A gut microbe could hold a key to help people benefit from healthy foods
2024-07-08
KEY TAKEAWAYS
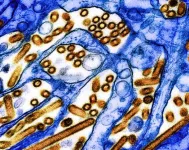
In a study involving 50,000+ individuals from around the world, higher gut levels of Blastocystis, a single-celled organism commonly found in the digestive system, were linked to more favorable indicators of health.
People with a healthy diet had higher levels of Blastocystis.
The study, which was conducted by an international team led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital, suggests that Blastocystis may play a beneficial role in how diet impacts health.
In an analysis of more than 50,000 individuals from around the world, carriers of gut Blastocystis, a single-celled organism that has been ...
Luther identifying road segments that bisect predicted movement corridors for small priority species in Virginia
2024-07-08
David Luther, Associate Professor, Biology, received funding for the project: “Identifying Road Segments that Bisect Predicted Movement Corridors for Small Priority Species in Virginia.”
The purpose of this study is to advance the work of the legislated Wildlife Corridor Action Plan (WCAP) and meet the intent of an awarded Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) grant by identifying road segments that may pose a high risk or impede movement of select small terrestrial and semiaquatic animal species that are ...
Employees prefer human performance monitors over AI, study finds
2024-07-08
ITHACA, N.Y. - Organizations using AI to monitor employees’ behavior and productivity can expect them to complain more, be less productive and want to quit more – unless the technology can be framed as supporting their development, Cornell University research finds.
Surveillance tools cause people to feel a greater loss of autonomy than oversight by humans, according to the research. Businesses and other organizations using the fast-changing technologies to evaluate employee behaviors should consider their unintended consequences, which may prompt resistance and hurt performance, the researchers say. They also suggest an opportunity to win buy-in, ...
Novel liquid biopsy methodology enables the monitoring of disease evolution in patients with metastatic prostate cancer
2024-07-08
Novel liquid biopsy methodology enables the monitoring of disease evolution in patients with metastatic prostate cancer
Extracellular vesicles shed by prostate cancer cells to the bloodstream contain tumor-derived material that can be used as biomarkers of therapy response and resistance in patients with metastatic disease.
Published today in the journal Cancer Cell, results of a VHIO-led study show that a newly developed liquid biopsy-based approach can monitor tumor gene expression through RNA contained ...
Schrag studying history Of Dulles Corridor Metrorail Project
2024-07-08
Zachary Schrag, Professor, History and Art History, College of Humanities and Social Sciences (CHSS), received funding for the project: “Rail Against Sprawl: A History of the Dulles Corridor Metrorail Project.”
Schrag said, “I am writing the history of the Dulles Corridor Metrorail Project, among the nation’s most ambitious efforts to reshape daily transportation choices. After decades of planning and construction, the project was completed in 2022, extending the Washington ...
Study identifies racial and gender disparities in youth psychiatric emergency department boarding
2024-07-08
A new study led by researchers at McLean Hospital and Harvard Medical School, in collaboration with researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital and Cambridge Health Alliance, has uncovered concerning disparities in boarding rates of children and adolescents with severe mental health symptoms in emergency departments.
When reviewing more than 4,900 boarding episodes of youth under 17 years old in Massachusetts over an 18-month period, the researchers found there were numerous racial and gender disparities: Black youth were less likely to be admitted to inpatient psychiatric care than White youth. Additionally, transgender and nonbinary youth experienced ...
Raw milk is risky, but airborne transmission of H5N1 from cow's milk is inefficient in mammals
2024-07-08
While H5N1 avian influenza virus taken from infected cow’s milk makes mice and ferrets sick when dripped into their noses, airborne transmission of the virus between ferrets — a common model for human transmission — appears to be limited.
These and other new findings about the strain of H5N1 circulating among North American dairy cattle this year come from a set of laboratory experiments led by University of Wisconsin–Madison researchers, reported today in the journal Nature. Together, they suggest that exposure to raw milk infected with the currently circulating virus poses a real risk of infecting humans, but that the virus may not ...
Features of H5N1 influenza viruses in dairy cows may facilitate infection, transmission in mammals
2024-07-08
WHAT:
A series of experiments with highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza (HPAI H5N1) viruses circulating in infected U.S. dairy cattle found that viruses derived from lactating dairy cattle induced severe disease in mice and ferrets when administered via intranasal inoculation. The virus from the H5N1-infected cows bound to both avian (bird) and human-type cellular receptors, but, importantly, did not transmit efficiently among ferrets exposed via respiratory droplets. The findings, published in Nature, suggest that bovine (cow) ...
Scientists discover how to improve vaccine responses to potentially deadly bacterium
2024-07-08
Researchers from Trinity College Dublin have taken a leap forward in understanding how we might fight back against the potentially deadly MRSA bacterium. They have shown in an animal model that targeting a key suppressive immune molecule (IL-10) during the delivery of a vaccine improves the ability of the vaccine to protect against infection.
The bacterium Staphylococcus aureus is one of the leading causes of community- and hospital-acquired bacterial infection, and is associated with over one million deaths worldwide each year. Unfortunately, antibiotics are becoming increasingly less effective against this bacterium with the antibiotic-resistant ...
Sauer receives funding for project studying tunable RF atomic magnetometer as an electrically small receiver
2024-07-08
Sauer Receives Funding For Project Studying Tunable RF Atomic Magnetometer As An Electrically Small Receiver
Karen Sauer, Professor, Physics and Astronomy, College of Science, received funding for the project: “Tunable RF Atomic Magnetometer as an Electrically Small Receiver.”
Sauer will complete work for this project in three phases.
In Phase 1, she will focus on developing and investigating novel bias-field control based on fully atom-based measurements as well as testing the performance ...
Study highlights the importance of infection prevention after CAR-T cell therapy
2024-07-08
RESEARCH SUMMARY
Study highlights the importance of infection prevention after CAR-T cell therapy
Study Title: A systematic review and meta-analysis of nonrelapse mortality after CAR T cell therapy
Publication: Nature Medicine
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute authors: David M. Cordas dos Santos, MD, Irene M. Ghobrial, MD, Jean-Baptiste Alberge, PhD
Summary: Researchers at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, in collaboration with colleagues from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York (Dr. Kai Rejeski) and the LMU Hospital in Munich, Germany (Dr. Tobias Tix), have found ...
New gold standard survey shows alarmingly high rate of sexual exploitation across the United States
2024-07-08
A revised version of the Sexual Experiences Survey – Victimization (SES-V), the gold standard measurement of sexual exploitation designed for adults over age 18, has been released in a special issue of the Journal of Sex Research.
As the first revision since 2007, the new SES-V is an interdisciplinary collaboration among experts across more than 10 U.S. universities and the Kinsey Institute, led and coordinated by Dr. Mary Koss from the University of Arizona. It adopts more inclusive language and ...
Stench of a gas giant? Nearby exoplanet reeks of rotten eggs. And that’s a good thing
2024-07-08
An exoplanet infamous for its deadly weather has been hiding another bizarre feature—it reeks of rotten eggs, according to a new Johns Hopkins University study of data from the James Webb Space Telescope.
The atmosphere of HD 189733 b, a Jupiter-sized gas giant, has trace amounts of hydrogen sulfide, a molecule that not only gives off a stench but also offers scientists new clues about how sulfur, a building block of planets, might influence the insides and atmospheres of gas worlds beyond the solar system.
The findings are published today ...
Study backs RSV vaccine safety during pregnancy
2024-07-08
Vaccinating mothers against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) during late pregnancy to protect their newborns is not associated with an increased risk of preterm birth or other poor outcomes, according to a study by Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian investigators. Infants are particularly vulnerable to the virus which can cause a serious lower respiratory illness.
The study published in JAMA Network Open on July 8 adds real-world evidence to the existing data from clinical trials about the safety of Pfizer’s Abrysvo vaccine. The researchers found that there ...
Brigham study finds new program streamlined hospice transitions from the emergency department
2024-07-08
KEY TAKEAWAYS
After implementing a new hospice transition program, 210 out of 388 patients (54.1 percent) at Brigham and Women’s Hospital transitioned to hospice from the emergency department (ED) within 96 hours, compared to 61 of 270 patients (22.1 percent) in the control period.
Across all groups, the presence of a Medical Order for Life-Sustaining Treatment plan (MOLST), was independently associated with hospice transition.
These findings suggest that hospice transition programs can help improve use of hospice for patients presenting at the ED near the end ...
Diet quality among children
2024-07-08
About The Study: Although total dietary quality scores among U.S. children improved overall during 2005-2020, the increase remained suboptimal: lower than 5 points, a significant threshold for children in this analysis of changes in diet quality.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Yongjun Zhang, Ph.D., M.D., email zhangyongjun@sjtu.edu.cn.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2024.1880)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
Acceptability of hospital-at-home care and capacity for caregiver burden
2024-07-08
About The Study: Survey respondents reported substantial acceptability of hospital-at-home care, which did not vary across sociodemographics, health insurance coverage, health status, prior hospitalizations, or telehealth use. Approximately half of respondents agreed that hospital-at-home care was effective, safe, and convenient. Most indicated capacity to perform many caregiver tasks.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Melissa A. Frasco, Ph.D., email mfrasco@usc.edu.
To access the embargoed ...
Semaglutide vs tirzepatide for weight loss in adults with overweight or obesity
2024-07-08
About The Study: In this population of adults with overweight or obesity, use of tirzepatide was associated with significantly greater weight loss than semaglutide. Future study is needed to understand differences in other important outcomes.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Nicholas L. Stucky, M.D., email nicholass@truveta.com.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2024.2525)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest ...
AJPH study shows that permit to purchase laws are a promising avenue to reduce suicides in young adults
2024-07-08
In 2020, suicide ranked as the third leading cause of death for adults aged 18 to 20 years in the United States. Firearms were implicated in approximately half of these cases, and by 2017, they had surpassed motor vehicles as the leading cause of death in this age group. While ongoing debates on gun violence and mental health have increased public support for restricted firearm access, not much is known about the impact of gun control policies on young adults.
To fill this knowledge gap, a recent study published in the August issue of the American Journal of Public Health on July 03, ...
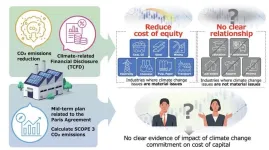
Companies that mitigate climate change reduce their cost of capital
2024-07-08
Fukuoka, Japan —The climate crisis is hitting home with more frequent extreme weather events. Companies, particularly those in high-emission industries, are major contributors to global carbon emissions, therefore making them key players in the fight against climate change. Recognizing this responsibility, many businesses are now taking proactive measures to reduce their carbon footprint, by reducing carbon emissions and transparently sharing their environmental strategies and data.
The Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures ...
Case Western Reserve University receives $1.5M grant from Foundation Fighting Blindness to test possible new treatment for inherited retinal disease
2024-07-08
CLEVELAND—There’s only one U.S. Food and Drug Administration-approved therapy for an inherited retinal disease, and dozens of retinitis pigmentosa (RP) genes for which no therapy is available.
With a new three-year, $1.5 million grant from the Foundation Fighting Blindness, Shigemi Matsuyama, an associate professor of ophthalmology and visual sciences at the Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, will test a possible breakthrough drug that can be taken by mouth—one that may address many RP disease manifestations, regardless of the underlying genetic mutation.
“We believe it can serve as the basis of an oral medicine to prevent blindness in RP ...
How to stop cancer cachexia? Start at the top
2024-07-08
Cancer is insidious. Throughout tumor progression, the disease hijacks otherwise healthy biological processes—like the body’s immune response—to grow and spread. When tumors elevate levels of an immune system molecule called Interleukin-6 (IL-6), it can cause severe brain dysfunction. In about 50%-80% of cancer patients, this leads to a lethal wasting disease called cachexia. “It’s a very severe syndrome,” says Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor Bo Li.
“Most people with cancer die of cachexia instead of cancer. And once the patient enters this stage, there’s ...
Pulsed field ablation procedures found safe and effective for atrial fibrillation patients
2024-07-08
Pulsed field ablation (PFA) is safe for treating patients with common types of atrial fibrillation (AF), according to the largest study of its kind on this new technology, led by the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
The “MANIFEST-17K” international study is the first to show important safety outcomes in a large patient population, including no significant risk of esophageal damage, with PFA. PFA is the latest ablation modality approved by the Food and Drug Administration that can be used to restore a regular heartbeat. The findings, published July 8 in Nature Medicine, could lead to more frequent use of PFA instead of conventional therapies to manage AF patients.
“MANIEFST-17K ...
Why some abusive bosses get a pass from their employees
2024-07-08
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Why do employees sometimes accept working for an abusive boss?
A new study suggests that when a leader is seen as a high performer, employees are more likely to label abuse as just “tough love.”
Results showed that workers were less likely to show hostility to abusive bosses when the leader’s performance was high, and employees were even likely to think their career could be boosted by a successful – if abusive – boss.
The findings suggest that employees may be reluctant to call a successful boss abusive – ...
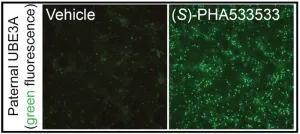
UNC researchers identify potential treatment for Angelman syndrome
2024-07-08
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Angelman syndrome is a rare genetic disorder caused by mutations in the maternally-inherited UBE3A gene and characterized by poor muscle control, limited speech, epilepsy, and intellectual disabilities. Though there isn't a cure for the condition, new research at the UNC School of Medicine is setting the stage for one.
Ben Philpot, PhD, the Kenan Distinguished Professor of Cell Biology and Physiology at the UNC School of Medicine and associate director of the UNC Neuroscience Center, and his lab have identified a small molecule that could be safe, non-invasively delivered, and capable of ...
[1] ... [1070]
[1071]
[1072]
[1073]
[1074]
[1075]
[1076]
[1077]
1078
[1079]
[1080]
[1081]
[1082]
[1083]
[1084]
[1085]
[1086]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.