Pandemic’s impact on primary care: Significant drop in visits and uneven telehealth use across patient groups
2024-07-22
Background and Goal: The COVID-19 pandemic likely worsened disparities in access to primary care. The goal of this study was to quantify the nationwide decline in primary care visits and the increase in telehealth utilization and explore whether certain groups of patients were disproportionately impacted.
Study Approach: Researchers used primary care electronic health record data from the American Family Cohort— to examine the percentage change in total visit volume, change in in-person visit volume, and telehealth ...
Transforming clinical practice initiative linked to reduced emergency department visits
2024-07-22
Background and Goal: The Transforming Clinical Practice Initiative was a four-year nationwide program aimed at improving outpatient health care quality. The initiative, funded by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, also prepared practices for payment systems based on care quality rather than service quantity and included a Change Package to guide practice transformations. This research brief examines whether these transformations were associated with reductions in emergency department visits among both primary and specialty care practices.
Study Approach: Researchers analyzed data from 3,773 practices in the Transforming Clinical Practice ...
Dutch version of the person-centered primary care measure survey demonstrates sufficient validity and sufficient reliability for use in Dutch primary care practices
2024-07-22
Person-centered care focuses on treating patients as individuals with unique needs and involving them actively in their care decisions. The Person-Centered Primary Care Measure (PCPCM) is a recently developed, patient-reported survey able to assess person-centeredness. The PCPCM has demonstrated strong validity and reliability. The goal of this study was to translate the original PCPCM survey into Dutch, adapt the survey for people with low literacy, and evaluate its structure, consistency, and accuracy.
Study Approach: The survey was translated into Dutch and then back to English to ensure accuracy. The Dutch version was then tested to make sure it worked well for Dutch-speaking ...
Sexual and gender minority adults avoid necessary care due to identity discordance with clinicians and experiences of discrimination
2024-07-22
Background and Goal: Identity discordance between patients and clinicians is associated with worse self-rated patient experience and less receipt of necessary care. Most prior studies have focused on racial discordance. However, whether these phenomena also apply to sexual and gender minority adults is currently unknown. This study evaluated how prevalent avoidance due to patient-clinician identity discordance is and its potential association with health care discrimination among sexual and gender minority ...
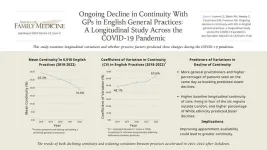
Pandemic lockdown exacerbated ongoing declines in continuity of care within English general practices
2024-07-22
Background and Goal: Longitudinal continuity of care is the repeated contact between an individual and the same general practitioner (GP). This type of continuity of care is widely regarded as a cornerstone of primary care. Higher levels of longitudinal continuity of care are associated with better health outcomes, greater patient satisfaction, and more cost-effective use of health care resources. This study aimed to describe more recent variations between practices in the slopes of longitudinal continuity of care levels across the COVID-19 pandemic. The study also set out to determine if practice-related ...
July/August Annals of Family Medicine Tip Sheet
2024-07-22
Original Research
Structural Racism and Inconsistent Hospital Policies Result in Health Care Professionals Disproportionately Testing Black Newborns for Prenatal Drug Exposure
Background and Goal: Black birthing parents and their newborns disproportionately experience newborn drug testing for prenatal substance exposure by health care professionals. This practice contributes to Child Protective Services reporting, family separation, and termination of parental rights. This qualitative study, conducted at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, MI, explored knowledge, attitudes, and experiences ...
Teens benefit from a new primary care virtual driving assessment model
2024-07-22
Integrating driving support into a primary care setting can address a leading cause of family stress as well as teen adolescent morbidity and mortality. Motor vehicle crashes are a leading cause of death for adolescents, and a leading cause of crashes is driver error. To address this, researchers at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania implemented a 15-minute self-administered virtual driving assessment test in 19 primary care practices. 3,037 adolescents 15 years and older completed the virtual driving ...
Implementing diabetic retinopathy screening using in-clinic retinal photographs and automated software analysis increases screening rates for diabetic retinopathy among low-income minority patients
2024-07-22
One-third of diabetic adults in the U.S. do not receive annual eye exams. Additionally, lack of pupillary dilation before exams is associated with ungradable, or insufficient exams. In September 2022, the OhioHealth Grant Medical Center Family Medicine practice implemented on-site diabetic retinopathy screening using digital fundus photography and automated retinal imaging without dilation. The practice later introduced eye dilation for specific patients.
By identifying patients needing screening before appointments and using electronic health record reminders, the clinic increased the rate of interpretable exams from 20% in November 2022 to 35% in May 2023. That same month, the ...
Structural racism and inconsistent hospital policies result in health care professionals disproportionately testing black newborns for prenatal drug exposure
2024-07-22
Background and Goal: Black birthing parents and their newborns disproportionately experience newborn drug testing for prenatal substance exposure by health care professionals. This practice contributes to Child Protective Services reporting, family separation, and termination of parental rights. This qualitative study, conducted at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, MI, explored knowledge, attitudes, and experiences of health care professionals and Child Protective Services professionals regarding the influence of structural ...
Study examines the impact of social connections and professional networks of NAPCRG members in driving scientific success
2024-07-22
Background and Goal: This study marks the 50th anniversary of the North American Primary Care Research Group (NAPCRG)—the premiere primary care research organization, particularly in family medicine—by examining social connections among members.
Study Approach: Researchers used social network analysis to characterize individual members and the relational structure among NAPCRG community members.
The study invited 5,905 current and past NAPCRG members and participants. The survey, based on the validated Program to Analyze, Record, and Track Networks to Enhance Relationships ...
Media Tip Sheet: Fire Ecology at ESA2024
2024-07-22
Experts in fire ecology will converge at the Ecological Society of America’s upcoming Annual Meeting in Long Beach, Calif., Aug. 4–9, presenting the latest research on the causes and consequences of wildland fire in dozens of talks and posters.
The growing threat of wildfire makes understanding the past, present and future of fire regimes essential. Fire ecology addresses crucial questions such as how different species and ecosystems respond to burns, which habitats are most vulnerable and how forests recover—or fail to recover—after ...
Researchers enhance tool to better predict where and when wildfires will occur
2024-07-22
CORVALLIS, Ore. – A newly enhanced database is expected to help wildfire managers and scientists better predict where and when wildfires may occur by incorporating hundreds of additional factors that impact the ignition and spread of fire.
“There is a tremendous amount of interest in what enables wildfire ignitions and what can be done to prevent them,” said Erica Fleishman, an Oregon State University professor. “This database increases the ability to access relevant information and contribute to wildfire ...
A new drug target identified for diseases associated with leukemia-causing virus
2024-07-22
HERSHEY, Pa. — A team of researchers from Penn State College of Medicine found a new target for treating diseases associated with human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1). They determined that blocking a class of enzymes called kinases, which regulates cellular functions, leads to cell death caused by the degradation of Tax, a protein essential for viral gene expression, viral transmission and survival of cells infected by HTLV-1. The team published the findings in Nature Communications.
HTLV-1 is a retrovirus — a type of virus that hijacks a cell by inserting ...
Astrophysicists uncover supermassive blackhole/dark matter connection in solving the ‘final parsec problem’
2024-07-22
Researchers have found a link between some of the largest and smallest objects in the cosmos: supermassive black holes and dark matter particles.
Their new calculations reveal that pairs of supermassive black holes (SMBHs) can merge into a single larger black hole because of previously overlooked behaviour of dark matter particles, proposing a solution to the longstanding “final parsec problem” in astronomy.
The research is described in Self-interacting dark matter solves the final parsec problem of supermassive black hole mergers published this month in the journal Physical Review Letters.
In ...
Can we predict who will develop migraine headaches?
2024-07-22
A migraine is not just a bad headache. It is a much-dreaded part of a neurologic disorder that has an array of possible symptoms, including pulsating cranial pain, waves of queasiness, bouts of vomiting, and hypersensitivity to light and sound. They frequently materialize unannounced and at the most inopportune of moments.
Pubescent girls with a family history of migraine headaches are especially vulnerable — yet there remain many unknowns regarding the who, when and why of the disorder. Hadas Nahman-Averbuch, PhD, a scientist at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis with expertise ...
On the origin of academic traditions — and some alternatives for debate
2024-07-22
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — The field of science aims to be objective, repeatable and justified in its choices and methods. These principles are what distinguish accepted scientific findings from pseudo-science. Yet the experience of learning and working in the field of science, including graduate school activities and scientific conferences, might not always follow the same principles. These practices and gatherings of scientists may be just as organic and random as evolution.
Have the traditions of science — rituals of poster presentations and tenure positions — evolved by chance? ...
Tropical plant species are as threatened by climate change as widely feared, study confirms
2024-07-22
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Brown University biologists who set out to better understand the effects of climate change on plant species in tropical mountain regions found that even small variations in temperature and moisture can have massive impacts, threatening not only plants that live there, but also the ecosystems they support.
Emily Hollenbeck, who conducted the research while earning her Ph.D. in ecology and evolutionary biology from Brown, made the discoveries through a series of laborious yet informative experiments conducted in the Monteverde mountain ...
SNIS 2024: New study shows updated stroke evaluation protocols increase patient access to lifesaving stroke treatment
2024-07-22
COLORADO SPRINGS, Colo. — Changing standard procedures for evaluating and treating patients with suspected stroke has led to improved access to lifesaving stroke surgery across the state of Delaware and should inform triage and treatment nationwide, according to research released today at the Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery’s (SNIS) 21st Annual Meeting.
In “Direct From the Field Bypass to CSC Improves Timeliness and Likelihood of Thrombectomy for Patients with Emergent Large Vessel Occlusion,” the members of the Delaware Stroke System worked with the state’s emergency medical services (EMS) director ...
Development of ‘living robots’ needs regulation and public debate
2024-07-22
EMBARGOED: NOT FOR RELEASE UNTIL 8PM UK TIME (3PM EASTERN TIME) ON 22 JULY 2024
Development of ‘living robots’ needs regulation and public debate
Bio-hybrid robotics creates unique ethical challenges, say researchers
Researchers are calling for regulation to guide the responsible and ethical development of bio-hybrid robotics – a ground-breaking science which fuses artificial components with living tissue and cells.
In a paper published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences a multidisciplinary ...
Ore-some: New date for Earth's largest iron deposits offers clues for future exploration
2024-07-22
Research led by Curtin University reveals that Earth’s largest iron ore deposits – in the Hamersley Province of Western Australia – are about one billion years younger than previously believed, a discovery which could greatly boost the search for more of the resource.
Using a new geochronology technique to accurately measure the age of iron oxide minerals, researchers found the Hamersley deposits formed between 1.4 and 1.1 billion years ago, rather than 2.2 billion years ago as previously estimated.
Lead author Dr Liam Courtney-Davies, who was a Postdoctoral Research Associate at Curtin University’s John de Laeter ...
Political campaigns can induce stress in minorities
2024-07-22
How did the 2021 national marriage equality referendum campaign in Switzerland affect the well-being of the LGBTIQ+ community? A team led by researchers at UZH has shown that LGBTIQ+ individuals and their cisgender heterosexual allies exhibited more stress hormones during the controversial campaign.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, trans, intersex and queer (LGBTIQ+) individuals face persistent structural inequalities and discrimination that can adversely affect their well-being. When concerns of the LGBTIQ+ community are discussed in widespread public debates, such as during political initiative and referendum campaigns, that can ...
Rice researchers explore the effects of stellar magnetism on potential habitability of exoplanets
2024-07-22
Interest in Earth-like planets orbiting within the habitable zone of their host stars has surged, driven by the quest to discover life beyond our solar system. But the habitability of such planets, known as exoplanets, is influenced by more than just their distance from the star.
A new study by Rice University’s David Alexander and Anthony Atkinson extends the definition of a habitable zone for planets to include their star’s magnetic field. This factor, well studied in our solar system, can have significant implications for life on other planets, according ...
Lehigh University researchers awarded $1 million NSF grant to investigate floating offshore wind turbines
2024-07-22
In the past few years, we’ve seen a push toward renewable energy. One focus is wind, which is harvested via turbines–you may have seen them in mountainous areas, turning in the wind. But the United States’s most abundant wind potential lies offshore; wind speeds are highest off both coasts. This means offshore wind turbines promise high energy yields, akin to the offshore wind production in the North Sea near northern Europe.
But constructing wind turbine platforms in water deeper than ~60 meters presents problems. Turbines in shallow waters, like those in the North Sea, can be mounted on fixed-bottom platforms, held ...
SNIS 2024: New study reveals possible link between gastrointestinal syndromes and risk of brain aneurysm
2024-07-22
COLORADO SPRINGS, Colo. — There is a potential connection between a diagnosis of certain gastrointestinal (GI) syndromes and the formation and rupture of intracranial (brain) aneurysms, according to research presented today at the Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery’s (SNIS) 21st Annual Meeting.
An intracranial aneurysm (IA) occurs when a blood vessel in the brain bulges, putting pressure on the vessel wall. IAs that rupture cause brain bleeding and lead to a hemorrhagic stroke, a life-threatening emergency requiring immediate medical attention ...
More Black Americans die from effects of air pollution
2024-07-22
Everyone knows that air pollution is bad for health, but how bad depends a lot on who you are. People of different races and ethnicities, education levels, locations and socioeconomic situations tend to be exposed to different degrees of air pollution. Even at the same exposure levels, people’s ability to cope with its effects — by accessing timely health care, for example — varies.
A new study by Stanford Medicine researchers and collaborators, which takes into account both exposure to air pollution and susceptibility to its harms, found that Black Americans are significantly more likely to die from causes related to air pollution, compared ...
[1] ... [1049]
[1050]
[1051]
[1052]
[1053]
[1054]
[1055]
[1056]
1057
[1058]
[1059]
[1060]
[1061]
[1062]
[1063]
[1064]
[1065]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.