State gun laws have mixed impact on suicide and homicide rates
2024-07-11
DURHAM, N.C. – Certain state gun laws are associated with decreased suicide rates for children under age 18, but the laws have little influence on homicide rates, according to a study from Duke Health researchers examining the relationship between gun laws and child deaths.
Since 2020, firearms rank as the leading cause of death among U.S. children ages 1-18, raising the need for research to help guide prevention efforts.
“Our analysis of suicide and homicide mortality data from ...
Treatment approaches for opioid use disorder offered in us substance use treatment facilities
2024-07-11
About The Study: Substance use treatment facilities reported significant gaps in provision of effective treatments for opioid use disorder (OUD). More than one-third of facilities did not offer medications for OUD (MOUD) and less than half offered multiple MOUD types, limiting MOUD treatment options for patients and clinicians.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Tae Woo Park, M.D., M.Sc., email parkt4@upmc.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.11913)
Editor’s ...
Secondhand nicotine absorption from E-cigarette vapor vs tobacco smoke in children
2024-07-11
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study of U.S. children, nicotine absorption was much lower in children who were exposed to secondhand vapor versus secondhand smoke, but higher than in those exposed to neither. These findings suggest that switching from smoking to vaping indoors may substantially reduce, but not eliminate, children’s secondhand exposure to nicotine and other noxious substances.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Harry Tattan-Birch, Ph.D., email h.tattan-birch@ucl.ac.uk.
To ...
Long-term outcomes of self-fit vs audiologist-fit hearing aids
2024-07-11
About The Study: This comparative effectiveness research study demonstrated that self-fit over-the-counter hearing aids can offer comparable long-term benefits to audiologist-fit hearing aids for individuals with mild to moderate hearing loss.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Karina C. De Sousa, Ph.D., email karina.swanepoel@up.ac.za.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2024.1825)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
Second-hand vaping exposure very low compared to second-hand smoking
2024-07-11
Children exposed to vaping indoors absorb less than one seventh the amount of nicotine as children who are exposed to indoor smoking, but more than those exposed to neither, according to a new study led by UCL researchers.
The study, published in JAMA Network Open and funded by Cancer Research UK, looked at blood tests and survey data for 1,777 children aged three to 11 in the United States.
The researchers said that second-hand exposure to harmful substances in e-cigarettes would likely be much lower still, as e-cigarettes deliver similar levels of nicotine to tobacco but contain only a fraction of the toxicants and ...
Biological science helps fuel the future of electric air travel
2024-07-11
– By William Ferguson
When it comes to figuring out why electric aircraft batteries lose power over time, one typically wouldn’t think to turn to a decades-old approach biologists use to study the structure and function of components in living organisms. However, it turns out that omics, a field that helped scientists unravel the secrets of the human genome, could also soon play a key role in making carbon-free air travel a reality.
In a new study in the journal Joule, a team of researchers led ...
Electric aviation: Batteries that stay strong for the flight duration
2024-07-11
Images
A battery component innovation could help keep power delivery high when electric aircraft land with low charge, according to a study led by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory with expertise from the University of Michigan.
The research provides a solution to a problem identified in 2018 in a study led by Venkat Viswanathan, a professor of aerospace engineering at U-M and a coauthor of the new work published in Joule.
"Both takeoff and landing require high power, and landing is more challenging because you’re not fully charged," Viswanathan said. "To get high power you ...
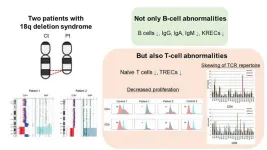
Uncovering late-onset combined immune deficiency in chromosome 18q deletion syndrome
2024-07-11
Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) researchers have discovered that patients with 18q deletion syndrome can experience both cellular and humoral immunodeficiency
Tokyo, Japan – Chromosome 18q deletion (18q del) syndromeis a rare genetic condition disorder, affecting approximately 1 in 40,000 to 55,000 individuals, caused by the deletion of genetic material on the long arm of chromosome 18. This genetic anomaly disrupts normal growth and development, and critically, can impair the immune system's functionality. Patients with 18q del syndrome often exhibit humoral immunodeficiency or a common ...
SciOpen, an international digital publishing platform for STM journals, unveils new updates
2024-07-11
On June 30, 2024, SciOpen 2.0 was officially launched. Developed by Tsinghua University Press, SciOpen initially made its debut in June 2022 as an international digital publishing platform for STM journals. After two years of global operation and continuous iterative upgrades, SciOpen 2.0 has fully embraced the best practices of mainstream publishing models. SciOpen has completed a comprehensive upgrade of its interactive system design and has integrated advanced large-model AI reading capabilities, marking a significant leap forward in its functionality.
These updates steer SciOpen towards ...
JMIR Bioinformatics and Biotechnology is inviting submissions for a new theme issue titled “Artificial Intelligence in Oncology”
2024-07-11
(Toronto, July 11, 2024) JMIR Publications invites submissions to a new theme issue titled “Artificial Intelligence in Oncology” in its premier open access journal JMIR Bioinformatics and Biotechnology indexed in PubMed Central and PubMed, SCOPUS, Sherpa/Romeo, DOAJ and EBSCO/EBSCO Essentials.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to revolutionize oncology by enhancing diagnostic accuracy, personalizing treatment plans, predicting patient outcomes, and accelerating drug discovery. Researchers, clinicians, and industry experts are invited ...
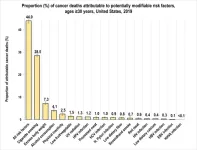
New study finds 40-percent of cancer cases and almost half of all deaths in the US linked to modifiable risk factors
2024-07-11
A new study led by researchers at the American Cancer Society (ACS) finds four in 10 cancer cases and about one-half of all cancer deaths in adults 30 years old and older in the United States (or 713,340 cancer cases and 262,120 cancer deaths in 2019) could be attributed to modifiable risk factors, including cigarette smoking, excess body weight, alcohol consumption, physical inactivity, diet, and infections. Cigarette smoking was by far the leading risk factor, contributing to nearly 20% of all cancer cases and 30% of all cancer deaths. The findings are ...
Pathogen prioritization for wastewater surveillance ahead of the Paris 2024 Olympic and Paralympic Games, France
2024-07-11
The study by researchers from the French national public health institute aimed to identify priority pathogens that could be suitable for wastewater surveillance (WWS) during the Paris 2024 Olympic and Paralympic Games taking place from 26 July to 11 August and 28 August to 8 September, respectively. The pathogens were evaluated using a Delphi method which integrated evidence from peer-reviewed publications and expert opinion.
WWS has become more prominent due to its role during the COVID-19 pandemic. As a non-intrusive, cost-effective surveillance tool, WWS offers ...
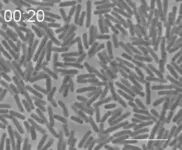
Bacteria form glasslike state
2024-07-11
Dense E.coli bacteria have several similar qualities to colloidal glass, according to new research at the University of Tokyo. Colloids are substances made up of small particles suspended within a fluid, like ink for example. When these particles become higher in density and more packed together, they form a “glassy state.” When researchers multiplied E.coli bacteria within a confined area, they found that they exhibited similar characteristics. More surprisingly, they also showed some other unique properties not typically found in glass-state materials. This study contributes to our understanding of glassy “active matter,” a relatively new field of ...
Prestigious MERIT grant funds research on how the immune system can banish HIV
2024-07-11
Weill Cornell Medicine has received $4.2 million to study how the immune system in some people infected with HIV can keep the virus under control, which could lead to novel therapeutic strategies for thwarting or eliminating HIV. Dr. Brad Jones, associate professor of immunology in medicine in the Division of Infectious Diseases at Weill Cornell Medicine, was awarded a MERIT grant from the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) at the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
The “Method for Extending Research in Time” (MERIT) grant provides ...
Research reveals novel CARS E795V mutation as cause of inherited Parkinson's disease
2024-07-11
According to Science Alert, neuroscientists from Johns Hopkins University have recently discovered a new treatment for Parkinson's disease using an FDA-approved cancer drug. A recent study published in Neuroscience Bulletin reveals the genetic cause of Parkinson's disease. The study discovered that a mutation in the Cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase (CARS) gene (c.2384A>T; p.Glu795Val; E795V) is responsible, offering a new path for prevention and control of the disease. This research was conducted by a team led by Zhang Jianguo, including researcher ...
Narcissism decreases with age, study finds
2024-07-11
People tend to become less narcissistic as they age from childhood through older adulthood, according to a study published by the American Psychological Association. However, differences among individuals remain stable over time -- people who are more narcissistic than their peers as children tend to remain that way as adults, the study found.
“These findings have important implications given that high levels of narcissism influence people’s lives in many ways -- both the lives of the narcissistic individuals themselves and, maybe even more, the lives of their families and friends,” said lead author Ulrich Orth, PhD, of the University of Bern in Switzerland.
The ...
Scientists call for ‘major initiative’ to study whether geoengineering should be used on glaciers
2024-07-11
A group of scientists have released a landmark report on glacial geoengineering—an emerging field studying whether technology could halt the melting of glaciers and ice sheets as climate change progresses.
The white paper represents the first public efforts by glaciologists to assess possible technological interventions that could help address catastrophic sea-level rise scenarios.
While it does not endorse any specific interventions, it calls for a “major initiative” in the next decades to research which, if any, interventions could and should be ...
Mount Sinai secures over $4 million grant from National Institutes of Health to study alopecia areata and atopic dermatitis in people with Down Syndrome
2024-07-11
New York, NY (July 11, 2024) – The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai is embarking on biomedical research aiming to set new standard-of-care protocols for treating alopecia areata and atopic dermatitis in people with Down syndrome, or trisomy 21.
Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, the Waldman Professor and Chair of Dermatology at Icahn Mount Sinai, has been awarded more than $4 million for a five-year National Institutes of Health (NIH) R61/R33 grant to evaluate the long-term safety, efficacy, and mechanisms of medications known as JAK inhibitors in patients with Down syndrome. The medications have been approved ...
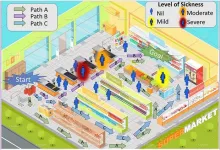
How risk-averse are humans when interacting with robots?
2024-07-11
How do people like to interact with robots when navigating a crowded environment? And what algorithms should roboticists use to program robots to interact with humans?
These are the questions that a team of mechanical engineers and computer scientists at the University of California San Diego sought to answer in a study presented recently at the ICRA 2024 conference in Japan.
“To our knowledge, this is the first study investigating robots that infer human perception of risk for intelligent decision-making in everyday settings,” said Aamodh Suresh, first author of the study, who earned his Ph.D. in the research group of Professor Sonia Martinez Diaz ...
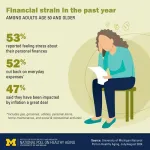
An unequal toll of financial stress: Poll of older adults shows different impacts related to health and age
2024-07-11
Inflation rates may have cooled off recently, but a new poll shows many older adults are experiencing financial stress – especially those who say they’re in fair or poor physical health or mental health.
Women and those age 50 to 64 are more likely than men or people over age 65 to report feeling a lot of stress related to their personal finances. So are people age 50 and older who say they’re in fair or poor physical or mental health.
In all, 47% of people age 50 and older said inflation had impacted them a great deal in the past year, and 52% said they ...
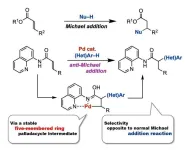
One-step synthesis of pharmaceutical building blocks: new method for anti-Michael reaction
2024-07-11
In 1887, chemist Sir Arthur Michael reported a nucleophilic addition reaction to the β-position of α,β- unsaturated carbonyl compounds. These reactions, named Michael addition reactions, have been extensively studied to date. In contrast, the anti-Michael addition reaction, referring to the nucleophilic addition reaction to the α-position, has been difficult to achieve. This is due to the higher electrophilicity of the β-position compared to the α-position. Previous attempts to overcome these difficulties have involved two main methods. The first is restricting the addition position via intramolecular reactions, ...
Urban seagulls still prefer seafood
2024-07-11
Seagull chicks raised on an “urban” diet still prefer seafood, new research shows.
University of Exeter scientists studied herring gull chicks that had been rescued after falling off roofs in towns across Cornwall, UK.
Raised in captivity (before being released), they were given either a “marine” diet consisting mainly of fish and mussels, or an “urban” diet containing mostly bread and cat food.
Every few days the gull chicks were presented with a choice of all four foods in different bowls, to test which they preferred – and all gulls strongly favoured fish.
“Our results suggest that, even when reared on an ‘urban’ ...
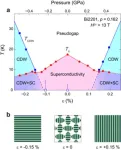
Understanding the origin of superconductivity in high-temperature copper oxide superconductors
2024-07-11
Superconductors are materials that can conduct electricity with zero resistance when cooled to a certain temperature, called the critical temperature. They have applications in many fields, including power grids, maglev trains, and medical imaging. High-temperature superconductors, which have critical temperatures higher than normal superconductors have significant potential for advancing these technologies. However, the mechanisms behind their superconductivity remain unclear.
Copper oxides or cuprates, a class of high-temperature superconductors, exhibit superconductivity ...
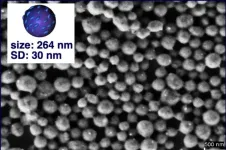
Shaping the future of polymer nanocarriers
2024-07-11
Scientists have taken a significant step towards the development of tailor-made chiral nanocarriers with controllable release properties. These nanocarriers, inspired by nature's helical molecules like DNA and proteins, hold immense potential for targeted drug delivery and other biomedical applications.
The study, led by Professors Emilio Quiñoá and Félix Freire at the Center for Research in Biological Chemistry and Molecular Materials (CiQUS), highlights the intricate relationship between the structure of helical polymers and their self-assembly into nanospheres. By carefully designing ...
2000th ERC Proof of Concept grant awarded
2024-07-11
The grants – each worth €150,000 – help researchers to bridge the gap between the discoveries stemming from their frontier research and the practical application of the findings, including early phases of their commercialisation.
Nanda Rea’s new project, called DeepSpacePULSE, aims to facilitate deep space exploration. Currently, to find their way, spacecraft and satellites use up a lot of energy exchanging vital navigation information with mission coordinators on Earth. Using ERC Proof of Concept funding, Prof. Nanda Rea ...
[1] ... [1061]
[1062]
[1063]
[1064]
[1065]
[1066]
[1067]
[1068]
1069
[1070]
[1071]
[1072]
[1073]
[1074]
[1075]
[1076]
[1077]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.