(Press-News.org) Kyoto, Japan – Working with a group from Nagasaki University, a research group at the Center for iPS Cell Research and Application (CiRA) at Japan's Kyoto University has announced in the Feb. 21 online publication of Cell Stem Cell has successfully modeled Alzheimer's disease (AD) using both familial and sporadic patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), and revealed stress phenotypes and differential drug responsiveness associated with intracellular amyloid beta oligomers in AD neurons and astrocytes.
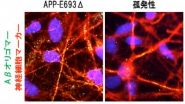
In a study published online in Cell Stem Cell, Associate Professor Haruhisa Inoue and his team at CiRA and a research group led by Professor Nobuhisa Iwata of Nagasaki University generated cortical neurons and astrocytes from iPSCs derived from two familial AD patients with mutations in amyloid precursor protein (APP), and two sporadic AD patients. The neural cells from one of the familial and one of the sporadic patients showed endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-stress and oxidative-stress phenotypes associated with intracellular amyloid beta oligomers. The team also found that these stress phenotypes were attenuated with docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) treatment. These findings may help explain the variable clinical results obtained using DHA treatment, and suggest that DHA may in fact be effective only for a subset of patients.
Using both familial and sporadic AD iPSCs, the researchers discovered that pathogenesis differed between individual AD patients. For example, secreted amyloid beta 42 levels were depressed in familial AD with APP E693 delta mutation, elevated in familial AD with APP V717L mutation, but normal in sporadic AD.
``This shows that patient classification by iPSC technology may contribute to a preemptive therapeutic approach toward AD,'' said Inoue, a principal investigator at CiRA who is also a research director for the CREST research program funded by the Japan Science and Technology Agency. ``Further advances in iPSC technology will be required before large-scale analysis of AD patient-specific iPSCs is possible.''
INFORMATION:
Kondo et al. "Modeling Alzheimer's disease using iPSCs reveals stress phenotypes associated with intracellular amyloid beta and differential drug responsiveness.''
About CiRA
The Center for iPS Cell Research and Application (CiRA) was founded in 2008 at Kyoto University in Japan, and is a leading institute in the field of induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) research. Headed by director Professor Shinya Yamanaka, who won the 2012 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, CiRA currently has 28 principal investigators working on various studies from basic research to applied studies using patient-specific iPSCs with the goal of bringing iPSC technology to the clinical frontline.
URL: http://www.cira.kyoto-u.ac.jp/e/
Japanese version is available at http://www.cira.kyoto-u.ac.jp/
Modeling Alzheimer's disease using iPSCs
Study reveals stress phenotypes associated with intracellular amyloid beta and differential drug responsiveness
2013-02-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Schizophrenia genes increase chance of IQ loss
2013-02-21
People who are at greater genetic risk of schizophrenia are more likely to see a fall in IQ as they age, even if they do not develop the condition.
Scientists at the University of
Edinburgh say the findings could lead to new research into how different genes for schizophrenia affect brain function over time. They also show that genes associated with schizophrenia influence people in other important ways besides causing the illness itself.
The researchers used the latest genetic analysis techniques to reach their conclusion on how thinking skills change with age.
They ...
EASL publishes first comprehensive literature review on the burden of liver disease in Europe
2013-02-21
Brussels and Geneva, 20th February 2013 --- Major progress has been made in the past 30 years in the knowledge and management of liver disease, yet approximately 29 million Europeans still suffer from a chronic liver condition.
The European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL) today unveiled its new publication The burden of liver disease in Europe: a review of available epidemiological data. Key findings in the report suggest that alcohol consumption, viral hepatitis B and C and metabolic syndromes related to overweight and obesity are the leading causes of ...
Omega-3s inhibit breast cancer tumor growth, study finds
2013-02-21
A lifelong diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids can inhibit growth of breast cancer tumours by 30 per cent, according to new research from the University of Guelph.
The study, published recently in the Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, is believed to be the first to provide unequivocal evidence that omega-3s reduce cancer risk.
"It's a significant finding," said David Ma, a professor in Guelph's Department of Human Health and Nutritional Sciences, and one of the study's authors.
"We show that lifelong exposure to omega-3s has a beneficial role in disease prevention ...
Microbubbles improve myocardial remodelling after infarction
2013-02-21
Scientists from the Bonn University Hospital successfully tested a method in mice allowing the morphological and functional sequelae of a myocardial infarction to be reduced. Tiny gas bubbles are made to oscillate within the heart via focused ultrasound - this improves microcirculation and decreases the size of the scar tissue. The results show that the mice, following myocardial infarction, have improved cardiac output as a result of this method, as compared to untreated animals. The study is now being presented in the professional journal PLOS ONE.
Every year in Germany, ...
Inhaled betadine leads to rare complication
2013-02-21
Philadelphia, Pa. (February 21, 2013) - A routine step in preparing for cleft palate surgery in a child led to an unusual—but not unprecedented—case of lung inflammation (pneumonitis), according to a report in the The Journal of Craniofacial Surgery. The journal, edited by Mutaz B. Habal, MD, FRCSC, is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
The complication resulted from accidental inhalation of povidone-iodine (PI), or Betadine—an antiseptic widely used before surgery. The rare complication led to new surgical "prep" steps to reduce ...
Human heart development slower than other mammals
2013-02-21
The walls of the human heart are a disorganised jumble of tissue until relatively late in pregnancy, despite having the shape of a fully functioning heart, according to a pioneering study.
Experts from the University of Sheffield's Medical School collaborated on research to create the first comprehensive model of human heart development using observations of living foetal hearts. The results showed surprising differences from existing animal models.
Although scientists saw four clearly defined chambers in the foetal heart from the eighth week of pregnancy, they did ...
The age from when children can hop on one leg
2013-02-21
This press release is available in German. Motor development in children under five years of age can now be tested reliably: Together with colleagues from Lausanne, researchers from the University Children's Hospital Zurich and the University of Zurich have determined normative data for different exercises such as hopping or running. This enables parents and experts to gage the motor skills of young children for the first time objectively and thus identify abnormalities at an early stage.
My child still can't stand on one leg or walk down the stairs in alternating ...
Scientists unveil secrets of important natural antibiotic
2013-02-21
An international team of scientists has discovered how an important natural antibiotic called dermcidin, produced by our skin when we sweat, is a highly efficient tool to fight tuberculosis germs and other dangerous bugs.
Their results could contribute to the development of new antibiotics that control multi-resistant bacteria.
Scientists have uncovered the atomic structure of the compound, enabling them to pinpoint for the first time what makes dermcidin such an efficient weapon in the battle against dangerous bugs.
Although about 1700 types of these natural antibiotics ...
In rich and poor nations, giving makes people feel better than getting, research finds
2013-02-21
WASHINGTON - Feeling good about spending money on someone else rather than for personal benefit may be a universal response among people in both impoverished countries and rich nations, according to new research published by the American Psychological Association.
"Our findings suggest that the psychological reward experienced from helping others may be deeply ingrained in human nature, emerging in diverse cultural and economic contexts," said lead author Lara Aknin, PhD, of Simon Fraser University in Canada.
The findings provide the first empirical evidence that "the ...
Cell therapy a little more concrete thanks to VIB research
2013-02-21
Cell therapy is a promising alternative to tissue and organ transplantation for diseases that are caused by death or poor functioning of cells. Considering the ethical discussions surrounding human embryonic stem cells, a lot is expected of the so-called 'induced pluripotent stem cells' (iPS cells). However, before this technique can be applied effectively, a lot of research is required into the safety and efficacy of such iPS cells. VIB scientists associated to the UGent have developed a mouse model that can advance this research to the next step.
Lieven Haenebalcke ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Of crocodiles, counting and conferences
AERA announces 2026 award winners in education research
Saving two lives with one fruit drop
Photonic chips advance real-time learning in spiking neural systems
Share of migratory wild animal species with declining populations despite UN treaty protections worsens from 44% to 49% in two years; 24% face extinction, up 2%
One in 20 babies experiences physical abuse, global review finds
Tundra tongue: The science behind a very cold mistake
Targeting a dangerous gut infection
Scientists successfully harvest chickpeas from “moon dirt”
Teen aggression a warning sign for faster aging later in life
Study confirms food fortification is highly cost-effective in fighting hidden hunger across 63 countries
Special issue elevates disease ecology in marine management
A kaleidoscope of cosmic collisions: the new catalogue of gravitational signals from LIGO, Virgo and KAGRA
New catalog more than doubles the number of gravitational-wave detections made by LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA observatories
Antifibrotic drug shows promise for premature ovarian insufficiency
Altered copper metabolism is a crucial factor in inflammatory bone diseases
Real-time imaging of microplastics in the body improves understanding of health risks
Reconstructing the world’s ant diversity in 3D
UMD entomologist helps bring the world’s ant diversity to life in 3D imagery
ESA’s Mars orbiters watch solar superstorm hit the Red Planet
The secret lives of catalysts: How microscopic networks power reactions
Molecular ‘catapult’ fires electrons at the limits of physics
Researcher finds evidence supporting sucrose can help manage painful procedures in infants
New study identifies key factors supporting indigenous well-being
Bureaucracy Index 2026: Business sector hit hardest
ECMWF’s portable global forecasting model OpenIFS now available for all
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
[Press-News.org] Modeling Alzheimer's disease using iPSCsStudy reveals stress phenotypes associated with intracellular amyloid beta and differential drug responsiveness