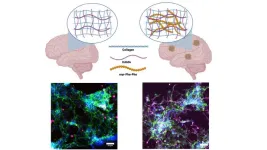
Survey finds most americans believe pain and urinary leakage is normal for women after having children
2024-07-15
Orlando, Fla - A new national survey by the Orlando Health Advanced Rehabilitation Institute finds most Americans believe it’s normal for women to experience pain, pressure and incontinence after having children. But experts say these are actually signs of pelvic floor issues, and while they are extremely common, affecting about a third of women, they are not normal.
“When we say it's not normal, what we mean is it's not something you should have to live with. It's something ...
Opioid prescribing to reduce overdoses, misuse
2024-07-15
New research aims to help reduce the quantity of unused prescription opioids after emergency department visits and lessen the risk of opioid misuse and overdose. The study is published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231640.
VIEW EMBARGOED ARTICLE
Overprescribing is linked to opioid misuse and overdose, with household supplies of opioids associated with an increased risk of overdose, as many people do not dispose of unused medications safely. In Canada, ...
Health research on South Asian communities must be led by South Asians
2024-07-15
Funding agencies in Canada need to review their policies for evaluating research proposals to ensure that South Asian research is conducted by South Asians, write authors in a commentary in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231189
VIEW EMBARGOED ARTICLE
Much of the health research conducted in Canada on South Asian diaspora communities has historically been marked by unequal power relations, rather than meaningfully engaging and benefitting these communities.
As the largest and fastest growing diverse ...
Big boost for new epigenetics paradigm: CoRSIVs, first discovered in humans, now found in cattle
2024-07-15
A study published in Genome Biology opens new possibilities to improve production efficiency in the cattle industry and potentially animal agriculture more broadly. A team of researchers at Baylor College of Medicine, Cornell University and the USDA discovered that, like humans, cattle have CoRSIVs. CoRSIVs are regions of the genome carrying chemical markers on the DNA that provide information that may allow farmers to predict and select desirable cattle characteristics, such as milk production, female fertility and resistance to disease.
“Most people know that each person ...
Cancer is the biggest health concern among the public, poll reveals
2024-07-15
Late detection biggest worry in relation to cancer diagnosis, with 55% of people wanting to see future advances in early cancer detection
Public overwhelmingly support use of AI to tackle cancer
43% of people recognise major impact universities can have on reducing deaths from cancer
Cambridge University partnering with NHS to build revolutionary new Cambridge Cancer Research Hospital
Two-thirds of the public say they are very or somewhat worried about being told they have the disease – higher than ...
Doctors suffering burnout need compassion not blame, says top GP
2024-07-15
Doctors, nurses and other healthcare staff suffering burnout should be shown compassion and not blamed for being unwell, according to a leading GP.
Clare Gerada says employers often treat physicians as ‘naughty schoolchildren’ when they go sick or suffer mental health problems. Professor Dame Gerada, past president of the Royal College of General Practitioners (RCGP), is calling for more comprehensive guidance that focuses on ‘kindness’ and ‘sensitivity’.
The doctor, who helped found mental health charity, Doctors in Distress, addresses the need for major reform in a new book aimed at reforming care for doctors and nurses ...
Study on post-COVID-19 condition: Which factors have an impact on the risk
2024-07-14
Early on during the coronavirus pandemic, there were reports of cases of persistent post-infection symptoms. The World Health Organization (WHO) refers to such new or persistent symptoms twelve weeks after a corona infection that cannot be explained by other causes as a post-COVID-19 condition. In a recent study, scientists led by the University Medicine Halle evaluated the information from 109,707 participants in the German National Cohort (NAKO Gesundheitsstudie) on their self-reported health status with respect to post-infection symptoms. The survey took place in autumn 2022, in retrospect of the pandemic.
At the time of the survey, more than 80 percent of respondents had ...
Artificial intelligence outperforms clinical tests at predicting progress of Alzheimer’s disease
2024-07-13
Cambridge scientists have developed an artificially-intelligent tool capable of predicting in four cases out of five whether people with early signs of dementia will remain stable or develop Alzheimer’s disease.
The team say this new approach could reduce the need for invasive and costly diagnostic tests while improving treatment outcomes early when interventions such as lifestyle changes or new medicines may have a chance to work best.
Dementia poses a significant global healthcare challenge, affecting over 55 million people worldwide ...
ReMDO announces inaugural Piedmont Triad Regenerative Medicine Engine Ecosystem Summit in Winston-Salem, North Carolina
2024-07-12
Winston-Salem, North Carolina – July 12, 2024 - The RegenMed Development Organization (ReMDO) invites researchers, industry and academia to the inaugural Piedmont Triad Regenerative Medicine Engine Ecosystem Summit (The Summit) on Monday, August 12th in Winston-Salem, North Carolina. Registration is open to new and current partners, with required onboarding for prospective organizations to be completed by August 12. The summit will consist of speaker sessions, discussion panels, breakouts, and networking events with complete details ...
HarvestHub app tackles supply chain, food insecurity issues
2024-07-12
The COVID-19 pandemic infiltrated almost every aspect of society and life in 2020, even in ways people wouldn’t have immediately expected. Stores that typically have no problem stocking shelves were struggling to keep pace with the sudden demand for cleaning supplies along with everything from toilet paper to Sriracha chili sauce.
While these issues aren’t as devastating as the larger health ramifications, they did shed new light on supply chain weaknesses and how that system adapts to rapid and vast market shifts. Factory closures ...
Mathematics outreach program awarded Dolciani grant
2024-07-12
Two years after launching a new mathematics outreach program, a team of Texas A&M University professors has been awarded a Dolciani Mathematics Enrichment Grant to support their program's efforts to promote math enrichment for high school students.
The Program for Research in Mathematics (PReMa) was established in 2022 by four members of Texas A&M’s Department of Mathematics: Dr. Sherry Gong, Dr. Wencai Liu, Dr. Kun Wang and Dr. Zhizhang Xie. The program, directed by Wang, targets high school students living in Texas and neighboring states. Designed to cultivate a deep appreciation and understanding of advanced ...
Groundbreaking study reveals insights into Alzheimer's disease mechanisms through novel hydrogel matrix
2024-07-12
Los Angeles, California - May 20, 2024 - Researchers at the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI) have unveiled a pioneering study shedding light on the intricate mechanisms underlying Alzheimer's disease (AD). The study, titled "Effects of amyloid-β-mimicking peptide hydrogel matrix on neuronal progenitor cell phenotype," represents a significant leap forward in understanding the interplay between amyloid-like structures and neuronal cells.
Led by Natashya Falcone and co-first authors Tess Grett Mathes and Mahsa Monirizad, the research team delved into the realm of self-assembling ...
Study examines urban forests across the United States
2024-07-12
In recent years, tree-planting campaigns have been underway in the United States, especially in cities, as part of climate mitigation efforts.
Urban forests can help improve air quality, generate cooling effects, and provide green spaces for outdoor recreation while also serving as an ecological habitat.
Just last year, the U.S. Forest Service announced a $1 billion campaign to expand access to trees and green spaces throughout the country, including in cities.
But a new Dartmouth-led study finds that some areas within urban forests in the U.S., may be more capable than trees growing around city home lawns in adapting to a warmer climate.
The findings are published ...
2023 Rolling Hills Estates landslide likely began the winter before
2024-07-12
Key takeaways
Landslides triggered by intense rainfall can sometimes be predicted along with incoming storms, but dry-season landslides often take people by surprise.
The July 2023 Rolling Hills Estates landslide that destroyed 12 homes seemed to come out of nowhere, but new research shows it began as early as December 2022.
Researchers are developing a database that will enable scientists to plug in new data to monitor potential landslides in real time and possibly predict them.
Californians are familiar with landslides that occur around storms, when saturated soil and ...
Rutgers researchers spot potential hazard with private well water treatment
2024-07-12
Systems designed to treat arsenic in private well water may be malfunctioning and endangering the health of people who count on them to keep their water safe, according to Rutgers researchers.
Megan Rockafellow-Baldoni, an assistant professor of environmental and occupational health and justice at the Rutgers School of Public Health, together with co-authors including Rutgers alum Steven Spayd, a retired research scientist formerly with the New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection, tested the water of 62 New Jersey homes with whole-house arsenic-removing water treatment systems. Their study was ...
When to trust an AI model
2024-07-12
CAMBRIDGE, MA – Because machine-learning models can give false predictions, researchers often equip them with the ability to tell a user how confident they are about a certain decision. This is especially important in high-stake settings, such as when models are used to help identify disease in medical images or filter job applications.
But a model’s uncertainty quantifications are only useful if they are accurate. If a model says it is 49% confident that a medical image shows a pleural effusion, then 49% of the time, the model should be right.
MIT ...
Research shows gamified investment sites have risks for novice investors
2024-07-12
TORONTO - What happens when online investment trading platforms start to resemble games that keep people playing for hours, with badges and exploding confetti to reward investors for their engagement?
For those who know what they’re doing, it won’t make much of a difference. New research from the University of Toronto engaging nearly 1,000 volunteers in artificial investment scenarios shows that more informational features such as price change notifications might even help savvy investors execute ...
Specially equipped natural killer cells show effectiveness against the most common form of ovarian cancer
2024-07-12
RESEARCH SUMMARY
Study Title: CAR memory-like NK cells targeting the membrane proximal domain of mesothelin demonstrate promising activity in ovarian cancer
Publication: Science Advances
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute authors include: Rizwan Romee, MD, senior author; and Mubin Tarannum, PhD, KhanhLinh Dinh, and Juliana Vergara, MD, MMSc, co-first authors
Summary: Natural killer, or NK, cells endowed with memory-like abilities and armed with a novel chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) have generated encouraging results in experiments in epithelial ovarian cancer ...
Entering the golden age for antibody-drug conjugates in gynecologic cancer
2024-07-12
“We are optimistic that the incorporation of ADCs into the treatment of aggressive tumors and treatment refractory gynecologic cancers will improve quality of life and survival outcomes in our patients.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 12, 2024 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncoscience (Volume 11) on May 20, 2024, entitled, “Entering the golden age for antibody-drug conjugates in gynecologic cancer.”
In this new editorial, researchers Michelle Greenman, Blair McNamara, Levent Mutlu, and Alessandro D. Santin from Yale University School of Medicine discuss gynecologic cancers. Biologically aggressive ...
Judge: Texas university must release records on research study that resulted in deaths of dozens of animals
2024-07-12
SAN ANGELO, Texas —Tom Green County District Court Judge Barbara L. Walther ruled Thursday, July 11, 2024, that Angelo State University must release public records relating to an experiment conducted on dozens of mice that resulted in the animals’ unnecessary suffering and death, reportedly to study the impact of the foster care system on human children.
The ruling overturns Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton’s Nov. 17, 2022 decision to side with the university in denying the records.
On July 13, 2023, the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine, a Washington, D.C. based health advocacy group of more than 17,000 doctor members that encourages higher standards ...
UMass Amherst food scientist rises to the challenge of giving marbled fatty feel and taste to plant-based meat
2024-07-12
One of the challenges of creating realistic-looking and delectable plant-based meat is mimicking the marbled effect of animal fat that many carnivores expect and enjoy.
A University of Massachusetts Amherst food scientist has a plan to tackle this quandary by developing new technology supported by a $250,000 grant from the Good Food Institute. The not-for-profit think tank promotes plant-based alternatives to meat, dairy and eggs, as well as cultivated “clean meat” grown from animal cells in a facility.
The technology proposed ...
Complex impact of large wildfires on ozone layer dynamics unveiled by new study
2024-07-12
In a revelation that highlights the fragile balance of our planet's atmosphere, scientists from China, Germany, and the USA have uncovered an unexpected link between massive wildfire events and the chemistry of the ozone layer. Published in Science Advances, this study reveals how wildfires, such as the catastrophic 2019/20 Australian bushfires, impact the stratosphere in previously unseen ways.
The ozone layer, a crucial shield protecting life on Earth from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation, has been on a path to ...
Brain inflammation triggers muscle weakness after infections
2024-07-12
Infections and neurodegenerative diseases cause inflammation in the brain. But for unknown reasons, patients with brain inflammation often develop muscle problems that seem to be independent of the central nervous system. Now, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have revealed how brain inflammation releases a specific protein that travels from the brain to the muscles and causes a loss of muscle function.
The study, in fruit flies and mice, also identified ways to block this process, which could have ...
Research alert: All stem cell therapies are not created equal
2024-07-12
Researchers from University of California San Diego have found that two of the most frequently administered stem cell therapies, which are often used interchangeably, actually contain completely different types of cells. The results challenge the current “one-cell-cures-all” paradigm in orthopedic stem cell therapeutics and highlight the need for more informed and rigorous characterization of injectable stem cell therapies before they are marketed for use in patients.
The researchers analyzed cell populations of autologous bone marrow aspirate concentrate (BMAC) and adipose-derived ...
Complex impact of large wildfires on ozone layer dynamics
2024-07-12
The ozone layer, a crucial shield protecting life on Earth from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation, has been on a path to recovery thanks to the Montreal Protocol. This landmark international treaty, adopted in 1987, successfully led to phasing out the production of numerous substances responsible for ozone depletion. Over the past decades, the ozone layer has shown significant signs of healing, a testament to global cooperation and environmental policy.
However, the stability of this vital atmospheric layer is now facing a new and unexpected challenge. During the 2019/20 Australian wildfires, ...
[1] ... [1057]
[1058]
[1059]
[1060]
[1061]
[1062]
[1063]
[1064]
1065
[1066]
[1067]
[1068]
[1069]
[1070]
[1071]
[1072]
[1073]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.