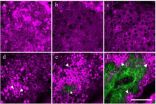
(Press-News.org) (TORONTO, Canada – Dec. 13, 2012 ) – Cancer scientists led by Dr. John Dick at the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre have found a way to follow single tumour cells and observe their growth over time. By using special immune-deficient mice to propagate human colorectal cancer, they found that genetic mutations, regarded by many as the chief suspect driving cancer growth, are only one piece of the puzzle. The team discovered that biological factors and cell behaviour – not only genes – drive tumour growth, contributing to therapy failure and relapse.
The findings, published today online ahead of print in Science, are "a major conceptual advance in understanding tumour growth and treatment response," says Dr. Dick, who holds a Canada Research Chair in Stem Cell Biology and is a Senior Scientist at University Health Network's McEwen Centre for Regenerative Medicine and Ontario Cancer Institute, the research arm of the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre. He is also a Professor in the Department of Molecular Genetics, University of Toronto. The research work was primarily carried out in Toronto by Antonija Kreso, Catherine O'Brien, and other members of the Dick lab with support from clinician-scientists at Mount Sinai Hospital and at the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research, and from genome scientists at St Jude Research Hospital, Memphis, and the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
By tracking individual tumour cells, they found that not all cancer cells are equal: only some cancer cells are responsible for keeping the cancer growing. Within this small subset of propagating cancer cells, some kept the cancer growing for long time periods (up to 500 days of repeated tumour transplantation), while others were transient and stopped within 100 days. They also discovered a class of propagating cancer cells that could lie dormant before being activated. Importantly, the mutated cancer genes were identical for all of these different cell behaviours.
When chemotherapy was given to mice in which the human tumours were growing, the team made the unexpected finding that the long-term propagating cells were generally sensitive to treatment. Instead, the dormant cells were not killed by drug treatment and became activated, causing the tumour to grow again. The cancer cells that survived therapy had the same mutations as the sensitive cancer cells proving that cellular factors not linked to genetic mutation can be responsible for therapy failure.
The research challenges conventional wisdom in the cancer research field that the variable growth properties and resistance to therapy of cancer cells are solely based on the spectrum of genetic mutations within a tumour, says Dr. Dick. Instead, the scientists have validated a developmental view of cancer growth where other biological factors and cell functions outside genetic mutations are very much at play in sustaining disease and contributing to therapy failure.
The research published today builds on decades of experience by Dr. Dick, who focuses on understanding the cellular processes that maintain tumour growth. In 2004, Dr. Dick published related findings in leukaemia, but in the present study his team was able to compare the importance of genetic events with cellular mechanisms for the first time. It is also the first study of its kind in a solid tumour system.
Dr. Dick says the findings convinced him that the conventional view that only explores gene mutations is no longer enough in the quest to accelerate delivery of personalized cancer medicine to patients – targeted, effective treatments customized for individuals.
"The data show that gene sequencing of tumours to find the spectrum of their mutations is definitely not the whole story when it comes to determining which therapies will be most effective," says Dr. Dick.
"This is a paradigm shift that shows research also needs to focus on the biological properties of cells. For example, finding a way to put dormant cells into growth cycles could make them more sensitive to chemotherapy treatment. Targeting the biology and growth properties of cancer cells could expand the repertoire of usable therapeutic agents and provide better outcomes for patients."
Dr. Dick is renowned for pioneering the cancer stem cell field by identifying leukemia stem cells in 1994 and colon cancer stem cells in 2007. Also in 2011, Dr. Dick isolated the normal human blood stem cell in its purest form – as a single stem cell capable of regenerating the entire blood system. Collectively, Dr. Dick's research is paving the way for better clinical cancer therapy.
###
The research was funded by Genome Canada through the Ontario Genomics Institute, the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research and a Premier's Summit Award with funds from the Province of Ontario, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the Canada Research Chairs Program, the Canada Foundation for Innovation, and the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care, as well as The Princess Margaret Cancer Foundation.
About the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre, University Health Network
The Princess Margaret Cancer Centre and its research arm, Ontario Cancer Institute, have achieved an international reputation as global leaders in the fight against cancer and delivering personalized cancer medicine. The Princess Margaret, one of the top five international cancer research centres, is a member of the University Health Network, which also includes Toronto General Hospital, Toronto Western Hospital and Toronto Rehabilitation Institute. All are research hospitals affiliated with the University of Toronto. For more information, go to www.theprincessmargaret.ca or www.uhn.ca . END
Wrinkles, dryness, and a translucent and fragile appearance are hallmarks of old skin, caused by the natural aging of skin cells. But while most of us can recognize the signs of lost youth when we peer into the mirror each morning, scientists do not have a standardized way to measure the extent of age damage in skin. Now a group of Taiwanese researchers has used a specialized microscope to peer harmlessly beneath the skin surface to measure natural age-related changes in the sizes of skin cells. The results, which are published in the Optical Society's (OSA) open-access ...
The insurance industry, the world's largest business with $4.6 trillion in revenues, is making larger efforts to manage climate change-related risks, according to a new study published today in the journal Science.
"Weather- and climate-related insurance losses today average $50 billion a year. These losses have more than doubled each decade since the 1980s, adjusted for inflation," says the study's author Evan Mills, a scientist in Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab)'s Environmental Energy Technologies Division. "Insurers have become quite adept at quantifying ...
BOSTON—Scientists at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute have discovered a molecular switch that enables advanced prostate cancers to spread without stimulation by male hormones, which normally are needed to spur the cancer's growth. They say the finding could lead to a new treatment for prostate cancers that are no longer controlled by hormone-blocking drugs.
The researchers report in the Dec. 14 issue of Science that the molecular switch occurs in a protein, EZH2, which is increased in these tumors, termed castration-resistant prostate cancers (CRPC).
EZH2 is part of a ...
Montreal, December 13, 2012 – From Gran Turismo to WWE Smackdown, sports-based video games represent a wide variety of pursuits. When it comes to the people who actually play those games, however, little is known. How do sports video game players fit their games into a larger sports-related context? How does their video game play inform their media usage and general sports fandom?
That's what Concordia University communications professor Mia Consalvo sought to discover when she embarked on a large-scale study of video game players, the results of which were recently published ...
CHICAGO -- Northwestern Medicine researchers have discovered a "two-faced" group of cells at work in human colon cancer, with opposing functions that can suppress or promote tumor growth. These cells are a subset of T-regulatory (Treg) cells, known to suppress immune responses in healthy individuals
In this previously unknown Treg subset, the presence of the protein RORγt has been shown to differentiate between cancer-protecting and cancer-promoting properties.
The Northwestern team, led by Khashayarsha Khazaie, research associate professor at the Robert H. ...
ARGONNE, Ill. – For the first time, scientists witnessed the details of the full, ultrafast process of liquid droplets evolving into a bubble when they strike a surface. Their research determined that surface wetness affects the bubble's fate.
This research could one day help eliminate bubbles formed during spray coating, metal casting and ink-jet printing. It also could impact studies on fuel efficiency and engine life by understanding the splashing caused by fuel hitting engine walls.
"How liquid coalesces into a drop or breaks up into a splash when hitting something ...
Prostate cancer patients receiving the costly treatment known as proton radiotherapy experienced minimal relief from side effects such as incontinence and erectile dysfunction, compared to patients undergoing a standard radiation treatment called intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT), Yale School of Medicine researchers report in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Standard treatments for men with prostate cancer, such as radical prostatectomy and IMRT, are known for causing adverse side effects such as incontinence and erectile dysfunction. Proponents of ...
New research by a University of Alberta archeologist may lead to a rethinking of how, when and from where our ancestors left Africa.
U of A researcher and anthropology chair Pamela Willoughby's explorations in the Iringa region of southern Tanzania yielded fossils and other evidence that records the beginnings of our own species, Homo sapiens. Her research, recently published in the journal Quaternary International, may be key to answering questions about early human occupation and the migration out of Africa about 60,000 to 50,000 years ago, which led to modern humans ...
Peach growers in California may soon have better tools for saving water because of work by U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientists in Parlier, Calif.
Agricultural Research Service (ARS) scientist Dong Wang is evaluating whether infrared sensors and thermal technology can help peach growers decide precisely when to irrigate in California's San Joaquin Valley. ARS is USDA's principal intramural scientific research agency, and the research supports the USDA priority of promoting international food security.
Irrigation is the primary source of water for agriculture ...
The plague-causing bacteria Yersinia pestis evades detection and establishes a stronghold without setting off the body's early alarms.
New discoveries reported this week help explain how the stealthy agent of Black Death avoids tripping a self-destruct mechanism inside germ-destroying cells.
The authors of the study, appearing in the Dec. 13 issue of Cell Host & Microbe, are Dr. Christopher N. LaRock of the University of Washington Department of Microbiology and Dr. Brad Cookson, UW professor of microbiology and laboratory medicine.
Normally, certain defender cells ...