(Press-News.org) Philadelphia - According to a new study by researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, patients with Barrett's esophagus and early or pre-cancerous cells have been shown to significantly benefit from minimally invasive therapy delivered through an endoscope – a medical instrument used to look inside an organ or cavity in the body. Until recently, patients with these conditions were treated by surgery to remove the whole esophagus. Study results show that endoscope-based therapies have a high success rate; all of the damaged cells were removed in up to 95 percent of cases, greatly reducing the chances of cancer progression. Additionally, in over two-thirds of cases, patients had no biological signs of the return of disease for years. The study appears in the February issue of GIE: Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.
The esophagus is the tube that connects the mouth with the stomach. Barrett's esophagus, which can be a precursor to cancer of the esophagus, is a condition in which the cells of the lower esophagus become damaged, typically from persistent exposure to stomach acid. Barrett's esophagus affects over three million people in the United States. Men develop Barrett's esophagus twice as often as women.
"This study is one of only a few that focuses on the long-term effects of minimally invasive techniques for the treatment of Barrett's esophagus," said Gregory G. Ginsberg, MD, professor of Medicine and director of Endoscopic Services at Penn Medicine, and corresponding author on the study. "We examined patients from as far back as 1998 and had an average follow-up of nearly three years. This gives us a more complete measure of assessing the longer-term benefits of these types of intervention."
Among the therapies evaluated in the new study were radiofrequency ablation and endoscopic resection. In radiofrequency ablation, a balloon or small paddle that transmits energy is attached to the endoscope to burn away a thin layer of the esophageal mucosa, removing the damaged cells. It is a half-hour outpatient procedure performed under mild sedation.
In an endoscopic resection, an endoscope is inserted down the throat to reach the esophagus. Its light and camera enable the doctor to see and navigate, and it has tools for removal of the affected tissue. Both procedures are far less invasive and less expensive than an esophagectomy, a major surgery that removes the esophagus in patients with advanced conditions.
Approximately 10 percent of patients with long-term gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) will develop Barrett's esophagus. GERD is a chronic regurgitation of acid from the stomach into the lower esophagus, which often results in recurring heartburn and, less commonly, difficulty swallowing. A small percentage of patients with Barrett's esophagus will develop high grade dysplasia, a more serious condition. High grade dysplasia isn't cancer, but it is the step before cancer. The risk of developing esophageal cancer from high grade dysplasia has been examined in several studies and ranges from 20 percent to 50 percent. Overall, patients with Barrett's esophagus have a less than 1 percent risk of developing esophageal cancer over their lifetimes. Esophageal cancer is especially invidious; it has a less than 15 percent five-year survival rate.
Results of the study also show that in as many as one-third of the cases, manifestations of the disease returned. "These findings of recurrence make it clear that Barrett's esophagus patients should undergo life-long periodic endoscopic exams to watch for precancerous esophagus cells. If we find these cells, we can treat them via the endoscope to prevent esophageal cancer," said Ginsberg.
Barrett's esophagus is named after Norman Barrett (1903-1979), who described the condition in 1950.
Other study authors from Penn include Carlos Guarner-Argente, MD, PhD; Thomas Buoncristiano, Emma E. Furth, MD, and Gary W. Falk, MD, MSc.
INFORMATION:
Penn Medicine is one of the world's leading academic medical centers, dedicated to the related missions of medical education, biomedical research, and excellence in patient care. Penn Medicine consists of the Raymond and Ruth Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania (founded in 1765 as the nation's first medical school) and the University of Pennsylvania Health System, which together form a $4.3 billion enterprise.
The Perelman School of Medicine is currently ranked #2 in U.S. News & World Report's survey of research-oriented medical schools. The School is consistently among the nation's top recipients of funding from the National Institutes of Health, with $479.3 million awarded in the 2011 fiscal year.
The University of Pennsylvania Health System's patient care facilities include: The Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania -- recognized as one of the nation's top "Honor Roll" hospitals by U.S. News & World Report; Penn Presbyterian Medical Center; and Pennsylvania Hospital — the nation's first hospital, founded in 1751. Penn Medicine also includes additional patient care facilities and services throughout the Philadelphia region.
Penn Medicine is committed to improving lives and health through a variety of community-based programs and activities. In fiscal year 2011, Penn Medicine provided $854 million to benefit our community.
END
SEATTLE – An international research team co-led by cancer prevention researcher Ulrike "Riki" Peters, Ph.D., M.P.H., and biostatistician Hsu Li, Ph.D., at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center has identified variations in four genes that are linked to an increased risk of colorectal cancer. Peters and colleagues from 40 institutes throughout the world published their findings online ahead of the April print issue of Gastroenterology.
Peters and colleagues for the past four years have been studying the genes linked to colorectal cancer through the Genetics and Epidemiology ...
CHICAGO --- U.S. veterans diagnosed with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) are frequently prescribed doses of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), such as omeprazole (commonly known by brand names such as Prilosec), that are much higher than recommended --- and they are kept on the drug far too long, according to a new Northwestern Medicine® study.
PPIs are among the most widely used drugs in the nation, resulting in more than $11 billion in annual direct health care costs in the U.S. PPI overuse has been documented in previous studies, but this is the first study to examine ...
As magnetic fields on the sun rearrange and realign, dark spots known as sunspots can appear on its surface. Over the course of Feb. 19-20, 2013, scientists watched a giant sunspot form in under 48 hours. It has grown to over six Earth diameters across but its full extent is hard to judge since the spot lies on a sphere not a flat disk.
The spot quickly evolved into what's called a delta region, in which the lighter areas around the sunspot, the penumbra, exhibit magnetic fields that point in the opposite direction of those fields in the center, dark area. This is a fairly ...
VIDEO:
On July 19, 2012, an eruption occurred on the sun that produced a moderately powerful solar flare and a dazzling magnetic display known as coronal rain. Hot plasma in the...
Click here for more information.
Eruptive events on the sun can be wildly different. Some come just with a solar flare, some with an additional ejection of solar material called a coronal mass ejection (CME), and some with complex moving structures in association with changes in magnetic field lines ...
INDIANAPOLIS -- Advances in electronic medical record systems and health information exchange are shifting efforts in public health toward greater use of information systems to automate disease surveillance, but a study from the Regenstrief Institute has found that these technologies' capabilities are underutilized by those on the front lines of preventing and reporting infections.
The new study measured the awareness, adoption and use of electronic medical record systems and health information exchange by hospital-based infection preventionists (formerly known as infection ...
VIDEO:
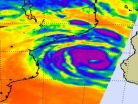
The TRMM satellite flew above Haruna on Feb. 20 at 0717 UTC. Some powerful storms Haruna's northern edge showed rainfall over 108 mm (~4.25 inches) per hour and cloud tops...
Click here for more information.
Cyclone Haruna strengthened into a cyclone and quickly developed an eye that became apparent on visible and infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite. NASA's TRMM satellite analyzed Haruna's heavy rainfall, and NASA and NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite captured a ...
AUDIO:
This is an example of a trill song type that tells listeners how big the singer is. Their larger physical size means that bigger male purple-crowned fairy-wrens can sing this...
Click here for more information.
A male fairy-wren's low pitch song indicates body size, a new international study has shown.
The study led by University of Melbourne researcher Dr Michelle Hall, is the first to show that the larger the male fairy wren, the lower the pitch of his song.
"This ...
INDIANAPOLIS -- A study combining genetic data with brain imaging, designed to identify genes associated with the amyloid plaque deposits found in Alzheimer's disease patients, has not only identified the APOE gene -- long associated with development of Alzheimer's -- but has uncovered an association with a second gene, called BCHE.
A national research team, led by scientists at the Indiana University School of Medicine, reported the results of the study in an article in Molecular Psychiatry posted online Tuesday. The study is believed to be the first genome-wide association ...
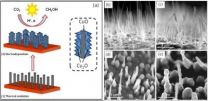
Researchers from The University of Texas at Arlington are pioneering a new method for using carbon dioxide, or CO2, to make liquid methanol fuel by using copper oxide nanowires and sunlight.
The process is safer, simpler and less expensive than previous methods to convert the greenhouse gas associated with climate change to a useful product, said Krishnan Rajeshwar, interim associate vice president for research at UT Arlington and one of the authors of a paper recently published in the journal Chemical Communications. Researchers began by coating the walls of copper oxide, ...
Gravity remains the dominant force on large astronomical scales, but when it comes to stars in young star clusters the dynamics in these crowded environments cannot be simply explained by the pull of gravity.
After analyzing Hubble Space Telescope images of star cluster NGC 1818 in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way, researchers at the Kavli Institute for Astronomy and Astrophysics (KIAA) at Peking University in Beijing found more binary star systems toward the periphery of cluster than in the center – the opposite of what they expected. The ...