(Press-News.org) This press release is available in German.
Researchers of the KIT Institute of Functional Interfaces (IFG), Jacobs University Bremen, and other institutions have developed a new method to produce metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). By means of the so-called liquid-phase epitaxy, the scientists succeeded in producing a new class of MOFs with a pore size never reached before. These frameworks open up interesting applications in medicine, optics, and photonics. The new class of MOFs, called "SURMOF 2", is presented in the "Nature Scientific Reports" journal.
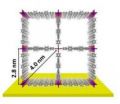
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) can store nanoscaled objects and make them available for various applications. For this reason, they are of particular interest in many research areas, including materials sciences, biology, and medicine. MOFs are highly ordered molecular systems, consisting of metal nodes and organic rods. The pores in these frameworks are freely accessible. MOFs are used in powder form to store hydrogen and other small molecules, such as carbon dioxide or methane. For more complex applications, such as the storage and subsequent release of antibiotics, MOF coatings of higher mechanical loadability are required.
At the KIT Institute of Functional Interfaces (IFG), the team of the head of institute Professor Christof Wöll is working on new methods for the production of MOFs. They make the MOF structures grow epitaxially, i.e. in layer-by-layer scheme, on the surface of substrates (SURMOFs – Surface-mounted Metal-organic Frameworks). In this way, the size and shape of the pores as well as their chemical functionality can be adjusted to the planned application. A special method developed by the IFG, the so-called liquid-phase epitaxy (LPE), allows for the production of framework structures that cannot be generated by conventional wet chemical methods. Detailed theoretical analysis by the group of Professor Heine of Jacobs University Bremen revealed that the interactions between the organic rods are responsible for the stability of these frameworks with large pores. In the Nature Scientific Reports journal, the researchers from IFG and the Institute of Organic Chemistry (IOC) of KIT, Jacobs University Bremen, and other institutions in Mainz, Bielefeld, and Thuwal/Saudi Arabia present a series of structurally related, highly symmetric frameworks with very large pores, which were produced by means of the LPE method.
These novel MOFs that are referred to as "SURMOFs 2" are produced by synthesizing various special organic molecules of variable lengths. The pore size of the new metal-organic frameworks is three times three nanometers. Hence, the pores have sufficient space for small proteins. Now, the researchers are working on increasing the length of the organic rods in order to be able to store even larger proteins and possibly also metallic nanoparticles in the next step. This will allow for interesting applications in optics and photonics.
"We think that SURMOFs 2 will have considerable potentials as optical materials. In the next step, we plan to produce
heterolayers, in which different materials will be stacked on top of each other," explains Professor Christof Wöll from the IFG. "The application potential of metal-organic frameworks can hardly be predicted at the moment. MOFs are composed structures. Chemists have learned how the components may be combined in a framework. Now, it will be important to use the variety of molecules known in chemistry to develop new materials with new application potentials that might revolutionize catalysis, sensor technology, or logical storage materials. Computer simulations are ideal to determine the components to be used for producing frameworks with optimum properties at the laboratory," explains Professor Thomas Heine from Jacobs University Bremen.
INFORMATION:
Jinxuan Liu, Binit Lukose, Osama Shekhah, Hasan Kemal Arslan, Peter Weidler, Hartmut Gliemann, Stefan Bräse, Sylvain Grosjean, Adelheid Godt, Xinliang Feng, Klaus Müllen, Ioan Bogdan Magdau, Thomas Heine, Christof Wöll: A novel series of isoreticular metal organic frameworks: realizing metastable structures by liquid phase epitaxy. In: Nature Scientific Reports 2, Article number: 921 bzw. doi: 10.1038/srep00921
www.nature.com/srep/2012/121204/srep00921/full/srep00921.html
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) is a public corporation according to the legislation of the state of Baden-Württemberg. It fulfills the mission of a university and the mission of a national research center of the Helmholtz Association. KIT focuses on a knowledge triangle that links the tasks of research, teaching, and innovation.
This press release is available on the internet at www.kit.edu.
Large pores
KIT researchers develop new method to produce metal-organic frameworks
2012-12-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pokemon provides rare opening for IU study of face-recognition processes
2012-12-05
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. -- At a Bloomington, Ind., toy store, kids ages 8 to 12 gather weekly to trade Pokemon cards and share their mutual absorption in the intrigue and adventure of Pokemon.
This may seem an unlikely source of material to test theories in cognitive neuroscience. But that is where Indiana University brain scientists Karin Harman James and Tom James were when an idea took hold.
"We were down at the club with our son, watching the way the kids talked about the cards, and noticed it was bigger than just a trading game," Tom James said.
Pokemon has since ...
'Resistance' to low-dose aspirin therapy extremely rare
2012-12-05
PHILADELPHIA — Roughly one-fifth of Americans take low-dose aspirin every day for heart-healthy benefits. But, based on either urine or blood tests of how aspirin blocks the stickiness of platelets – blood cells that clump together in the first stages of forming harmful clots – up to one third of patients are deemed unlikely to benefit from daily use. Such patients are called "aspirin resistant." Clots are the main cause of most heart attacks and strokes.
In people who have suffered a heart attack, low-dose aspirin reduces the chances of a second event by about one fifth, ...
RI Hospital: Standardized road test results differ from older adults' natural driving
2012-12-05
PROVIDENCE, R.I. – If you're thinking that little old lady driving 35 miles per hour in the passing lane shouldn't be behind the wheel, you may be right. Studies at Rhode Island Hospital, and elsewhere, have shown that our driving abilities decline with age, and for those with cognitive issues such as dementia, it can be even worse.
A standardized road test – much like the one teenagers take to receive their learner's permit and driver's license – is often used to measure an individual's performance, including those of older adults. But researchers at the Rhode Island ...
New test adds to scientists' understanding of Earth's history, resources
2012-12-05
GAINESVILLE, Fla. — A new study co-authored by a University of Florida researcher provides the first direct chronological test of sequence stratigraphy, a powerful tool for exploring Earth's natural resources.
The model allows geologists to better understand how sedimentary rocks are related to one another in time and space and predict what types of rocks are located in different areas. The information may help scientists more reliably interpret various aspects of Earth's history such as long-term climate changes or extinction events, and also benefit companies searching ...
Studying marrow, URMC researchers accelerate blood stem cells
2012-12-05
University of Rochester Medical Center scientists are testing a new approach to speed a patient's recovery of blood counts during a vulnerable period after a stem-cell transplant, according to a study published in the journal Stem Cells.
Laura M. Calvi, M.D., and Rebecca L. Porter, an M.D./Ph.D. student in Calvi's lab, reported that prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), a drug previously used to treat stomach ulcers, boosts blood production following an assault on the bone marrow from radiation or chemotherapy. Although their study was done in mice, Calvi believes it has significance ...
Women and men appear to benefit in different ways from AA participation
2012-12-05
A new study finds differences in the ways that participation in Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) helps men and women maintain sobriety. Two Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) investigators found that, while many factors are helpful to all AA participants, some were stronger in men and some in women. For example, avoidance of companions who encourage drinking and social situations in which drinking is common had more powerful benefits for men, while increased confidence in the ability to avoid drinking while feeling sad, depressed or anxious appeared to be more important for ...
Research identifies a way to block memories associated with PTSD or drug addiction
2012-12-05
VIDEO:
New research from Western University could lead to better treatments for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) and drug addiction by effectively blocking memories. Steven Laviolette and Nicole Lauzon describe how...
Click here for more information.
New research from Western University could lead to better treatments for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) and drug addiction by effectively blocking memories. The research performed by Nicole Lauzon, a PhD candidate ...
Morphing DNA hydrogel flows like liquid but remembers its original shape
2012-12-05
ITHACA, N.Y. – A bit reminiscent of the Terminator T-1000, a new material created by Cornell researchers is so soft that it can flow like a liquid and then, strangely, return to its original shape.
Rather than liquid metal, it is a hydrogel, a mesh of organic molecules with many small empty spaces that can absorb water like a sponge. It qualifies as a "metamaterial" with properties not found in nature and may be the first organic metamaterial with mechanical meta-properties.
Hydrogels have already been considered for use in drug delivery – the spaces can be filled with ...
Microchoreography: Researchers use synthetic molecule to guide cellular 'dance'
2012-12-05
Johns Hopkins researchers have used a small synthetic molecule to stimulate cells to move and change shape, bypassing the cells' usual way of sensing and responding to their environment. The experiment pioneers a new tool for studying cell movement, a phenomenon involved in everything from development to immunity to the spread of cancer.
"We were able to use synthetic molecules small enough to slip inside the cell and activate a chemical reaction controlling cell movement, bypassing most of the steps that usually lead up to this reaction," says Andre Levchenko, Ph.D., ...
Advice for bag-in-box wine drinkers: Keep it cool
2012-12-05
Bag-in-box wines are more likely than their bottled counterparts to develop unpleasant flavors, aromas and colors when stored at warm temperatures, a new study has found. Published in ACS' Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, it emphasizes the importance of storing these popular, economical vintages at cool temperatures.
Helene Hopfer and colleagues explain that compounds in wine react with oxygen in the air to change the way wine looks, tastes and smells. These reactions speed up with increasing temperature. Many winemakers are moving away from the traditional ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Hairdressers could be a secret weapon in tackling climate change, new research finds
Genetic risk for mental illness is far less disorder-specific than clinicians have assumed, massive Swedish study reveals
A therapeutic target that would curb the spread of coronaviruses has been identified
Modern twist on wildfire management methods found also to have a bonus feature that protects water supplies
AI enables defect-aware prediction of metal 3D-printed part quality
Miniscule fossil discovery reveals fresh clues into the evolution of the earliest-known relative of all primates
World Water Day 2026: Applied Microbiology International to hold Gender Equality and Water webinar
The unprecedented transformation in energy: The Third Energy Revolution toward carbon neutrality
Building on the far side: AI analysis suggests sturdier foundation for future lunar bases
Far-field superresolution imaging via k-space superoscillation
10 Years, 70% shift: Wastewater upgrades quietly transform river microbiomes
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
Improve education and transitional support for autistic people to prevent death by suicide, say experts
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic could cut risk of major heart complications after heart attack, study finds
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
[Press-News.org] Large poresKIT researchers develop new method to produce metal-organic frameworks