ions in the electrode, reducing how fast the materials charge and discharge. Published last week in Nano Letters, the research also suggests a way to improve the materials.
The researchers, led by the Department of Energy's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory's Chongmin Wang, created high-resolution 3D ...
Measuring the universe's 'exit door'
2012-09-28
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- The point of no return: In astronomy, it's known as a black hole — a region in space where the pull of gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape. Black holes that can be billions of times more massive than our sun may reside at the heart of most galaxies. Such supermassive black holes are so powerful that activity at their boundaries can ripple throughout their host galaxies.
Now, an international team, led by researchers at MIT's Haystack Observatory, has for the first time measured the radius of a black hole at the center of a distant ...
World's first glimpse of a black hole 'launchpad'
2012-09-28
A strange thing about black holes: they shine.
The current issue of Science Express features a paper by the Event Horizon telescope team – a collaboration that includes Avery Broderick, Associate Faculty at Perimeter Institute – that may shed light on the origin of the bright jets given off by some black holes. In a world first, the team has been able to look at a distant black hole and find out where its jets are launched from: the "launchpad".
Many galaxies, including our own Milky Way, have a huge black hole lurking at their cores. In about 10 percent of such galaxies, ...
Newspaper sales suffer due to lack of stimulating content
2012-09-28
Los Angeles, CA (September 27, 2012) – Since the newspaper industry started to experience a major decrease in readership in recent years, many people have deemed the internet and other forms of new media as the culprits. However, a recent study published in the Journalism & Mass Communication Quarterly, a SAGE Journal, finds that sales are down because readers need more engaging and stimulating content.
Study authors Rachel Davis Mersey, Edward C. Malthouse, and Bobby J. Calder suggested that it is crucial for journalists and practitioners to focus their efforts on creating ...
Researchers investigate aggression among kindergartners
2012-09-28
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Not all aggressive children are aggressive for the same reasons, according to Penn State researchers, who found that some kindergartners who are aggressive show low verbal abilities while others are more easily physiologically aroused. The findings suggest that different types of treatments may be needed to help kids with different underlying causes for problem behavior.
"Aggressive responses to being frustrated are a normal part of early childhood, but children are increasingly expected to manage their emotions and control their behavior when ...
Liver cells, insulin-producing cells, thymus can be grown in lymph nodes, Pitt team finds
2012-09-28
PITTSBURGH, Sept. 27, 2012 – Lymph nodes can provide a suitable home for a variety of cells and tissues from other organs, suggesting that a cell-based alternative to whole organ transplantation might one day be feasible, according to researchers at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine and its McGowan Institute for Regenerative Medicine. In a report recently published online in Nature Biotechnology, the research team showed for the first time that liver cells, thymus tissue and insulin-producing pancreatic islet cells, in an animal model, can thrive in lymph ...
Genetic sleuthing uncovers deadly new virus in Africa
2012-09-28
An isolated outbreak of a deadly disease known as acute hemorrhagic fever, which killed two people and left one gravely ill in the Democratic Republic of Congo in the summer of 2009, was probably caused by a novel virus scientists have never seen before.
Described this week in the open-access journal PLoS Pathogens, the new microbe has been named Bas-Congo virus (BASV) after the province in the southwest corner of the Congo where the three people lived.
It was discovered by an international research consortium that included the University of California, San Francisco ...
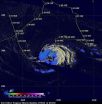
NASA sees light rainfall in Tropical Storm Nadine
2012-09-28
NASA's TRMM satellite noticed that the intensity of rainfall in Tropical Storm Nadine has diminished today, Sept. 27.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite passed over Tropical Storm Nadine on Sept. 27 at 0739 UTC (4:39 a.m. EDT) and at 0917 UTC (5:17 a.m. EDT). At NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., several TRMM instruments were used to create a full picture of Nadine's weakened rainfall. The image was created with an enhanced infrared image from TRMM's Visible and InfraRed Scanner (VIRS) overlaid with rainfall data derived from ...
Simulations uncover 'flashy' secrets of merging black holes
2012-09-28
VIDEO:
Supercomputer models of merging black holes reveal properties that are crucial to understanding future detections of gravitational waves. This movie follows two orbiting black holes and their accretion disk during...
Click here for more information.
According to Einstein, whenever massive objects interact, they produce gravitational waves -- distortions in the very fabric of space and time -- that ripple outward across the universe at the speed of light. While astronomers ...
Landsat satellites find the 'sweet spot' for crops
2012-09-28
Farmers are using maps created with free data from NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey's Landsat satellites that show locations that are good and not good for growing crops.
Farmer Gary Wagner walks into his field where the summer leaves on the sugar beet plants are a rich emerald hue -- not necessarily a good color when it comes to sugar beets, either for the environment or the farmer. That hue tells Wagner that he's leaving money in the field in unused nitrogen fertilizer, which if left in the soil can act as a pollutant when washed into waterways, and in unproduced ...