(Press-News.org) CHAMPAIGN, lll. — New insights into a protein complex that regulates the very tips of chromosomes could improve methods of screening anti-cancer drugs.
Led by bioengineering professor Sua Myong, the research group's findings are published in the journal Structure.
Myong's group focused on understanding the proteins that protect and regulate telomeres, segments of repeating DNA units that cap the ends of chromosomes. Telomeres protect the important gene-coding sections of DNA from loss or damage, the genetic equivalent of aglets – the covering at the tips of shoelaces that keep the ends of the laces from unraveling or fraying.
Telomeres play an important role in cell aging and death, since each time a cell divides, a little bit is lost from the end of the telomere. Thus, cell biologists postulate that telomere length can determine the lifespan of a cell. Cancer cells, however, have a way to get around this limitation: An enzyme called telomerase that adds length to telomeres is highly active in cancer cells. This allows cancer cells to divide in perpetuity, running amok through tissues and systems.
"Cancer researchers want to get a hold of this problem, control this indefinite lengthening of the telomeres," said Myong, who also is affiliated with the Institute for Genomic Biology at the U. of I. "A lot of the anti-cancer drugs are targeted directly to these telomeres so that they can inhibit telomerase activity. The proteins we study regulate the activity of telomerase."
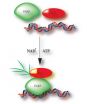
Using a technique developed at Illinois that allows researchers to watch single molecules interact in real time, Myong's group determined how two proteins called POT-1 and TTP-1 bind to the telomere. POT-1 protects the fragile telomere ends from being attacked by other regulatory proteins that might mistake the end for a broken or damaged area of DNA. When POT-1 and TTP-1 work together in a complex, they promote telomerase activity, an interesting target for cancer researchers.
The group found that on its own, POT-1 binds to the folded-up telomere in distinct steps at particular points in the telomere's DNA sequence, unfolding the telomere in a stepwise manner. However, the POT-1/TTP-1 complex surprised the researchers by binding, then freely sliding back and forth along the telomere end.
"Instead of stepwise binding, what we saw was a mobile protein complex, a dynamic sliding motion," Myong said. "Somehow it was as if the static binding activity of POT-1 is completely lost – the protein complex just slid back and forth. We were able to reproduce the data and confirm it with many different tail lengths of the telomeric DNA and we know now that the contact between POT-1 and the telomere is somehow altered when the partner protein comes and binds."
Next, the researchers will add telomerase and see how the sliding activity of the POT-1/TTP-1 complex affects telomerase activity. Myong postulates that the sliding may promote telomerase activity – and thus telomere lengthening – by making the end of the telomere accessible for the telomerase enzyme to bind.
"We are excited about the possibility that this kind of mobility can increase the telomerase extension activity," Myong said. "It's somehow engaging the enzyme so that it can stay bound to the DNA longer. So it must involve a direct interaction."
Ultimately, understanding the POT-1/TTP-1 complex gives drug developers a new target for anti-cancer drugs, and the assay Myong's group used to monitor the complex could offer a venue for evaluating telomere-targeting drugs.
"We want to extend our a basic science knowledge in telomere biology into causes of cancer and we hope that our assay can be useful for telomere-targeted drug screening," Myong said.
INFORMATION:
The American Cancer Society and the Human Frontier Science Research Program supported this work.
Editor's note: To reach Sua Myong, call 217-244-6703; email smyong@illinois.edu. The paper, "POT1-TPP1 Regulates Telomeric Overhang Structural Dynamics'" is available online.
Proteins that work at the ends of DNA could provide cancer insight
2012-11-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Defining career paths in health systems improvement
2012-11-30
The sheer number of efforts aimed at improving the quality and efficiency of the U.S. health care system – ranging from portions of the national Affordable Care Act to local programs at individual hospitals and practices – reflects the urgency and importance of the task. One aspect that has received inadequate attention, according to three physicians writing in the January 2013 issue of Academic Medicine, is training the next generation of experts needed to help lead these efforts. In their Perspective article, which has been released online, the authors propose a framework ...
More evidence for an ancient Grand Canyon
2012-11-30
PASADENA, Calif.—For over 150 years, geologists have debated how and when one of the most dramatic features on our planet—the Grand Canyon—was formed. New data unearthed by researchers at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) builds support for the idea that conventional models, which say the enormous ravine is 5 to 6 million years old, are way off.
In fact, the Caltech research points to a Grand Canyon that is many millions of years older than previously thought, says Kenneth A. Farley, Keck Foundation Professor of Geochemistry at Caltech and coauthor of the ...
Marketing analytics ups Fortune 1000 return on assets 8 percent, says operations research study
2012-11-30
Fortune 1000 companies that increase their use of marketing analytics improve their return on assets an average 8% and as much as 21%, with returns ranging from $70 million to $180 million in net income, according to a paper written by two key members of the Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences (INFORMS®).
The research was conducted by Penn State University Management Science Professor Gary L. Lilien, former president of an INFORMS predecessor society; Arvind Rangaswamy of the Smeal College of Business at Penn State, former president of the INFORMS ...
Brief interventions can help college students return to a healthy lifestyle
2012-11-30
COLUMBIA, Mo. ¬— The weight gain commonly known as the "Freshman 15" is a negative aspect of the college experience for many college freshmen who are independent for the first time, most making lifestyle decisions about eating and exercise. Researchers say it's no surprise freshmen experience one of the largest weight gains in their lifetimes when they attend college. A new study from the University of Missouri has found that a brief intervention, sometimes as little as 30 minutes, can help put students back on the right track to a healthy lifestyle – a change that can ...
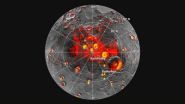
UCLA researchers find evidence for water ice deposits and organic material on Mercury
2012-11-30
Planetary scientists have identified water ice and unusually dark deposits within permanently shadowed areas at Mercury's north pole.
Using data collected by NASA's MESSENGER spacecraft, a team from UCLA crafted the first accurate thermal model of the solar system's innermost planet, successfully pinpointing the extremely cold regions where ice has been found on or below the surface.
The researchers say the newly discovered black deposits are a thin crust of residual organic material brought to the planet over the past several million years through impacts by water-rich ...
Activating ALC1: With a little help from friends
2012-11-30
KANSAS CITY, MO –Chromatin remodeling—the packaging and unpackaging of genomic DNA and its associated proteins—regulates a host of fundamental cellular processes including gene transcription, DNA repair, programmed cell death as well as cell fate. In their latest study, scientists at the Stowers Institute for Medical Research are continuing to unravel the finicky details of how these architectural alterations are controlled.
Through a series of biochemical experiments, Stowers Investigators Ron Conaway, Ph.D., and Joan Conaway, Ph.D., and their team discovered that chromatin ...
Garbage bug may help lower the cost of biofuel
2012-11-30
One reason that biofuels are expensive to make is that the organisms used to ferment the biomass cannot make effective use of hemicellulose, the next most abundant cell wall component after cellulose. They convert only the glucose in the cellulose, thus using less than half of the available plant material.
"Here at the EBI and other places in the biofuel world, people are trying to engineer microbes that can use both," said University of Illinois microbiologist Isaac Cann. "Most of the time what they do is they take genes from different locations and try and stitch all ...
Controversial treatment for autism may do more harm than good, Baylor University researchers find
2012-11-30
ABOUT BAYLOR SCHOOL OF EDUCATION
The Baylor School of Education is accredited by the National Council for Accreditation of Teacher Education and consists of four departments: Curriculum and Instruction (preparation for classroom teachers and specialists); Educational Administration (post-graduate preparation for school leadership); Educational Psychology (undergraduate and graduate programs for those who are interested in learning, development, measurement, and exceptionalities); and Health, Human Performance and Recreation (preparing for sport- and health-related careers, ...
St. Joseph's researchers identify gene involved in lung tumor growth
2012-11-30
(Phoenix, AZ Nov. 27, 2012) – Lung cancer researchers at St. Joseph's Hospital and Medical Center in Phoenix, Ariz., in collaboration with researchers at the Translational Genomics Research Institute and other institutions, have identified a gene that plays a role in the growth and spread of non-small cell lung cancer tumors, opening the door for potential new treatment options.
The study, titled "Elevated Expression of Fn14 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Correlates with Activated EGFR and Promotes Tumor Cell Migration and Invasion," was published in the May 2012 issue ...
Altimeter built at Goddard helped identify ice on Mercury
2012-11-30
VIDEO:
MESSENGER's Mercury Laser Altimeter sends out laser pulses that hit the ground and return to the instrument. The amount of light that returns for each pulse gives the reflectance at...
Click here for more information.
A Goddard-built instrument on NASA's MESSENGER mission provided one of three new lines of evidence that water ice exists near the north pole of Mercury. Most of the ice is covered by a thin layer of material that blankets and protects the ice, but in ...