Globally significant upwelling is driven by topographical features on seafloor
2024-07-09
Irvine, Calif., July 9, 2024 – Exactly how the turbulent mixing of ocean water relates to global overturning circulation has been little understood by oceanographers, but an international research team, including an Earth system scientist at the University of California, Irvine, has found that bumpy topographical features along the sloping ocean floor contribute significantly to ocean seawater upwelling.
In a paper published recently in Nature, the researchers describe a “vigorous near-bottom upwelling” that results in the upward transition of water from denser to lighter ocean layers at a rate ...
Dolls and trucks: Political right and left share some parenting beliefs
2024-07-09
Key takeaways
Virtually all study respondents on the political left and more than 75% on the right supported allowing children to play with both traditionally “girl” and “boy” toys.
Those on both sides of the political spectrum also supported the idea that girls should be able to aspire to traditionally male pursuits.
However, while most left-wing activists supported the idea of a child living in a way that does not align with their birth sex, most right-wing activists rejected the idea.
Society appears deeply divided on how to parent with regard to gender.
For example, some parents throw “gender reveal” ...
Delaying diabetes with diet and exercise for 4 years results in better long-term health
2024-07-09
Individuals diagnosed with prediabetes can reduce their long-term risk of death and diabetes-related health complications if they delay the onset of diabetes for just four years through diet and exercise. Guangwei Li of the China-Japan Friendship Hospital and colleagues report these findings in a new study published July 9th in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine.
Type 2 diabetes is associated with an increased risk of death and disability, and imposes a significant economic burden on individuals and societies worldwide. Lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet and getting more exercise, can delay or reduce the risk of developing diabetes in people ...
Global database reveals large gaps in our knowledge of four-footed animals
2024-07-09
Researchers developed TetrapodTraits – a global database of animals with four feet – which can now be applied for better ecology, evolution and conservation research. Mario Moura of the Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Brazil, and Walter Jetz of Yale University, US, published this work on July 9th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology.
Tetrapods, which include amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals, are generally well-documented species, which makes them useful as models in global biodiversity studies. However, gaps in our knowledge about many of these species, data inconsistencies and shifting scientific names can lead to biased conclusions about biodiversity. To help ...
Regorafenib synergizes with TAS102 against multiple gastrointestinal cancers
2024-07-09
“In this study, we investigated the therapeutic effects and the underlying mechanisms of TAS-102 in combination with regorafenib against gastrointestinal cancers.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 9, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on July 2, 2024, entitled, “Regorafenib synergizes with TAS102 against multiple gastrointestinal cancers and overcomes cancer stemness, trifluridine-induced angiogenesis, ERK1/2 and STAT3 signaling regardless of KRAS or BRAF mutational status.”
Single-agent TAS102 (trifluridine/tipiracil) and regorafenib ...
Stem cell-derived therapy shows promise against treatment-resistant liver cancer
2024-07-09
Researchers at University of California San Diego have found that the most common form of liver cancer — one with a high mortality rate — can be better targeted and treated using an innovative new stem cell-derived therapy, according to a recently published study in Cell Stem Cell.
The treatment, not yet studied in patients, involves the lab engineering of natural killer (NK) cells — white blood cells that destroy tumor cells — to more effectively battle hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), one of the most treatment-resistant types of solid tumor.
Genetically modified NK-cell therapy doesn't require ...
Innovations in polyphenols research: Highlights from the upcoming 17th Annual 2024 World Congress in Milan
2024-07-09
The 17th World Congress on Polyphenols Applications, taking place on September 19-20, 2024, at Università degli Studi di Milano Statale in Milan, Italy, will gather more than 140 attendees coming from 30+ countries. More than 20 international speakers will cover the latest advances in polyphenols research and their practical applications.
Key Topics
Polyphenols Applications 2024 will cover a wide range of topics, including the challenges in demonstrating the health benefits of polyphenols, the ...
Groundbreaking study reveals oceanic seabirds chase tropical cyclones
2024-07-09
A new study published today in Current Biology, "Oceanic Seabirds Chase Tropical Cyclones," reveals that the rare Desertas Petrels (Pterodroma deserta), a wide-ranging seabird in the North Atlantic, exhibit unique foraging behaviors during hurricane season. Contrary to other pelagic seabirds, these petrels do not avoid intense tropical cyclones but instead exploit the dynamic conditions for their benefit, providing new insights into the impact of cyclones on open ocean marine life.
"Initial studies suggested that seabirds either circumnavigate cyclones or seek refuge in the calm eye of the storm. However, the Desertas Petrels we tracked did neither; instead, one-third of ...
Study examines tree adaptability to climate change
2024-07-09
During his recent yearlong sabbatical, Daniel Laughlin led a study that found trees can sustain life in temperatures higher or lower than where they are currently growing.
While tree species appear to prefer distinct climatic conditions, the true nature of these preferences is obscured by species interactions and dispersal, which limit tree species’ ranges.
“We were amazed. The result was crystal clear, and that doesn’t always happen in ecology,” says Laughlin, a professor in the University of Wyoming Department of Botany. “We found that tree species could grow and survive at one common moderate temperature, even though many ...
Advocate Health champions health equity through new, innovative dementia care model
2024-07-09
CHARLOTTE, N.C. – Advocate Health has been selected by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) to participate in the Guiding an Improved Dementia Experience (GUIDE) Model, aimed to support advanced dementia patients and their caregivers in bridging the gaps associated with inequalities in dementia care. Following years of neurocognitive disorders research pioneered by Advocate Health's academic core, Wake Forest University School of Medicine, patients across the health system’s footprint now will benefit from the GUIDE Model’s new standardized approach to care for patients with dementia and their caregivers. Only 400 health organizations ...
Study points at novel approach to treat Group 3 medulloblastoma
2024-07-09
A team of researchers at Baylor College of Medicine, Texas Children’s Hospital, the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto and collaborating institutions has identified and located a population of stem-like cells that initiates and maintains Group 3 medulloblastoma (Gr3-MB) in the developing brain. Gr3-MB is one of the most aggressive forms of brain cancer in children and is associated with metastatic spread and poor survival.
The researchers showed that eliminating the small population of stem-like ...
Could a dietary fiber supplement offer long-awaited treatment for food allergy sufferers?
2024-07-09
A study from the University of Michigan has identified a potential new treatment for food allergies in inulin, a naturally occurring plant fiber commonly used as a supplement, a prebiotic in soda, a replacement for sweeteners and for other products and purposes.
In what appears to be a major advancement that offers the promise of relief to food allergy sufferers around the world, the paper published in Nature Materials describes inulin gel-based oral immunotherapy's success in stopping allergic reactions in mice by, in part, targeting bacteria in the gut. The gel prevented severe allergic reactions ...
The new paradigm in volunteering -- and how organizations can adapt to "neither-growing-nor-fading" brand relationships
2024-07-09
Researchers from Emlyon Business School and HEC Montreal published a new Journal of Marketing study that examines the new breed of volunteers who often show a weaker sense of affiliation with organizations and how best to engage them for mutual benefit.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Managing Brand Relationship Plurality: Insights from the Nonprofit Sector” and is authored by Verena Gruber and Jonathan Deschênes.
Volunteers stand as vital pillars in the operation and survival of nonprofit organizations. Across ...
From empowering women to being empowered by women: A gendered social innovation framework for tourism-led development initiatives
2024-07-09
Gendered Social Innovation: Social Change and Female Entrepreneurship in Tourism
Gendered social innovation is a crucial process that intertwines social change with female entrepreneurship, empowerment, and the evolution of work among women in the tourism industry.
Questioning Common Perceptions
Why question the usual perceptions about the role and status of women entrepreneurs in a globalized and capitalist industry? Where does power, creativity, and innovation truly reside in tourism development?
Often, discussions about gender equality in tourism revolve around a vision that confines women to the role of service providers, perpetuating stereotypes ...
Survey finds most women with uterine fibroids are offered hysterectomies over minimally invasive treatments
2024-07-09
FAIRFAX, Va. (July 9, 2024)— Among women who have personally been diagnosed with uterine fibroids, more than half (53%) were presented with a hysterectomy, while fewer than 1 in 5 (20%) were presented with other less invasive options such as over-the-counter NSAIDs (19%), uterine fibroid embolization (17%), oral contraceptives (17%), and endometrial ablation (17%), according to new survey data by The Harris Poll on behalf of the Society of Interventional Radiology. Moreover, some women (17%) mistakenly ...
Patient out-of-pocket costs for type 2 diabetes medications when aging into Medicare
2024-07-09
About The Study: In this cohort study of individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D), the increase in spending upon reaching age 65 (when most people enroll in Medicare) was associated with patient coinsurance in the coverage gap and catastrophic coverage phases of Medicare Part D. The increased patient cost burden at age 65 and a modest reduction in overall T2D drug utilization suggest that as people with T2D age into Medicare, there is potentially an increase in nonadherence and diabetes complications.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Douglas ...
Prenatal exposure to ambient air pollution and cerebral palsy
2024-07-09
About The Study: In this large cohort study of singleton full term births in Canada, prenatal ambient PM2.5 exposure was associated with an increased risk of cerebral palsy in offspring. Further studies are needed to explore this association and its potential biological pathways, which could advance the identification of environmental risk factors of cerebral palsy in early life.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Carmen Messerlian, Ph.D., email cmesser@hsph.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
Whale remains tracked to highlight sustainable disposal benefits
2024-07-09
A string of whale strandings on the East Australian Coastline and questions around the appropriate disposal methods for the remains has prompted a new study that highlights a sustainable, cultural and ecosystem beneficial offshore removal or decomposition.
Dr Olaf Meynecke, from Griffith University’s Whales and Climate Research Program, led the case study, in which a 14m female humpback whale was found floating deceased – likely to due to ship strike – in the coastal waters off Queensland’s Noosa Heads in July 2023.
The remains were intercepted before washing up on the shoreline, then repositioned 30km offshore ...
Research Spotlight: Researchers find that adverse drug events are frequent and many are preventable in the outpatient setting
2024-07-09
Rachel L. Wasserman, PharmD, of the Department of General Internal Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, is the lead author and David W. Bates, MD, medical director of Clinical and Quality Analysis for Mass General Brigham and Co-Director of the Center for Artificial Intelligence and BioInformatics for Mass General Brigham, is the senior author of a new study published in BMJ Quality & Safety, “Frequency and preventability of adverse drug events in the outpatient setting.”
How would you summarize your study for a lay audience?
Many studies have analyzed ...
From genomes to gardens: introducing the HortGenome Search Engine for horticultural crops
2024-07-09
The HortGenome Search Engine (HSE) introduces a groundbreaking tool that transforms the exploration of horticultural crops' genetics. Enabling swift access and analysis of data from over 500 plant species, HSE enhances our ability to decode complex genetic networks. This launch marks a pivotal advancement in horticultural studies, offering detailed insights into crop genetics critical for human nutrition and health.
As genomics profoundly reshapes our understanding of horticultural crops, researchers often grapple with dispersed and complex genomic data. This fragmentation significantly hinders effective analysis ...
From winter's rest to spring's bloom: PmDAM6 gene steers plant bud dormancy
2024-07-09
This pivotal study explores the genetic orchestration of bud dormancy in woody perennials, a survival strategy crucial for enduring harsh climates. It focuses on the PmDAM6 gene, revealing its regulatory effects on lipid metabolism and phytohormone dynamics within dormant meristems, which dictate the plant's seasonal transition from rest to growth.
Plant dormancy's genetic mechanisms are vital for enhancing agricultural resilience and productivity. The interaction between lipid metabolism and hormone regulation significantly influences ...
From kale to carotenoid powerhouse: a breakthrough in plant nutrition
2024-07-09
A recent study has identified a crucial regulatory mechanism in Chinese kale, potentially revolutionizing its nutritional profile. By manipulating the BoaBZR1.1 transcription factor, researchers significantly enhanced carotenoid levels, crucial antioxidants for human health. This advancement opens pathways for improving vegetable nutrition through genetic engineering.
Carotenoids, vital antioxidants in plants, are integral for human health, enhancing immunity and preventing diseases. However, many vegetables, including Chinese kale, naturally exhibit low carotenoid levels. To address this nutritional gap, scientists are exploring genetic ...
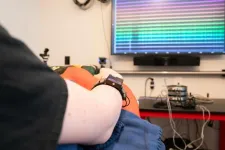
CMU, Meta announce research collaboration aimed at making computer-based tasks and gaming accessible to people with different motor abilities via wearable sensing technology
2024-07-09
PITTSBURGH - As part of a larger commitment to developing equitable technology, Carnegie Mellon University and Meta announce a collaborative project to make computer-based tasks accessible to more people. This project focuses on using wearable sensing technology to enable people with different motor abilities to perform everyday tasks and enjoy gaming in digital and mixed reality environments.
Meta’s research in electromyography uses sensors placed on the skin to measure the electrical signals the user generates through muscles in their wrist, which are translated into input signals for various devices. While Meta has already ...
Detecting defects in tomorrow’s technology
2024-07-09
Silicon computer chips have served us well for more than half a century. The tiniest features on chips currently sold are approximately 3 nanometers — a startlingly small size given that a human hair is roughly 80,000 nanometers wide. Reducing the size of features on chips will help us meet our endless need for more memory and processing power in the palm of our hand. But the limit of what can be achieved with standard materials and processes is near.
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) are applying their expertise in ...
It takes a cool microscope and antifreeze to really look at ice
2024-07-09
Ice in nature is surrounded by liquid most of the time, and therefore it is key to understand how ice and liquid interact. A Kobe University and Institute for Molecular Science study could now for the first time directly observe the precise shape of ice at the interface between ice and liquid – by using antifreeze and a refrigerated microscope.
When we slide on ice, when snowflakes form, when we lick ice cream, the surface of the ice is always covered with liquid water, and understanding the interaction between the ...
[1] ... [1067]
[1068]
[1069]
[1070]
[1071]
[1072]
[1073]
[1074]
1075
[1076]
[1077]
[1078]
[1079]
[1080]
[1081]
[1082]
[1083]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.