(Press-News.org) AMES, Iowa – Two Iowa State University graduate students are just back from the Gulf of Maine with another big catch of clam shells.
Shelly Griffin and Madelyn Mette recently boarded a lobster boat, dropped a scallop dredge into 30 meters of ocean water and pulled up load after load of Arctica islandica.
"These are the clams that end up in clam chowder," said Alan Wanamaker, an assistant professor of geological and atmospheric sciences in the College of Liberal Arts and Sciences. Wanamaker studies paleoclimatology, the variations and trends of past climates and environments, with the goal of better understanding future climate changes.
The Iowa State researchers only need a few live, meaty clams for their studies. They're really after the old, dead shells. Off the coast of Maine, clams can live up to 240 years, year after year adding another band to their shells, just like a tree adds another growth ring. In the colder waters of the North Atlantic near Iceland, the clams can live up to 500 years, recording even more information in what scientists call annual shell increments.
Wanamaker and his research team bring those shells back to Iowa State's Stable Isotope Laboratory where they're cleaned, sorted, measured, cut, polished, drilled and otherwise prepared for careful microscopic imaging, geochemical testing and radiocarbon analysis.
It turns out those shell increments are a lot like sensors at the bottom of the ocean – they record long records of information about the ocean, including growing conditions, temperatures and circulation patterns.
A paper published by Nature Communications in June 2012 reported how Wanamaker (the lead author) and an international team of researchers used radiocarbon data from shells to determine when clams collected north of Iceland were living in "young" or "old" water. Young water had been at the surface more recently and probably came from the Atlantic. Old water had been removed from the surface much longer and probably came from the Arctic Ocean.
The paper reports warmer, younger water from the Gulf Stream during the warmer Medieval Climate Anomaly from about A.D. 950 to 1250. The paper also reports that shell data showed older, colder water during Europe's Little Ice Age from about A.D. 1550 to 1850.
The researchers' interpretation of the data says the Gulf Stream carrying warm water from the subtropical Atlantic was strong in the medieval era, weakened during the Little Ice Age and strengthened again after A.D. 1940. Those fluctuations amplified the relative warmth and coolness of the times.
Wanamaker said a better understanding of the ocean's past can help researchers understand today's climate trends and changes.
"Is the natural variability only that, or is it influenced by burning fossil fuels?" he said. "Maybe we can understand what will happen in the next 100 years if we understand oceans over the past 1,000 years."
And so Wanamaker – a former high school science teacher in Maine whose fascination with climate change sent him back to graduate school – works with students to carefully collect, process and study clam shells.
The research is painstaking – the shell increments are measured in millionths of a meter and microscopes are required at the most important steps. And the tools are sophisticated – two mass spectrometers measure shell fragments for different isotopes of carbon and oxygen. (Isotopes are elements with varying numbers of neutrons. Heavier isotopes of oxygen in the shell material generally correspond to colder ocean temperatures.)
"Isotopes are just wonderful tracers in nature," Wanamaker said, noting he also takes isotope measurements for research projects across campus and beyond.
When it comes to Wanamaker's own work with clam shells, "In the broadest sense, we're trying to add to our understanding of oceans over the last several thousand years," he said. "We have a terrestrial record – we can get an excellent chronology from tree rings and there is a climate signal there. But that's missing 70 percent of the planet."
INFORMATION:
Contacts:
Alan Wanamaker, Geological and Atmospheric Sciences, (515) 294-5142, adw@iastate.edu
Mike Krapfl, News Service, 515-294-4917, mkrapfl@iastate.edu
Iowa State researchers study clam shells for clues to the Atlantic's climate history
2012-10-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers harness the immune system to improve stem cell transplant outcomes
2012-10-02
VIDEO:
Dr. Amir Toor from Virginia Commonwealth University Massey Cancer Center's Bone Marrow Transplant program explains a recent clinical trial evaluating a new therapy for multiple myeloma that harnesses the power...
Click here for more information.
Richmond, Va. – (October 1, 2012) – A novel therapy in the early stages of development at Virginia Commonwealth University Massey Cancer Center shows promise in providing lasting protection against the progression of multiple ...
GI societies issue new colonoscopy surveillance guidelines
2012-10-02
Bethesda, MD (Oct. 1, 2012) — Patients at average risk of colorectal cancer who have a clean colonoscopy do not need to repeat the test for 10 years. This and many other practical recommendations for cancer prevention were issued in "Guidelines for Colonoscopy Surveillance After Screening and Polypectomy,"1 a consensus update issued by the U.S. Multisociety Task Force on Colorectal Cancer.
Colorectal cancer is preventable when precancerous polyps (growths) are found and removed before they turn into cancer. Screening for average risk patients is recommended to begin ...
New technologies advance livestock genomics for agricultural and biomedical uses
2012-10-02
MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL (10/01/2012) —New genome editing technologies developed at the University of Minnesota for use on livestock will allow scientists to learn more about human diseases.
The genomic technique, known as TALENS, is described in a report published today in the scientific journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The technique is cheaper and faster than previous technologies that allow scientists to genetically modify livestock animals; the animals are used to learn more about human diseases, which in turn can help researchers develop cures. ...
The obese brain may thwart weight loss
2012-10-02
"Betcha can't eat just one!" For obese people trying to lose weight, the Lays potato chip advertising slogan hits a bit too close to home as it describes the daily battle to resist high calorie foods.
But new research by Terry Davidson, director of American University's Center for Behavioral Neuroscience, indicates that diets that lead to obesity—diets high in saturated fat and refined sugar—may cause changes to the brains of obese people that in turn may fuel overconsumption of those same foods and make weight loss more challenging.
"It is a vicious cycle that may ...
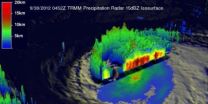
NASA sees Nadine weaken to a tropical storm again
2012-10-02
NASA satellites continue to watch the long-lived Nadine in the eastern Atlantic. Today, Oct. 1, NASA satellite data revealed that Nadine has weakened from a hurricane and is now a tropical storm.
Over the weekend of Sept. 29 and 30, Hurricane Nadine dramatically rebounded. On September 19, 2012 Nadine appeared to be dissipating quickly and was expected to become post-tropical but after over a week of meandering near the Azores, Nadine sprang to life again as a hurricane on Friday September 28, 2012.
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite's path ...
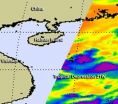
NASA observes another tropical depression birth in northwestern Pacific
2012-10-02
The twenty-first tropical depression of the northwestern Pacific Ocean was born as a NASA satellite flew overhead on Oct. 1, capturing its "baby picture" in infrared light.
On Monday, Oct. 1 at 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT), Tropical Depression 21W (TD21W) had maximum sustained winds near 25 knots. It was centered about300 nautical miles south of Hong Kong, near 17.4 North latitude and 114.8 East longitude. TD21W has tracked northward at 5 knots and is expected to curve to the northwest and west.
On Oct. 1, 2012, infrared imagery from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) ...
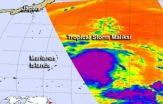
Tropical Storm Maliksi forms, Iwo To on guard
2012-10-02
The western North Pacific is in full swing, tropically speaking and NASA observed the birth of Tropical Storm Maliksi on Sept. 30. NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image of the storm when it was a depression and revealed a large area of powerful thunderstorms around its center that hinted at its strengthening.
Tropical Storm Maliksi formed from the twentieth tropical depression of the western North Pacific typhoon season. Tropical Depression 20W formed on Sept. 20 about 305 nautical miles from Guam near 16.3 North and 149.0 East. It is moving to the north-northwest ...
Digital mammography improves population-based breast cancer screening
2012-10-02
OAK BROOK, Ill. – New research from the Netherlands shows that the switch from screen film mammography (SFM) to digital mammography (DM) in large, population-based breast cancer screening programs improves the detection of life-threatening cancer without significantly increasing detection of clinically insignificant disease. Results of the study are published online in the journal Radiology.
DM's higher sensitivity at detecting breast cancer raised concerns that its introduction into screening programs would increase the diagnosis of clinically unimportant cancers—cancers ...
Novel MRI technique could reduce breast biopsies
2012-10-02
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Water diffusion measurements with MRI could decrease false-positive breast cancer results and reduce preventable biopsies, according to a new study published online in the journal Radiology. Researchers said the technique also could improve patient management by differentiating high-risk lesions requiring additional workup from other non-malignant subtypes.
Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI) has emerged in recent years as a useful tool in breast cancer detection and staging. One of its primary limitations is a substantial number of false-positive ...
PETA scientists analyze animal use in HPV chemicals challenge program
2012-10-02
Washington — In an article published today (October 2, 2012) in the peer-reviewed journal Environmental Health Perspectives (EHP), People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals reports that the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) High Production Volume (HPV) Chemicals Challenge Program had the potential to use 3.5 million animals in new testing, but after the application of animal-saving measures, approximately 127,000 were actually used. Although this toll in animal lives is high, it would have been many times worse had PETA not obtained major concessions from the ...