(Press-News.org) GAINESVILLE, Fla. --- An international team of scientists including University of Florida researchers has generated the most comprehensive tree of life to date on placental mammals, which are those bearing live young, including bats, rodents, whales and humans.
Appearing Thursday in the journal Science, the study details how researchers used both genetic and physical traits to reconstruct the common ancestor of placental mammals, the creature that gave rise to many mammals alive today. The data show that contrary to a commonly held theory, the group diversified after the extinction of dinosaurs 65 million years ago. The research may help scientists better understand how mammals survived past climate change and how they may be impacted by future environmental conditions.
UF researchers led the team that analyzed the anatomy of living and fossil primates, including lemurs, monkeys and humans, as well as their closest living relatives, flying lemurs and tree shrews. The multi-year collaborative project was funded by the National Science Foundation Assembling the Tree of Life Program.
"With regards to evolution, it's critical to understand the relationships of living and fossil mammals before asking questions about 'how' and 'why,' " said co-author Jonathan Bloch, associate curator of vertebrate paleontology at the Florida Museum of Natural History on the UF campus. "This gives us a new perspective of how major change can influence the history of life, like the extinction of the dinosaurs -- this was a major event in Earth's history that potentially then results in setting the framework for the entire ordinal diversification of mammals, including our own very distant ancestors."
Visual reconstruction of the placental ancestor -- a small, insect-eating animal – was made possible with the help of a powerful cloud-based and publicly accessible database called MorphoBank, www.morphobank.org. Unlike other reconstructions, the new study creates a clearer picture of the tree of life by combining two data types: Phenomic data includes observational traits such as anatomy and behavior, while genomic data is encoded by DNA.
"Discovering the tree of life is like piecing together a crime scene -- it is a story that happened in the past that you can't repeat," said lead author Maureen O'Leary, an associate professor in the department of anatomical sciences in the School of Medicine at Stony Brook University and research associate at the American Museum of Natural History. "Just like with a crime scene, the new tools of DNA add important information, but so do other physical clues like a body or, in the scientific realm, fossils and anatomy. Combining all the evidence produces the most informed reconstruction of a past event."
Researchers recorded observational traits for 86 placental mammal species, including 40 fossil species. The resulting database contains more than 12,000 images that correspond to more than 4,500 traits detailing characteristics like the presence or absence of wings, teeth and certain bones, type of hair cover and brain structures. The dataset is about 10 times larger than information used in previous studies of mammal relationships.
"It was a great way to learn anatomy, in a nutshell," said co-author Zachary Randall, a UF biology graduate student and research associate at the Florida Museum. "While coding for humans, I could clearly see which anatomical features are unique, shared or not shared with other groups of mammals. This study is a great backbone for future work."
Bloch and Randall collaborated with study co-authors Mary Silcox of the University of Toronto Scarborough and Eric Sargis of Yale University to characterize humans, plus seven other living and one fossil species from the clade Euarchonta, which includes primates, tree shrews and flying lemurs.
"I think this database is amazing because it's being presented in such a way that it will be reproducible for the future generations," Bloch said. "It illustrates exactly what we did and leaves nothing to the imagination – you can actually go to the pictures and see it."
The evolutionary history of placental mammals has been interpreted in very different ways depending on the data analyzed. One leading analysis based on genomic data alone predicted that a number of placental mammal lineages existed in the Late Cretaceous and survived the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction.
"It has been suggested that primates diverged from other mammals well before the extinction of the dinosaurs, but our work using direct evidence from the fossil record tells a different story," Bloch said.
The team reconstructed the anatomy of the placental common ancestor by mapping traits most strongly supported by the data to determine it had a two-horned uterus, a brain with a convoluted cerebral cortex, and a placenta in which maternal blood came in close contact with membranes surrounding the fetus, as in humans.
###
Writer: Danielle Torrent, dtorrent@flmnh.ufl.edu
Source: Jonathan Bloch, cell 352-514-1270, jbloch@flmnh.ufl.edu
Media contact: Paul Ramey, 352-213-0999, pramey@flmnh.ufl.edu
END
WASHINGON, D.C.—February 7, 2013—Today, The Lancet Infectious Diseases published a new report that examines the global economic burden of Chagas disease. In the first study of its kind, researchers measured the health and economic impact of Chagas disease and found that the total economic burden of Chagas disease matches or exceeds that of many more well-known diseases such as rotavirus, Lyme disease and cervical cancer.
Chagas disease infects an estimated 10 million people worldwide, with most cases occurring in Latin America. It is a parasitic infection transmitted ...
New Haven, Conn.— A team of scientists anchored at Yale University has demonstrated a new, highly versatile approach for quickly assembling drug-like compounds, establishing a broad new route to drug discovery and medical treatment. They report their results in the journal Science on Feb 8.
Drug molecules interact with their targets, such as proteins or enzymes, by attaching to them in a way that neutralizes the target's undesirable effects in the body. This is sometimes called the "lock-and-key" method. The new approach offers scientists far greater control over the ...
The cause of the fireworks seen in this Hubble image and video is hidden behind a dense disc and envelope of dust. However, astronomers think that the strobe effect is due to periodic interactions between two newly-formed stars that are gravitationally bound to each other.
These two stars drag material inwards from a surrounding disc of gas and dust. Astronomers propose that the light flashes seen in this video are due to this material suddenly being dumped onto the growing stars as they near one another in their orbits, unleashing a blast of radiation.
"The protostar ...
The scientific and ethical debate over the use of animals in medical research has raged for years, but perspectives are shifting, viewpoints are becoming more nuanced, and new initiatives are seeking alternatives to animal testing, according to a special report by The Hastings Center, "Animal Research Ethics: Evolving Views and Practices." The report is available on a new Web site, animalresearch.thehastingscenter.org, a hub of educational information that defines and interprets this changing landscape.
These resources are the outcome of a project on the ethics of medical ...
Researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine say overexpression of a protein called alpha-synuclein appears to disrupt vital recycling processes in neurons, starting with the terminal extensions of neurons and working its way back to the cells' center, with the potential consequence of progressive degeneration and eventual cell death.
The findings, published in the February 6, 2013 issue of the Journal of Neuroscience, have major implications for more fully understanding the causes and mechanisms of Parkinson's disease (PD), a neurodegenerative ...
VIDEO:
This video, created from a sequence of images from the Hubble Space Telescope, shows a pulse of light emanating from the protostellar object LRLL 54361. Most if not all of...
Click here for more information.
Two of NASA's great observatories, the Spitzer and Hubble space telescopes, have teamed up to uncover a mysterious infant star that behaves like a strobe light.
Every 25.34 days, the object, designated LRLL 54361, unleashes a burst of light. Although a similar ...
A recent study of the amphibians and reptiles of Sierra Madre Mountain Range, northeastern Luzon, reveals a preliminary enumeration of more than 100 species that contribute to the unique biodiversity of the region. At present, the Luzon region's herpetological range stands at more than 150 species. Out of these, a total of 49 amphibian species have been documented, 44 of which are native and a remarkable 32 endemic. In the world of reptiles, Luzon can boast with 106 native species, 76 of which are unique to this region.
The catalogue published in the open access journal ...
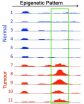
Tumourigenesis is driven by genetic alterations and by changes in the epigenome, for instance by the addition of methyl groups to cytosine bases in the DNA. A deeper understanding of the interaction between the genetic and epigenetic mechanisms is critical for the selection of tumour biomarkers and for the future development of therapies. Human tumour specimens and cell lines however contain a plethora of genetic and epigenetic changes, which complicate data analysis. In contrast, certain mouse tumour models contain only a single genetic mutation and allow the analysis ...
Researchers have identified a microRNA liver gene, miR-27b, which regulates lipid (cholesterol or fat) levels in the blood. This regulator gene controls multiple genes involved in dyslipidemia—abnormal blood cholesterol levels that can contribute to heart disease. Study details published in the February issue of Hepatology, a journal of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD), describe a new in silico approach to identify the significance of microRNAs in regulating disease-related gene pathways.
The Human Genome Project (HGP) was completed in ...
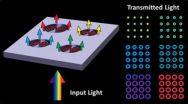
CHESTNUT HILL, MA (February 7, 2013) – Using the geometric and material properties of a unique nanostructure, Boston College researchers have uncovered a novel photonic effect where surface plasmons interact with light to form "plasmonic halos" of selectable output color. The findings appear in the journal Nano Letters.
The novel nanostructure proved capable of manipulating electron waves known as surface plasmon polaritons, or SPPs, which were discovered in the 1950s but of late have garnered the attention of scientists for their potential applications in fields that ...