(Press-News.org) (SALT LAKE CITY)—Vision scientists long have thought that lack of very long chain fatty acids in photoreceptor cells caused blindness in children with Stargardt type 3 retinal degeneration, an incurable eye disease. But researchers at the University of Utah's John A. Moran Eye Center have shown in a new study that lack of these fatty acids does not cause blindness, meaning that the search for the mechanism that robs sight from children with the disease must start anew.
Researchers led by David Krizaj, Ph.D., associate professor of ophthalmology and visual sciences at the Moran Eye Center, bred mice that lacked fatty acids in their photoreceptor cells and to their surprise found that the mice's eyesight was normal. "There was no defect in their daytime or nighttime vision," Krizaj says. "The lack of very long chain fatty acids does not appear to compromise vision in itself."
The research was published March 11, 2013, in PNAS online. Peter Barabas, Ph.D., a postdoctoral fellow at the Moran Eye Center, is first author on the study.
Stargardt disease is a form of macular degeneration that strikes about one in 10,000 children between the ages of 6 and 20. There is no treatment for the disease, although there is evidence that nutrition supplements and protecting eyes from UV rays might be beneficial in slowing the progression of blindness.
There are three types of Stargardt disease caused by three different gene mutations. (Paul Bernstein, M.D., Ph.D., professor of ophthalmology and visual sciences and a co-author in the PNAS study, discovered one of the mutations in a Utah family.) Type 3, a rare dominant form of Stargardt disease, is caused by a mutation in ELOVL4, a gene that encodes an enzyme that helps to make fatty acids obtained through our diet into forms that can be incorporated into cell membranes. The mutation displaces the enzyme from its location in an intracellular organelle called endoplasmic reticulum into the cell cytosol, which blocks the synthesizing of very long chain fatty acids in photoreceptor cells. But proving that the lack of these fatty acids actually causes blindness has been difficult to show in experiments, because mice in which the ELOVL4 was knocked out did not survive.
Krizaj and his colleagues overcame that problem by engineering mouse models that lacked ELOVL4 only in their photoreceptor cells, allowing the mice to survive but with the fatty acids in those cells reduced up to 90 percent. This allowed them to test directly whether loss of very long chain fatty acids replicates vision loss observed in children with Stargardt's disease. As they report in the journal, electrophysiological and behavioral testing of daytime and night vision in genetically engineered mice showed that sight was not affected despite the dramatic reduction in very long chain fatty acids in photoreceptor cells.
Researchers now must look for a different cause of Stargardt type 3. "If it's not the loss of fatty acids causing the disease, then we'll have to find other strategies to help these kids," Krizaj says.
One possibility, according to Krizaj, is that mutated proteins, escaping from the endoplasmic reticulum are aggregating in the cytoplasm causing large deposits consisting of mutated and normal proteins, which is "almost like causing photoreceptor cell death by blocking intracellular traffic and clogging the cells' drains."
### END
Long-suspected cause of blindness from eye disease disproved
Lack of fatty acid doesn't rob sight from children with Stargardt disease type 3
2013-03-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Common erectile dysfunction drug not helpful for heart failure patients, study finds
2013-03-12
SAN FRANCISCO -- A commonly used erectile dysfunction drug, sildenafil, doesn't help patients who have heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, a condition in which the heart's lower chambers are stiff and cannot relax and fill fully between beats. That is the finding of the RELAX study, presented today at the American College of Cardiology's 62nd Annual Scientific Session and simultaneously published in The Journal of the American Medical Association. The study's lead author called the results disappointing.
Sildenafil, a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor, had shown ...
Astronomers conduct first remote reconnaissance of another solar system
2013-03-12
Researchers have conducted a remote reconnaissance of a distant solar system with a new telescope imaging system that sifts through the blinding light of stars. Using a suite of high-tech instrumentation and software called Project 1640, the scientists collected the first chemical fingerprints, or spectra, of this system's four red exoplanets, which orbit a star 128 light years away from Earth. A detailed description of the planets—showing how drastically different they are from the known worlds in the universe—was accepted Friday for publication in The Astrophysical Journal. ...
Creating indestructible self-healing circuits
2013-03-12
PASADENA, Calif.—Imagine that the chips in your smart phone or computer could repair and defend themselves on the fly, recovering in microseconds from problems ranging from less-than-ideal battery power to total transistor failure. It might sound like the stuff of science fiction, but a team of engineers at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech), for the first time ever, has developed just such self-healing integrated chips.
The team, made up of members of the High-Speed Integrated Circuits laboratory in Caltech's Division of Engineering and Applied Science, ...
Epigenetics mechanism may help explain effects of mom's nutrition on her children's health
2013-03-12
This press release is available in Spanish.
Pioneering studies by U. S. Department of Agriculture-funded research molecular geneticist Robert A. Waterland are helping explain how the foods that soon-to-be-moms eat in the days and weeks around the time of conception—or what's known as periconceptional nutrition–may affect the way genes function in her children, and her children's health.
In an early study, Waterland and co-investigators examined gene function of 50 healthy children living in rural villages in the West African nation of The Gambia. The study has shaped ...
Study shows how one insect got its wings
2013-03-12
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Scientists have delved deeper into the evolutionary history of the fruit fly than ever before to reveal the genetic activity that led to the development of wings – a key to the insect's ability to survive.
The wings themselves are common research models for this and other species' appendages. But until now, scientists did not know how the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, first sprouted tiny buds that became flat wings.
A cluster of only 20 or so cells present in the fruit fly's first day of larval life was analyzed to connect a gene known to be active ...
Study predicts lag in summer rains over parts of US and Mexico
2013-03-12
A delay in the summer monsoon rains that fall over the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico is expected in the coming decades according to a new study in the Journal of Geophysical Research. The North American monsoon delivers as much as 70 percent of the region's annual rainfall, watering crops and rangelands for an estimated 20 million people.
"We hope this information can be used with other studies to build realistic expectations for water resource availability in the future," said study lead author, Benjamin Cook, a climate scientist with joint appointments ...
Study shows on-pump bypass comparable to off-pump at year mark
2013-03-12
SAN FRANCISCO (March 11, 2013) — Patients who underwent heart bypass surgery without a heart- lung machine did as well one year later as patients whose hearts were connected to a pump during surgery in a study presented today at the American College of Cardiology's 62nd Annual Scientific Session.
CORONARY, an international, multicenter trial of on-pump (with a heart-lung machine) versus off-pump bypass surgery, enrolled 4,752 patients already scheduled to undergo a bypass procedure. The study is the largest to compare the two approaches.
For the primary endpoint of ...
University of Maryland School of Medicine discovers adaptations to explain strategies for survival on Mars
2013-03-12
Research from the University of Maryland School of Medicine has revealed key features in proteins needed for life to function on Mars and other extreme environments. The researchers, funded by NASA, studied organisms that survive in the extreme environment of Antarctica. They found subtle but significant differences between the core proteins in ordinary organisms and Haloarchaea, organisms that can tolerate severe conditions such as high salinity, desiccation, and extreme temperatures. The research gives scientists a window into how life could possibly adapt to exist on ...
Similar outcomes in older patients with on- or off-pump bypass
2013-03-12
SAN FRANCISCO (March 11, 2013) — Older patients did as well after undergoing coronary bypass surgery off-pump as they did with the more costly "on-pump" procedure using a heart-lung machine to circulate blood and oxygen through the body during surgery, according to research presented today at the American College of Cardiology's 62nd Annual Scientific Session.
This large, multicenter trial—the German Off-Pump Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting in Elderly Patients, called GOPCABE—was the first to evaluate on-pump versus off-pump bypass surgery among patients aged 75 or older. ...
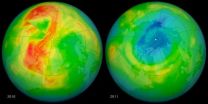
NASA pinpoints causes of 2011 Arctic ozone hole
2013-03-12
A combination of extreme cold temperatures, man-made chemicals and a stagnant atmosphere were behind what became known as the Arctic ozone hole of 2011, a new NASA study finds.
Even when both poles of the planet undergo ozone losses during the winter, the Arctic's ozone depletion tends to be milder and shorter-lived than the Antarctic's. This is because the three key ingredients needed for ozone-destroying chemical reactions —chlorine from man-made chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), frigid temperatures and sunlight— are not usually present in the Arctic at the same time: the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
[Press-News.org] Long-suspected cause of blindness from eye disease disprovedLack of fatty acid doesn't rob sight from children with Stargardt disease type 3