(Press-News.org) Bethesda, MD (Oct. 1, 2012) — Patients at average risk of colorectal cancer who have a clean colonoscopy do not need to repeat the test for 10 years. This and many other practical recommendations for cancer prevention were issued in "Guidelines for Colonoscopy Surveillance After Screening and Polypectomy,"1 a consensus update issued by the U.S. Multisociety Task Force on Colorectal Cancer.
Colorectal cancer is preventable when precancerous polyps (growths) are found and removed before they turn into cancer. Screening for average risk patients is recommended to begin at age 50, and there are many screening tests available. During a colonoscopy, a physician examines the full length of the large intestine and removes polyps. Surveillance refers to the schedule on which doctors recheck patients for recurring polyps after their first screening.
The U.S. Multisociety Task Force — comprised of representatives of the American College of Gastroenterology, the American Gastroenterological Association and the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy — evaluated the guidelines for colorectal cancer surveillance published in 2006 to determine if they should be updated based on new evidence.
"The U.S. Multisociety Task Force believes that the evidence supporting current recommendations for screening and surveillance intervals has become stronger in the past six years," said David Lieberman, MD, lead author of the guidelines. "While these guidelines are dynamic and will continue be revised in the future as new evidence emerges, we believe the guidelines represent the best science available for the screening, surveillance and prevention of colorectal cancer."
The task force recommends that all endoscopists monitor key quality indicators as part of a colonoscopy screening and surveillance program. The following colonoscopy schedule is recommended following a patient's initial high-quality exam:
Initial exam finds no polyps or small (< 10 mm) hyperplastic polyps in the rectum or sigmoid colon
Next colonoscopy in 10 years
Initial exam finds low-risk adenomas defined as 1-2 tubular adenomas =10mm, or with villous histology, high grade dysplasia; three or more adenomas; sessile serrated lesions which are dysplastic and/or >=10mm
Next colonoscopy in 3 years
The full guidelines are available online at http://www.gastrojournal.org/article/S0016-5085(12)00812-8/fulltext.
The guidelines also provide advice on murky areas related to colorectal cancer screening:
When should colonoscopy be repeated if the patient's bowel isn't properly prepared for colonoscopy? In most cases, repeat the exam within one year. Note that splitting the dose of bowel preparation yields better results.
Should stool tests (guaiac fecal occult blood test or fecal immunochemical test) be used in between colonoscopies to check for cancer? Fecal testing between colonoscopies isn't necessary within five years of colonoscopy.
Aspirin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may reduce risk of polyps — should screening intervals change for patients on these medications? There is insufficient evidence to recommend any change.
If new symptoms develop, should a patient receive a colonoscopy earlier than scheduled based on guidelines? The likelihood of finding significant pathology after a complete and adequate colonoscopy is uncertain, but likely to be low. However, if the colonoscopy will answer an important clinical question, it may be valuable to repeat.
Should surveillance be modified based on patient race, ethnicity or gender? If patients have had a high-quality colonoscopy, there's no reason to alter the surveillance interval based on these factors.
At what age should colorectal cancer surveillance stop? The decision to continue colonoscopy in the elderly should be individualized based on an assessment of benefit, risk and other medical conditions.
###
Task force members:
David A. Lieberman, Oregon Health and Science University, Portland
Douglas K. Rex, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis
Sidney J. Winawer, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY
Francis M. Giardiello, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD
David A. Johnson, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk
Theodore R. Levin, Kaiser Permanente Medical Center, Walnut Creek, CA
1 Lieberman DA, Rex, DK, Winawer SJ, et al. Guidelines for Colonoscopy Surveillance After Screening and Polypectomy: A Consensus Update by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology 2012; September; 143(3): 844-857
About the American College of Gastroenterology
Founded in 1932, the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) is an organization with an international membership of more than 12,000 individuals from 80 countries. The College is committed to serving the clinically oriented digestive disease specialist through its emphasis on scholarly practice, teaching and research. The mission of the College is to serve the evolving needs of physicians in the delivery of high quality, scientifically sound, humanistic, ethical, and cost-effective health care to gastroenterology patients. For more information, visit www.gi.org.
About the AGA Institute
The American Gastroenterological Association is the trusted voice of the GI community. Founded in 1897, the AGA has grown to include 17,000 members from around the globe who are involved in all aspects of the science, practice and advancement of gastroenterology. The AGA Institute administers the practice, research and educational programs of the organization. www.gastro.org. Like AGA on Facebook. Join AGA on LinkedIn. Follow us on Twitter @AmerGastroAssn. Check out our videos on YouTube.
About the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Since its founding in 1941, the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) has been dedicated to advancing patient care and digestive health by promoting excellence and innovation in gastrointestinal endoscopy. ASGE, with more than 12,000 members worldwide, promotes the highest standards for endoscopic training and practice, fosters endoscopic research, recognizes distinguished contributions to endoscopy, and is the foremost resource for endoscopic education. Visit www.asge.org and www.screen4coloncancer.org for more information and to find a qualified doctor in your area.
END
MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL (10/01/2012) —New genome editing technologies developed at the University of Minnesota for use on livestock will allow scientists to learn more about human diseases.
The genomic technique, known as TALENS, is described in a report published today in the scientific journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The technique is cheaper and faster than previous technologies that allow scientists to genetically modify livestock animals; the animals are used to learn more about human diseases, which in turn can help researchers develop cures. ...
"Betcha can't eat just one!" For obese people trying to lose weight, the Lays potato chip advertising slogan hits a bit too close to home as it describes the daily battle to resist high calorie foods.
But new research by Terry Davidson, director of American University's Center for Behavioral Neuroscience, indicates that diets that lead to obesity—diets high in saturated fat and refined sugar—may cause changes to the brains of obese people that in turn may fuel overconsumption of those same foods and make weight loss more challenging.
"It is a vicious cycle that may ...
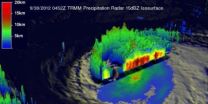
NASA satellites continue to watch the long-lived Nadine in the eastern Atlantic. Today, Oct. 1, NASA satellite data revealed that Nadine has weakened from a hurricane and is now a tropical storm.
Over the weekend of Sept. 29 and 30, Hurricane Nadine dramatically rebounded. On September 19, 2012 Nadine appeared to be dissipating quickly and was expected to become post-tropical but after over a week of meandering near the Azores, Nadine sprang to life again as a hurricane on Friday September 28, 2012.
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite's path ...
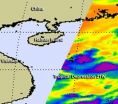
The twenty-first tropical depression of the northwestern Pacific Ocean was born as a NASA satellite flew overhead on Oct. 1, capturing its "baby picture" in infrared light.
On Monday, Oct. 1 at 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT), Tropical Depression 21W (TD21W) had maximum sustained winds near 25 knots. It was centered about300 nautical miles south of Hong Kong, near 17.4 North latitude and 114.8 East longitude. TD21W has tracked northward at 5 knots and is expected to curve to the northwest and west.
On Oct. 1, 2012, infrared imagery from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) ...
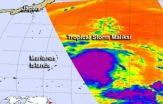
The western North Pacific is in full swing, tropically speaking and NASA observed the birth of Tropical Storm Maliksi on Sept. 30. NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image of the storm when it was a depression and revealed a large area of powerful thunderstorms around its center that hinted at its strengthening.
Tropical Storm Maliksi formed from the twentieth tropical depression of the western North Pacific typhoon season. Tropical Depression 20W formed on Sept. 20 about 305 nautical miles from Guam near 16.3 North and 149.0 East. It is moving to the north-northwest ...
OAK BROOK, Ill. – New research from the Netherlands shows that the switch from screen film mammography (SFM) to digital mammography (DM) in large, population-based breast cancer screening programs improves the detection of life-threatening cancer without significantly increasing detection of clinically insignificant disease. Results of the study are published online in the journal Radiology.
DM's higher sensitivity at detecting breast cancer raised concerns that its introduction into screening programs would increase the diagnosis of clinically unimportant cancers—cancers ...
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Water diffusion measurements with MRI could decrease false-positive breast cancer results and reduce preventable biopsies, according to a new study published online in the journal Radiology. Researchers said the technique also could improve patient management by differentiating high-risk lesions requiring additional workup from other non-malignant subtypes.
Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI) has emerged in recent years as a useful tool in breast cancer detection and staging. One of its primary limitations is a substantial number of false-positive ...
Washington — In an article published today (October 2, 2012) in the peer-reviewed journal Environmental Health Perspectives (EHP), People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals reports that the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) High Production Volume (HPV) Chemicals Challenge Program had the potential to use 3.5 million animals in new testing, but after the application of animal-saving measures, approximately 127,000 were actually used. Although this toll in animal lives is high, it would have been many times worse had PETA not obtained major concessions from the ...
Stroke care has improved considerably in Alberta following the implementation of the Alberta Provincial Stroke Strategy (APSS), leading to more targeted patient care and fewer health complications, according to a study presented today at the Canadian Stroke Congress.
Nearly 97 per cent of stroke patients received a brain-imaging scan during their admission to hospital in 2011, compared to 88 per cent before the APSS was implemented in 2006.
"The faster a patient has access to brain imaging, the faster they get the right diagnosis and the right treatment," says lead ...
Improvements to the diagnosis and screening of sleep apnea are critical to stroke prevention, according to new stroke care guidelines released today at the Canadian Stroke Congress.
Obstructive sleep apnea, a disorder where the flow of air to the brain pauses or decreases during sleep, is both a risk factor for stroke and a complication following stroke, according to the Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Stroke Care.
Among the general population sleep apnea increases the likelihood of having a stroke, even after controlling for other stroke risk factors, such ...