AI found to boost individual creativity – at the expense of less varied content
2024-07-12
Stories written with AI assistance have been deemed to be more creative, better written and more enjoyable.
A new study published in the journal Science Advances finds that AI enhances creativity by boosting the novelty of story ideas as well as the ‘usefulness’ of stories – their ability to engage the target audience and potential for publication.
It finds that AI “professionalizes” stories, making them more enjoyable, more likely to have plot twists, better written and less boring.
In ...
Texas A&M research collaboration uncovers how domestic rabbits become feral in the wild
2024-07-12
Researchers at the Texas A&M School of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences (VMBS) have uncovered how natural selection “rewilds” domestic rabbits.
The study, published in Nature Ecology and Evolution, helps answer the question of how normally tame rabbits — which have many natural predators — can become a force of ecological destruction when purposefully or accidentally reintroduced to the wild.
Here Comes Peter Cottontail
Every gardener knows how much of a nuisance rabbits can be, but ...
Scientists find new way global air churn makes particles
2024-07-12
By Leah Shaffer
You can think of our atmosphere as a big chemistry set, a global churn of gaseous molecules and particles that constantly bounce off and change each other in complicated ways. While the particles are very small, often less than 1% of the thickness of human hair, they have outsized impacts. For example, particles are the seeds of cloud droplets, and the abundance of the particles changes the reflectivity and the amount of clouds, rainfall and climate.
Now, researchers at Washington University in St. ...
Researchers discover a new neural biomarker for OCD
2024-07-12
A recent study from Baylor College of Medicine and Texas Children’s Hospital has identified a specific neural activity pattern as a novel biomarker to accurately predict and monitor the clinical status of individuals with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) who have undergone deep brain stimulation (DBS), a rapidly emerging therapeutic approach for severe psychiatric disorders. The study, led by led by Drs. Sameer Sheth and Wayne Goodman along with co-lead authors, Drs. Nicole Provenza, ...
Vivid portrait of interacting galaxies marks Webb’s second anniversary
2024-07-12
Two for two! A duo of interacting galaxies commemorates the second science anniversary of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, which takes constant observations, including images and highly detailed data known as spectra. Its operations have led to a “parade” of discoveries by astronomers around the world.
“Since President Biden and Vice President Harris unveiled the first image from the James Webb Space Telescope two years ago, Webb has continued to unlock the mysteries of the universe,” said NASA Administrator Bill Nelson. “With remarkable images from the ...
UMass Amherst awarded $2.1 million to advance the science of engagement in community-academic research partnerships
2024-07-12
University of Massachusetts Amherst researcher Thomas Mackie has received a $2.1 million funding award from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) to advance the meaningful engagement of communities that are affected by mental health disparities and underrepresented in research partnerships.
The study, entitled “Improving Research Partnership With Engagement Mapping: A Pilot Study to Advance Engagement Science” and co-led by Karen Tabb, a University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign researcher, is designed to empower community partners to have a greater role ...
With gene editing, mice with a form of inherited deafness can hear again
2024-07-12
Researchers have used gene editing to restore hearing in adult mice with a type of inherited hearing loss. They showed that shutting down a damaged copy of a gene called a microRNA (miRNA) enabled the animals to regain hearing. The approach by a research team supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), reported in Science Translational Medicine, may eventually lead to potential treatments for inherited hearing loss in people.
Zheng-Yi Chen, DPhil., and his colleagues at Mass Eye and Ear in Boston and other institutions studied a rare form of genetic deafness called autosomal dominant deafness-50 (DFNA50). ...
Sant Pau researchers discover a new gene that causes ALS
2024-07-12
Sant Pau researchers discover a new gene that causes ALS
Researchers from the Neuromuscular Diseases Group and the Dementia Neurobiology Group of the Sant Pau Research Institute (IR Sant Pau) and the Memory Unit of the Sant Pau Hospital, led by neurologist Dr. Ricard Rojas-García, have identified a new mutation in the ARPP21 gene that could be the cause of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), a devastating neurodegenerative disease.
Specifically, it is a shared mutation (c.1586C>T; p.Pro529Leu) in the ARPP21 gene that ...
Synthetic biology reveals the secrets of life without oxygen
2024-07-12
Long before photosynthesis brought free oxygen into the world, the earth was already populated by numerous organisms. Oxygen was life-threatening for them and therefore they developed completely different metabolic pathways to those we know from plants, animals and humans. Anaerobic bacteria have survived the ages in special, oxygen-free niches, some of them very close to us: as an essential part of the intestinal microbiome, where they are of enormous importance for the well-being of the organism. However, certain anaerobes can ...
UC3M student startup, Solaris Vita, awarded in Europe's largest entrepreneurship competition
2024-07-12
Solaris Vita, a startup created by students at Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M), has won second place in the "Innovation of the Year" category at Gen-E 2024, the largest European youth entrepreneurship competition, organized by Junior Achievement Europe. This is the first time that a Spanish university team has won this award.
The promoters of Solaris Vita, Miguel Iglesias (Industrial Engineering graduate from UC3M) and Yann Guichard (Economics student at the University), competed ...
How plant cold specialists can adapt to the environment
2024-07-12
Plant cold specialists like the spoonworts have adapted well to the cold climates of the Ice Ages. As cold and warm periods alternated, they developed a number of species that also resulted in a proliferation of the genome. Evolutionary biologists from the universities of Heidelberg, Nottingham, and Prague studied the influence this genome duplication has on the adaptive potential of plants. The results show that polyploids – species with more than two sets of chromosomes – can have an accumulation of structural mutations with signals for a possible local ...
Biomarkers reveal how patients with glaucoma may respond to treatment
2024-07-12
Markers in the blood that predict whether glaucoma patients are at higher risk of continued loss of vision following conventional treatment have been identified by researchers at UCL and Moorfields Eye Hospital.
Over 700,000 people in the UK have glaucoma and it is the leading cause of irreversible blindness worldwide. The condition occurs when the cells in the eye that help you see (called retinal ganglion cells) start to die.
The main risk factors for glaucoma are high eye pressure and older age.
Currently, all licenced treatments are designed to lower pressure in the eye – also known as intraocular pressure. However, some patients ...
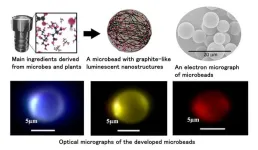
Microbeads with adaptable fluorescent colors from visible light to near-infrared
2024-07-12
1. A research team at NIMS has successfully developed an environmentally friendly, microspherical fluorescent material primarily made from citric acid. These microbeads emit various colors of light depending on the illuminating light and the size of the beads, which suggests a wide range of applications. Furthermore, the use of plant-derived materials allows for low-cost and energy-efficient synthesis.
2. Conventional luminescent devices commonly utilized thin films of compound semiconductors containing metals or sintered inorganic materials with rare earth elements. However, in a circular economy, there ...
Neighborhood disadvantage and prostate tumor RNA expression of stress-related genes
2024-07-12
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study, the expression of several stress-related genes in prostate tumors was higher among men residing in disadvantaged neighborhoods. This study is one of the first to suggest associations of neighborhood disadvantage with prostate tumor RNA expression. Additional research is needed in larger studies to replicate findings and further investigate interrelationships of neighborhood factors, tumor biology, and aggressive prostate cancer to inform interventions to reduce disparities.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, ...
Screen media use and mental health of children and adolescents
2024-07-12
About The Study: This secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial found that a short-term reduction in leisure-time screen media use within families positively affected psychological symptoms of children and adolescents, particularly by mitigating internalizing behavioral issues and enhancing prosocial behavior. More research is needed to confirm whether these effects are sustainable in the long term.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jesper Schmidt-Persson, Ph.D., email jesp@kp.dk.
To ...
Mediterranean diet and cardiometabolic biomarkers in children and adolescents
2024-07-12
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that Mediterranean diet-based interventions may be useful tools to optimize cardiometabolic health among children and adolescents.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jose Francisco Lopez-Gil, Ph.D., email josefranciscolopezgil@gmail.com.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.21976)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
A chemical claw machine bends and stretches when exposed to vapors
2024-07-12
Scientists at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) in Saudi Arabia have developed a tiny “claw machine” that is able to pick up and drop a marble-sized ball in response to exposure to chemical vapors.
The findings, published July 12 in the journal Chem, point to a technique that can enable soft actuators—the parts of a machine that make it move—to perform multiple tasks without the need for additional costly materials. While existing soft actuators can be “one-trick ponies” restricted to one type of movement, this novel composite film contorts itself ...
Living in disadvantaged neighborhoods influences stress-related genes, which may contribute to aggressive prostate cancer in African American men
2024-07-12
BALTIMORE, MD, July 12, 2024 — Those living in disadvantaged neighborhoods have significantly higher activity of stress-related genes, new research suggests, which could contribute to higher rates of aggressive prostate cancer in African American men. The study, which was co-led by the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) and Virginia Commonwealth University (VCU), was published today in JAMA Network Open.
African American men have a higher incidence of prostate cancer and are more than twice as likely to die from the disease than White men in the U.S. They are often diagnosed with an ...
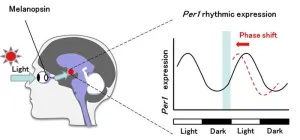
Melanopsin DNA aptamers can regulate input signals of mammalian circadian rhythms by altering the phase of the molecular clock
2024-07-12
Overview:
DNA aptamers of melanopsin that regulate the clock hands of biological rhythms were developed by the Toyohashi University of Technology and the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) group.
DNA aptamers can specifically bind to biomolecules to modify their function, potentially making them ideal oligonucleotide therapeutics. We screened the DNA aptamer melanopsin (OPN4), a blue light photopigment in the retina that plays a key role in the use of light signals to reset the phase of circadian rhythms in the central clock.
First, 15 DNA aptamers of melanopsin (Melapts) were identified following eight rounds of Cell-SELEX ...
Challenges and prospects for post-conflict peacebuilding in urban settings
2024-07-12
Wars and conflicts leave devastating destruction in their wake. With so many conflicts now taking place in urban environments, scientists are studying how post-conflict peacebuilding happens in these urban settings. Dahlia Simangan, an associate professor at The IDEC Institute, Hiroshima University, has analyzed the case of Marawi, a city in the Philippines, to better understand the urban environment’s influence on post-siege reconstruction and peacebuilding. This study contributes to a more comprehensive understanding of peacebuilding by integrating conventional peacebuilding components and urban characteristics.
The findings are published ...
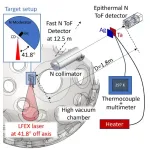
Neutrons give a hot new way to measure the temperature of electronic components
2024-07-12
Osaka, Japan – From LEDs to batteries, our lives are full of electronics, and there is a constant push to make them more efficient and reliable. But as components become increasingly sophisticated, getting reliable temperature measurements of specific elements inside an object can be a challenge.
This is problematic because measuring a device’s temperature is vital for monitoring its performance or designing the materials from which it’s manufactured. Now, in a new study led by Osaka ...
High and low tide cause low and high methane fluxes
2024-07-12
High and low tide cause low and high methane fluxes
Methane, a strong greenhouse gas that naturally escapes from the bottom of the North Sea, is affected by the pressure of high or low tide. Methane emissions from the seafloor can be just easily three times as much or as little, depending on the tide. This is shown by NIOZ oceanographer Tim de Groot, in a publication in Nature Communications Earth and Environment. "Our research shows that you can never rely on one measurement when you want to know how much methane escapes from the seafloor," De Groot emphasizes.
Swamp ...
A better way to make RNA drugs
2024-07-12
While the COVID-19 vaccines introduced many people to RNA-based medicines, RNA oligonucleotides have already been on the market for years to treat diseases like Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and amyloidosis. RNA therapies offer many advantages over traditional small molecule drugs, including their ability to address almost any genetic component within cells and to guide gene editing tools like CRISPR to their targets.
However, the promise of RNA is currently limited by the fact that rapidly growing global demand is outpacing the industry’s ability to manufacture it. The standard method of chemically ...
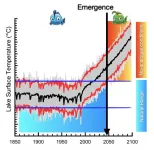
Unprecedented warming threatens earth’s lakes and their ecosystems
2024-07-12
Lakes, with their rich biodiversity and important ecological services, face a concerning trend: rapidly increasing temperatures. A recent study published in Nature Geoscience by an international team of limnologists and climate modelers reveals that if current anthropogenic warming continues until the end of this century, lakes worldwide will likely experience pervasive and unprecedented surface and subsurface warming, far outside the range of what they have encountered before.
The study uses lake temperature ...
Cellular inflammation uncovered in rare neurodegenerative condition
2024-07-12
Researchers at The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) have found that inflammation in an immune cell may be responsible in part for some severe symptoms in a group of rare genetic conditions called lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs).
LSDs affect about one in 7,700 live births worldwide. Children with the condition typically present at a young age with progressive neurodegeneration. Many children with LSDs die prematurely, and current treatments focus on symptom management.
Until now, the role of macrophages in the immune system and LSDs was ...
[1] ... [1058]
[1059]
[1060]
[1061]
[1062]
[1063]
[1064]
[1065]
1066
[1067]
[1068]
[1069]
[1070]
[1071]
[1072]
[1073]
[1074]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.