(Press-News.org) Philadelphia, Pa. (February 21, 2013) - A routine step in preparing for cleft palate surgery in a child led to an unusual—but not unprecedented—case of lung inflammation (pneumonitis), according to a report in the The Journal of Craniofacial Surgery. The journal, edited by Mutaz B. Habal, MD, FRCSC, is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
The complication resulted from accidental inhalation of povidone-iodine (PI), or Betadine—an antiseptic widely used before surgery. The rare complication led to new surgical "prep" steps to reduce the chances of inhaling PI during head and neck surgery, write Drs. Kyle J. Chepla and Arun K. Gosain of University Hospitals–Case Medical Center, Cleveland.
Betadine Inhlation Leads to Chemical Pneumonitis
Drs. Chepla and Gosain describe their experience with Betadine-induced pneumonitis in a seven-year-old girl undergoing surgery for a persistent cleft palate deformity. After a breathing tube was placed and anesthesia was induced, the patient underwent routine surgical prep—including scrubbing and rinsing the nose and mouth with Betadine.
Betadine is the familiar antiseptic, orange or yellow in color, used before many types of medical and surgical procedures. In the case report, Dr. Kepla writes that he has routinely used Betadine for prep before craniofacial surgery for more than 20 years with no complications.
But in this case, shortly after rinsing the inside of the nose, the surgeons noted Betadine in the patient's breathing tube. She rapidly developed difficulty breathing, with a drop in blood oxygen levels.
The procedure was stopped and the patient was rushed to the ICU for treatment. Although the child eventually recovered completely, she required seven days of mechanical ventilation.
This patient's condition was diagnosed as chemical pneumonitis—inflammation of the lungs caused by inhalation of some type of irritant. Pneumonitis most commonly results from inhalation (aspiration) of the stomach contents.
Because it is effective against a wide range of bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens, Betadine is one of the most commonly used disinfectants. It is useful in preparing for surgical procedures of the head and neck, because it does not irritate the mucosal lining. However, studies in animals have shown that Betadine can cause inflammatory damage to the lungs, if inhaled.
Prompted by their experience, Drs. Chepla and Gosain performed a comprehensive review of the medical literature to look for similar cases. The review identified three previous cases of chemical pneumonitis caused by Betadine after disinfection of the mouth. All patients recovered after a period of mechanical ventilation.
Although Betadine-induced pneumonitis appears very rare, Drs. Chepla and Gosain have modified their routines to reduce the risk of this complication. They write, "We conclude that PI is safe to use as a disinfectant before head and neck surgery, but surgeons need to be aware of the risk for PI aspiration and take the appropriate steps to prevent its passage into the tracheobronchial tree."
###
About The Journal of Craniofacial Surgery
The Journal of Craniofacial Surgery serves as a forum of communication for all those involved in craniofacial and maxillofacial surgery. Coverage ranges from practical aspects of craniofacial surgery to the basic science that underlies surgical practice. Affiliates include 14 major specialty societies around the world, including the American Association of Pediatric Plastic Surgeons, the American Academy of Pediatrics Section of Pediatric Plastic Surgery, the American Society of Craniofacial Surgeons, the American Society of Maxillofacial Surgeons, the Argentine Society of Plastic Surgery Section of Pediatric Plastic Surgery, the Asian Pacific Craniofacial Association, the Association of Military Plastic Surgeons of the U.S., the Brazilian Society of Craniofacial Surgeons, the European Society of Craniofacial Surgery, the International Society of Craniofacial Surgery, the Japanese Society of Craniofacial Surgery, the Korean Society of Craniofacial Surgery, the Thai Cleft and Craniofacial Association, and the World Craniofacial Foundation.
About Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (LWW) is a leading international publisher of trusted content delivered in innovative ways to practitioners, professionals and students to learn new skills, stay current on their practice, and make important decisions to improve patient care and clinical outcomes.
LWW is part of Wolters Kluwer Health, a leading global provider of information, business intelligence and point-of-care solutions for the healthcare industry. Wolters Kluwer Health is part of Wolters Kluwer, a market-leading global information services company with 2011 annual revenues of €3.4 billion ($4.7 billion). END
The walls of the human heart are a disorganised jumble of tissue until relatively late in pregnancy, despite having the shape of a fully functioning heart, according to a pioneering study.
Experts from the University of Sheffield's Medical School collaborated on research to create the first comprehensive model of human heart development using observations of living foetal hearts. The results showed surprising differences from existing animal models.
Although scientists saw four clearly defined chambers in the foetal heart from the eighth week of pregnancy, they did ...
This press release is available in German. Motor development in children under five years of age can now be tested reliably: Together with colleagues from Lausanne, researchers from the University Children's Hospital Zurich and the University of Zurich have determined normative data for different exercises such as hopping or running. This enables parents and experts to gage the motor skills of young children for the first time objectively and thus identify abnormalities at an early stage.
My child still can't stand on one leg or walk down the stairs in alternating ...
An international team of scientists has discovered how an important natural antibiotic called dermcidin, produced by our skin when we sweat, is a highly efficient tool to fight tuberculosis germs and other dangerous bugs.
Their results could contribute to the development of new antibiotics that control multi-resistant bacteria.
Scientists have uncovered the atomic structure of the compound, enabling them to pinpoint for the first time what makes dermcidin such an efficient weapon in the battle against dangerous bugs.
Although about 1700 types of these natural antibiotics ...
WASHINGTON - Feeling good about spending money on someone else rather than for personal benefit may be a universal response among people in both impoverished countries and rich nations, according to new research published by the American Psychological Association.
"Our findings suggest that the psychological reward experienced from helping others may be deeply ingrained in human nature, emerging in diverse cultural and economic contexts," said lead author Lara Aknin, PhD, of Simon Fraser University in Canada.
The findings provide the first empirical evidence that "the ...
Cell therapy is a promising alternative to tissue and organ transplantation for diseases that are caused by death or poor functioning of cells. Considering the ethical discussions surrounding human embryonic stem cells, a lot is expected of the so-called 'induced pluripotent stem cells' (iPS cells). However, before this technique can be applied effectively, a lot of research is required into the safety and efficacy of such iPS cells. VIB scientists associated to the UGent have developed a mouse model that can advance this research to the next step.
Lieven Haenebalcke ...
Philadelphia, Pa. (February 21, 2013) - The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is aiming to become a leader in using health information technology (HIT) to change the way patients experience medical care, to decrease medical mistakes, and to improve health outcomes. A special March supplement of Medical Care highlights new research into the many and varied types of HIT projects being explored to improve the quality of patient care throughout the VHA system. Medical Care is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
The special issue ...
On the front lines of our defenses against bacteria is the protein calprotectin, which "starves" invading pathogens of metal nutrients.
Vanderbilt investigators now report new insights to the workings of calprotectin – including a detailed structural view of how it binds the metal manganese. Their findings, published online before print in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, could guide efforts to develop novel antibacterials that limit a microbe's access to metals.
The increasing resistance of bacteria to existing antibiotics poses a severe threat to ...
Why certain catalyst materials work more efficiently when they are surrounded by water instead of a gas phase is unclear. RUB chemists have now gleamed some initial answers from computer simulations. They showed that water stabilises specific charge states on the catalyst surface. "The catalyst and the water sort of speak with each other" says Professor Dominik Marx, depicting the underlying complex charge transfer processes. His research group from the Centre for Theoretical Chemistry also calculated how to increase the efficiency of catalytic systems without water by ...
Researchers at the University of Warwick and The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust have completed a study that may lead to clinicians being able to more accurately predict which patients will suffer from the side effects of radiotherapy.
Gastrointestinal side effects are commonplace in radiotherapy patients and occasionally severe, yet there is no existing means of predicting which patients will suffer from them. The results of the pilot study, published in the journal Sensors, outline how the use of an electronic nose and a newer technology, FAIMS (Field Asymmetric ...
This press release is available in German.
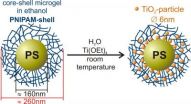
Now, Dr. Katja Henzler and a team of chemists at the Helmholtz Centre Berlin have developed a synthesis to produce nanoparticles at room temperature in a polymer network. Their analysis, conducted at BESSY II, Berlin's synchrotron radiation source, has revealed the crystalline structure of the nanoparticles. This represents a major step forward in the usage of polymeric nanoreactors since, until recently, the nanoparticles had to be thoroughly heated to get them to crystallize. The last synthesis step can be spared due ...