Brian Wachtel is promoted to Chief Development Officer at NFCR
2024-07-09
The National Foundation for Cancer Research (NFCR) proudly announces the promotion of Brian Wachtel to Chief Development Officer. Brian will continue his responsibilities as the Executive Director, and his expanded role will further enhance his leadership within the organization.
Brian joined the National Foundation for Cancer Research in September 2016 as the Director of Corporate Partnerships & Special Events. In that capacity, he was in charge of organizing and expanding NFCR’s community outreach events. One of his important ...
Digital self-harm surges among U.S. teens from 2016 to 2021
2024-07-09
Adolescents worldwide have embraced social media and online platforms for self-expression and to explore their identity. This freedom, however, can lead to risky behaviors, especially with limited adult supervision. For example, digital self-harm is a recent, emerging trend where individuals anonymously post or share hurtful content about themselves online. This behavior can be mistaken for mistreatment by others, yet the perpetrator and victim are the same person.
First identified in 2010, digital self-harm has not received the same amount of scholarly scrutiny as other forms of self-directed abuse and has not been widely addressed by adults ...
UTSA joins new consortium dedicated to nuclear security and nonproliferation
2024-07-09
The University of Texas at San Antonio (UTSA) has joined one of two newly established university consortia committed to nuclear security and nonproliferation. The consortia were awarded $50 million in cooperative agreements by the Office of Defense Nuclear Nonproliferation in the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration (DOE NNSA).
“The pressing challenges of nuclear security and nonproliferation require a concerted effort from experts across the country,” said JoAnn Browning, UTSA interim vice president for research. ...
Diabetes increases the risk of failure in spinal fusion procedures
2024-07-09
A new study from orthopaedic researchers at The University of Toledo has found lumbar spinal fusion procedures are far more likely to fail in individuals with diabetes.
“We’ve known for a long time that diabetic patients are at high risk of infection from any surgery, including spinal fusion,” said Dr. Hossein Elgafy, a professor of orthopaedics in the College of Medicine and Life Sciences and chief of spine surgery at UTMC. “More recently, however, physicians have taken a closer look at the high ...
Brain-computer interface therapy for stroke survivors
2024-07-09
A personalized brain-computer interface therapy, RehabSwift, significantly enhances hand mobility for stroke survivors. Strokes often lead to impaired hand function, presenting substantial challenges in daily activities. Sam Darvishi and colleagues developed and tested a brain-computer interface therapy that translates imagined hand movements into real actions using a personalized algorithm and bionic hands. The study involved twelve chronic stroke survivors from South Australia who had limited use of their arms but retained clear thinking abilities. Throughout 18 sessions, participants used the RehabSwift system, which included a special cap that ...
SynGAP Research Fund (SRF) increases support for SYNGAP1 organoid research at the University of Southern California’s Quadrato Lab
2024-07-09
MILL VALLEY, Calif. – July 9, 2024 – SynGAP Research Fund (SRF), a 501(c)(3) public charity whose mission is to improve the quality of life for patients suffering from SYNGAP1-Related Disorders (SRD) through the research and development of treatments, therapies, and support systems, has awarded a $130,000 grant to the University of Southern California’s Quadrato Lab to inspect and stratify the effects of specific SYNGAP1 variants on their patient-derived neuronal model system, furthering the world’s understanding ...
Study finds 1 in 12 patients labeled as having ‘benign’ results actually had high-risk prostate cancer
2024-07-09
New research highlights the challenge of balancing the risks of overdiagnosing and underdiagnosing prostate cancer early enough to intervene and minimize risk of death. Recently, some experts have called for the lowest grade of prostate cancer—biopsy Gleason Grade Group (GGG) 1—to be reclassified as ‘benign.’ But a new study led by a researcher from Mass General Brigham has found that many patients with a biopsy GGG1 may have a more aggressive cancer than their biopsy alone suggests.
By looking at data from more than 10,000 patients at a university in Germany, researchers found that at least 8 percent of patients with this ...
Marcos Vilela wins Lilly Research Award for Doctoral Students
2024-07-09
The Royal Spanish Society of Chemistry (RSEQ) and Lilly have announced the winning theses of the 22nd Research Awards for Doctoral Students, which acknowledge outstanding work in the fields of Organic, Pharmaceutical, and Analytical Chemistry. Marcos Vilela, currently pursuing his PhD at the Center for Research in Biological Chemistry and Molecular Materials (CiQUS) at the University of Santiago de Compostela (USC), was awarded alongside Andrea Palone from the University of Girona (UdG) and the University of Rome "Tor Vergata," and Beatriz Arévalo from the Complutense University of Madrid (UCM).
Marcos' thesis, supervised by CiQUS Principal ...
Trust, more than knowledge, critical for acceptance of fully autonomous vehicles
2024-07-09
PULLMAN, Wash. – While not yet on the market, fully autonomous vehicles are promoted as a way to make road travel dramatically safer, but a recent study found that knowing more about them did not improve people’s perception of their risk. They needed to have more trust in them too.
This study adds to the evidence from other research that knowledge alone is not enough to sway people’s attitudes toward complex technology and science, such as gene editing or climate change. In this case, Washington State University researchers found that trust in the autonomous vehicles’ reliability and performance played the strongest role in improving ...
Run screaming or slow retreat? New study advances understanding of brain responses to emotionally-charged scenes
2024-07-09
The ability to recognise and respond to emotionally-charged situations is essential to a species’ evolutionary success. A new study published today [July 9th] in Nature Communications advances our understanding of how the brain responds to emotionally charged objects and scenes.
The research, led by Trinity College Dublin neuroscientist Prof. Sonia Bishop and Google researcher Samy Abdel-Ghaffar while he was a PhD student in Prof. Bishop's lab at UC Berkeley, has identified how the brain represents different categories of emotional stimuli in a way that allows for ...
Brain neurotransmitter receptor antagonist found to prevent opioid addiction in mice
2024-07-09
New research led by UCLA Health has found a drug that treats insomnia works to prevent the addictive effects of the morphine opioids in mice while still providing effective pain relief.
The study, published in the journal Nature Mental Health, concluded that suvorexant, which blocks brain receptors for a neurotransmitter called hypocretin, prevents opioid addiction. At high doses in humans, suvorexant induces sleep and is used to treat insomnia. But sleep was not induced, and behavioral alertness was maintained, at the much lower doses effective in preventing ...
Nerve damage from breast cancer treatment can be predicted
2024-07-09
Many women treated for breast cancer using taxanes, a type of cytostatic drug, often experience side effects in the nervous system. Researchers at Linköping University have developed a tool that can predict the risk level for each individual. The tool could help doctors adapt treatment to avoid persistent side effects in those at the greatest risk.
More and more people are becoming cancer survivors. But even if they have survived the disease, an increasing number still suffer from the side effects of cancer treatment. In a recent study from Linköping University, researchers studied the side effects of taxanes, ...
Water stored under artificial turf could make cities cooler and safer to play in
2024-07-09
For those living in cities, space to play sports outside can be a scarcity. Recently, natural grass in parks or public sports courts has often been replaced with more durable artificial turf to allow heavy consecutive use.
There are, however, downsides to this practice, both for people and for cities as a whole. Now, scientists in the Netherlands have set out to change that by integrating a subsurface water storage and capillary irrigation system under artificial turf sports fields.
“Here we show that including a subsurface water storage and capillary ...
How a plant app helps identify the consequences of climate change
2024-07-09
Plants are known to respond to seasonal changes by budding, leafing, and flowering. As climate change stands to shift these so-called phenological stages in the life cycle of plants, access to data about phenological changes – from many different locations and in different plants – can be used to draw conclusions about the actual effects of climate change. However, conducting such analyses require a large amount of data and data collection of this scale would be unthinkable without the help of citizen scientists. “The problem is that the quality of the data suffers when fewer people engage ...
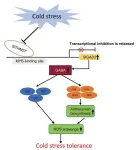
Tomato triumph: genetic key to chill-proof crops unveiled
2024-07-09
In a significant advancement for agricultural biotechnology, researchers have identified a genetic mechanism that enhances the cold tolerance of tomatoes. This breakthrough is pivotal for cultivating crops in cooler climates, ensuring stable yields and bolstering global food security. The study focuses on the SlGAD2 gene, which, when overexpressed, elevates the plant's γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) levels, boosts antioxidant activities, and stimulates anthocyanin production, collectively improving cold resilience.
Tomatoes play a vital role in global agriculture but are susceptible ...
Scientists exploring potential new treatments for glioblastoma
2024-07-09
A new approach to treating the most malignant type of brain cancer – glioblastoma – has shown strong promise in pre-clinical settings, raising hopes of increasing current average survival rates beyond 18 months.
Targeted alpha therapy (TAT) is emerging as a potential additional treatment for glioblastoma (GB), a disease which has confounded oncologists for decades due to its aggressive nature and strong resistance to existing therapies.
The current standard treatment for GB is surgery, followed by external beam radiotherapy and the chemotherapy drug, temozolomide. However, survival rates of less than 5-10% at five years have prompted researchers to explore ...
Tomato Time capsule: postharvest treatments and their role in ripening dynamics
2024-07-09
Tomato fruit ripening, a process initiated by key gene demethylation, is significantly influenced by postharvest handling practices. These practices, while extending shelf life, can alter ripening dynamics and affect fruit quality. This study explores the impact of various postharvest treatments on the fruit's methylome and transcriptome, shedding light on how physiological and molecular changes interplay to determine the final quality of tomatoes.
Postharvest handling practices, such as refrigeration and modified atmosphere storage, are commonly used to extend the shelf life of tomatoes. However, these methods can negatively impact fruit quality, ...
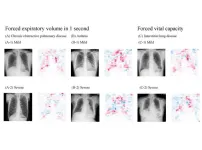
Innovative, highly accurate AI model can estimate lung function just by using chest x-rays
2024-07-09
If there is one medical exam that everyone in the world has taken, it’s a chest x-ray. Clinicians can use radiographs to tell if someone has tuberculosis, lung cancer, or other diseases, but they can’t use them to tell if the lungs are functioning well.
Until now, that is.
In findings published in The Lancet Digital Health, a research group led by Associate Professor Daiju Ueda and Professor Yukio Miki at Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Medicine has developed an artificial intelligence model that can estimate lung function from chest radiographs with high accuracy.
Conventionally, ...
University of Cincinnati, Swing Therapeutics study: Mobile app therapy leads to significant improvement in fibromyalgia management
2024-07-09
New research led by the University of Cincinnati and Swing Therapeutics found that a self-guided smartphone-based behavioral therapy led to significant improvements for patients with fibromyalgia.
The multicenter, randomized controlled trial tested Stanza, a smartphone app that delivers acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), a type of cognitive behavioral therapy recommended by international clinical guidelines for fibromyalgia management, with the results of the study published July 8 in The Lancet.
Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain condition that affects an estimated 10 million Americans, a majority ...
Anxiety and depression a more common consequence of cardiac arrest for women than for men
2024-07-09
Cardiac arrests affect around 350,000 people in Europe each year with less than 20% surviving an out of hospital cardiac arrest. Research from Amsterdam UMC shows that women who survive consequently have greater rates of anxiety and depression. Furthermore, both men and women are affected by negative population-wide changes in socioeconomic status as they age. Suggesting more support is necessary for those who have suffered a cardiac arrest. These results are published today in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality & Outcomes.
"We looked at many factors to determine the five-year consequences of a cardiac arrest, here we saw, most significantly, a 50% ...
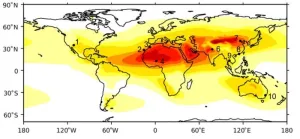
Engine wear risk as planes swallow more dust waiting to land
2024-07-09
Planes flying into one of the world's busiest airports are ingesting around 10kg of dust per 1,000 flights - with most of this dust ingested while they are waiting to land, new research has revealed.
Scientists used 17 years of ECMWF atmospheric data and data from the CALIPSO satellite to calculate the quantity of sand and dust swallowed by jet engines at ten major international airports located in desert regions or subject to seasonal dust storms.
The global study, published today (Tuesday, 9 July) in the journal Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, ...
Coral reefs: battlegrounds for survival in a changing climate
2024-07-09
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Coral reefs, those vibrant underwater cities, stand on the precipice of collapse. While rising ocean temperatures and coral bleaching grab headlines, a new essay in Current Biology reveals a hidden layer of complexity in this fight for survival: the often-overlooked roles of the reefs’ smallest inhabitants.
Scientists have long understood the vital partnership between corals and their symbiotic algae, but work by researchers at UC Santa Barbara and University of Georgia highlights how the fate of entire reefs may hinge ...
Study: Telehealth builds autonomy, trust in treating addiction
2024-07-09
Even as the nation’s opioid epidemic continues to ravage families and communities nationwide — with more than 100,000 Americans dying of drug overdoses each year — stigma remains a barrier for many people accessing treatment for addiction.
A new study from Oregon Health & Science University suggests telehealth may be an important antidote to overcoming stigma and reducing barriers for people seeking out the treatment they need.
The study, published recently in the Harm Reduction Journal, compiled in-depth interviews with 30 people treated for substance use disorder ...
New carbon storage technology is fastest of its kind
2024-07-09
A new way to store carbon captured from the atmosphere developed by researchers from The University of Texas at Austin works much faster than current methods without the harmful chemical accelerants they require.
In new research published in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, the team developed a technique for ultrafast formation of carbon dioxide hydrates. These unique ice-like materials can bury carbon dioxide in the ocean, preventing it from being released into the atmosphere.
“We’re staring at a huge challenge — finding a way ...
Socioeconomic status significantly affects fertility treatment outcomes, new study shows
2024-07-09
Novel research, presented today at the ESHRE 40th Annual Meeting in Amsterdam, reveals significant social disparities in achieving live births following assisted reproductive technology (ART) treatment. Women with a research education (PhD) were over three times more likely to achieve a live birth compared to those with a primary school education, while women in the highest income group were twice as likely than those in the lowest income group [1].
Conducted by researchers from the University of Copenhagen and Copenhagen University Hospital (Rigshospitalet), the national, register-based study analysed data from 68,738 women aged 18-45 who underwent ...
[1] ... [1068]
[1069]
[1070]
[1071]
[1072]
[1073]
[1074]
[1075]
1076
[1077]
[1078]
[1079]
[1080]
[1081]
[1082]
[1083]
[1084]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.