How to eliminate racial disparities in colon cancer
2024-07-24
A new paper in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, published by Oxford University Press, finds that eliminating the race disparity in colon cancer testing in the United States would reduce colon cancer, and colon cancer death rates, dramatically among Black people.
Colorectal cancer rates and deaths from the disease have decreased over time, but racial disparities remain and are significant. Compared to White Americans, Black Americans experience higher rates of colorectal cancer incidence and lower survival rates. Black adults are approximately 23% more likely to receive a colorectal cancer diagnosis than White adults. They are also about 31% more likely to ...
Cook like a Neanderthal: Scientists try to replicate ancient butchering methods to learn how Neanderthals ate birds
2024-07-24
It's hard to know what Neanderthals ate: food preparation, especially when it comes to smaller items like birds, can leave few archaeological traces. But understanding their diets is critical to understanding these incredibly adaptable hominins, who thrived for hundreds of thousands of years in wildly varied environments. To learn what food preparation could look like in the archaeological record, scientists tried cooking like Neanderthals.
“Using a flint flake for butchering required significant precision and effort, which we had not fully valued before this experiment,” said Dr Mariana Nabais of the Institut ...
New study finds alarming rise in persistent ‘forever chemicals’ in pesticides
2024-07-24
WASHINGTON — A peer-reviewed study published today in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives has found that per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), known as “forever chemicals,” are increasingly being added to U.S. pesticide products, contaminating waterways and posing potential threats to human health.
The study, Forever Pesticides: A Growing Source of PFAS Contamination in the Environment, is the first-ever comprehensive review of the many ways PFAS are introduced into U.S. pesticide products. Pesticides containing PFAS are used throughout the country on staple ...
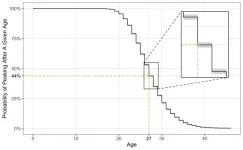
At what age do Olympic athletes peak?
2024-07-24
There’s a lot that goes into an Olympic athlete’s quest for gold – years of training and rigour – but also, an athlete’s age. A team of University of Waterloo students used statistics to figure out when an Olympic track-and-field athletes’ peak performance will be.
Track-and-field encompasses running, jumping, throwing, and combined event disciplines. Most athletes’ career performance progressions can typically be visualized as a bell curve, in which they train over several years to reach their best performance, or “peak,” at a ...
Link found between kneecap shape and debilitating joint disease
2024-07-24
The shape of a person’s kneecap could be an indicator of whether they’re more at risk of developing osteoarthritis, according to a new study from The Australian National University (ANU).
According to lead author of the study, Associate Professor Laura Wilson, women who develop knee osteoarthritis often experience more severe symptoms than men, but the reason for this is not well understood. Osteoarthritis, the most common form of arthritis, is a debilitating joint disease that causes pain, stiffness and swelling.
The research team set out to investigate whether kneecap shape might be a contributing factor.
“We wanted to focus on ...
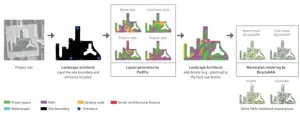
Generative AI tools like Pix2Pix–BicycleGAN are revolutionizing landscape design by enhancing masterplan generation and rendering
2024-07-24
In recent years, the rapid development and enhancement of image generation technologies and mapping tools driven by generative artificial intelligence (AI) have significantly impacted the traditional landscape design industry. Thus, it is pressing for landscape architects to delineate the relationship between image generation and landscape design and explore potential opportunities of practice and research. Research on masterplan generation primarily focuses on “image-to-image” generative adversarial network (GAN). The application of these tools has developed from the generation of architectural floor ...
Expanding APAC presence, Insilico Medicine seals strategic collaboration on AI-driven mash therapy development with Korean Biotech Therasid Bioscience
2024-07-24
Insilico Medicine(“Insilico”), a clinical-stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company, recently announces that the company has entered a strategic collaboration with Therasid Bioscience, an innovative biotechnology company founded in South Korea, to utilize advanced AI technology to co-develop novel therapies for the treatment of metabolic dysfunction associated steatohepatitis (MASH).
MASH, previously known as Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), is a severe form of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), characterized by liver inflammation and damage caused by a buildup of fat. Potentially progressing ...
When it comes to butterflies, people prefer pretty ones. That’s a problem for scientists.
2024-07-24
Research shows humans often perceive attractive people as more intelligent, healthier, better leaders and more trustworthy. It turns out this bias extends to the insect world.
A new study by scientists at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences reveals that data reported on a popular community science platform is biased. On iNaturalist, butterflies with captivating markings, easily identifiable features or those that are familiar species are reported more frequently than obscure species with no distinct qualities.
Why it matters: Online ...
UBC Okanagan study raises concerns about partner violence in queer relationships
2024-07-24
When people think of a concussion or a traumatic brain injury caused by intimate partner violence (IPV), they might picture people in a heterosexual relationship, or a man hurting a woman.
But a UBC Okanagan researcher points out that IPV, and its repercussions, is an issue in all relationships. Doctoral student Tori Stranges recently published a paper examining the prevalence and damage done by violence in Two-Spirit, Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Trans, Queer (or Questioning), Intersex and Asexual (2SLGBTQIA+) relationships.
“It’s very common for people to think that violence doesn’t ...
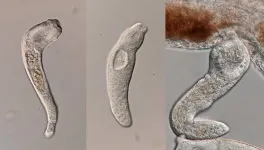
Human-infecting parasite produces sterile soldiers like ants and termites
2024-07-24
New research from scientists at UC San Diego’s Scripps Institution of Oceanography finds a tiny freshwater parasite known to cause health problems in humans defends its colonies with a class of soldiers that cannot reproduce.
The discovery, published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences and funded by the National Institutes of Health, vaults this species of parasitic flatworm into the ranks of complex animal societies such as ants, bees and termites, which also have distinct classes of workers and soldiers that have given up reproduction to serve their colony.
When it gets into humans, usually via the consumption of raw or undercooked fish, this species ...
The unintended consequences of success against malaria
2024-07-24
For decades, insecticide-treated bed nets and indoor insecticide spraying regimens have been important – and widely successful – treatments against mosquitoes that transmit malaria, a dangerous global disease. Yet these treatments also – for a time – suppressed undesirable household insects like bed bugs, cockroaches and flies.
Now, a new North Carolina State University study reviewing the academic literature on indoor pest control shows that as the household insects developed resistance ...
Taco-shaped arthropod from Royal Ontario Museum’s Burgess Shale fossils gives new insights into the history of the first mandibulates
2024-07-24
A new study, led by palaeontologists at the Royal Ontario Museum (ROM) is helping resolve the evolution and ecology of Odaraia, a taco-shaped marine animal that lived during the Cambrian period. Fossils collected by ROM reveal Odaraia had mandibles. Palaeontologists are finally able to place it as belonging to the mandibulates, ending its long enigmatic classification among the arthropods since it was first discovered in the Burgess Shale over 100 years ago and revealing more about early evolution and diversification. The study The Cambrian Odaraia alata and the colonization of nektonic suspension-feeding niches by early mandibulates was published ...
Butterflies accumulate enough static electricity to attract pollen without contact, new research finds
2024-07-24
Butterflies and moths collect so much static electricity whilst in flight, that pollen grains from flowers can be pulled by static electricity across air gaps of several millimetres or centimetres.
The finding, published today in the Journal of the Royal Society Interface, suggests that this likely increases their efficiency and effectiveness as pollinators.
The University of Bristol team also observed that the amount of static electricity carried by butterflies and moths varies between different species, and that these variations correlate with differences in their ecology, such as whether they visit flowers, are ...
Eyes for Love: Searching for light and a mate in the deep, dark sea, male dragonfishes grow larger eyes than the females they seek
2024-07-24
Chestnut Hill, Mass (07/24/2024) – A small but ferocious predator, the male dragonfish will apparently do anything for love. Or at least to find a mate.
A new study by researchers at Boston College found the eyes of the male dragonfish grow larger for mate-seeking purposes, making the dragonfish an anomaly in vertebrate evolution, the team reported today in the Royal Society journal Biology Letters.
Like many creatures that inhabit the dark depths of the sea, dragonfishes survive thanks to numerous ...
PNNL scientists tap nation’s fastest computers to explore critical science questions
2024-07-24
RICHLAND, Wash.—Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory have been awarded more than 3 million node hours on the nation’s most powerful computers to explore questions around pathogens, climate and energy-efficient microelectronics.
Access to the nation’s supercomputers, granted to Margaret Cheung, Daniel Mejia Rodriguez and Po-Lun Ma, is a coveted prize among scientists. The node hours represent an investment of several million dollars in computing time awarded to PNNL scientists to explore important science questions.
The awards are among 44 projects awarded through ...
Peri-operative care of transgender and gender-diverse individuals: new guidance for clinicians and departments published
2024-07-24
New guidance on peri-operative care of transgender and gender-diverse individuals is today published in Anaesthesia (the journal of the Association of Anaesthetists) to guide best practice to ensure the safety and dignity of transgender and gender-diverse people in the peri-operative period. The guidance has been produced by a working group of experts including Dr Stuart Edwardson, Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK, and Dr Luke Flower, Victor Philip Dahdaleh Heart and Lung Research Institute, Cambridge, UK, and colleagues.
The number of people openly identifying ...
Clinical psychologist’s book addresses largely ignored problem: social anxiety
2024-07-23
RIVERISDE, Calif. -- We all have some social anxiety. The nervousness we might feel before giving a speech is one example. Some people, however, have more social anxiety than others, and limit their social engagement due to excessive chronic fears of being embarrassed or humiliated. Although such social anxiety is common in both adolescents and adults, it is rarely diagnosed and treated.
In a new book titled “Social Anxiety: Hidden Fears and Shame in Teens and Adults,” Thomas E. Brown, a clinical professor of psychiatry and neuroscience in the University of California, Riverside's School of Medicine , explains ...
Researchers leveraging AI to train (robotic) dogs to respond to their masters
2024-07-23
An international collaboration seeks to innovate the future of how a mechanical man’s best friend interacts with its owner, using a combination of AI and edge computing called edge intelligence.
The project is sponsored through a one-year seed grant from the Institute for Future Technologies (IFT), a partnership between New Jersey Institute of Technology (NJIT) and Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU).
Assistant Professor Kasthuri Jayarajah in NJIT’s Ying Wu College of Computing is researching how to design a socially assistive model ...
Drawing water from dry air
2024-07-23
Earth’s atmosphere holds an ocean of water, enough liquid to fill Utah’s Great Salt Lake 800 times.
Extracting some of that moisture is seen as a potential way to provide clean drinking water to billions of people globally who face chronic shortages.
Existing technologies for atmospheric water harvesting (AWH) are saddled with numerous downsides associated with size, cost and efficiency. But new research from University of Utah engineering researchers has yielded insights that could improve efficiencies and bring the world one step closer to tapping the air as a culinary water source in arid places.
The study unveils the first-of-its-kind ...
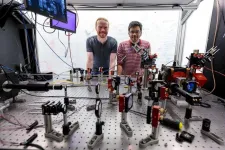
Combining trapped atoms and photonics for new quantum devices
2024-07-23
Quantum information systems offer faster, more powerful computing methods than standard computers to help solve many of the world’s toughest problems. Yet fulfilling this ultimate promise will require bigger and more interconnected quantum computers than scientists have yet built. Scaling quantum systems up to larger sizes, and connecting multiple systems, has proved challenging.
Now, researchers at the University of Chicago’s Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (PME) have discovered how to combine two powerful technologies—trapped atom arrays and photonic devices—to ...
A new way to make element 116 opens the door to heavier atoms
2024-07-23
Scientists at the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) are credited in the discovery of 16 of the 118 known elements. Now they’ve completed the crucial first step to potentially create yet another: element 120.
Today, an international team of researchers led by Berkeley Lab’s Heavy Element Group announced that they have made known superheavy element 116 using a titanium beam, a breakthrough that is a key stepping stone towards making element 120. The result was presented today at the Nuclear Structure 2024 conference; the science paper will be posted on the online repository ...
New genetic tool could identify drug targets for diseases associated with metabolic dysfunction
2024-07-23
There’s a glaring gap in our knowledge of cell metabolism: in many cases, we still don’t know exactly how nutrients are transported into the cell. Without that understanding, it’s extremely difficult, if not impossible, to develop treatments for the many diseases linked to the protein transporters that drive metabolism. Now, a new study in Nature Genetics presents a tool to map these metabolic gene functions more precisely. The platform, dubbed GeneMAP, has already identified one key gene-metabolite association at the heart of mitochondrial metabolism.
GeneMAP was developed in the laboratory of Kivanç Birsoy, ...
Plant Biologist Siobhan Brady named HHMI Investigator
2024-07-23
iobhan Brady, a professor in the Department of Plant Biology and Genome Center at the University of California, Davis, has been selected as a Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) Investigator. The prestigious Investigator program, which Brady describes as “life changing,” will provide her with roughly $9 million in research support over a seven-year term, with the option to renew.
Brady’s research aims to understand how plants use their roots to respond to environmental stressors, and to use this information to develop plants that are better able to respond to climate ...
Long-acting injectable cabotegravir for HIV prevention is safe in pregnancy
2024-07-23
Long-acting injectable cabotegravir (CAB-LA) was safe and well tolerated as HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) before and during pregnancy in the follow-up phase of a global study among cisgender women. The analysis of outcomes from more than 300 pregnancies and infants will be presented at the 2024 International AIDS Conference (AIDS 2024) in Munich, Germany.
“Cisgender women experience biological changes and social dynamics that can increase their likelihood of acquiring HIV during pregnancy and the postnatal period, and we need to offer them evidence-based options when they may need them most,” said Jeanne Marrazzo, M.D., M.P.H., ...
Large language models don’t behave like people, even though we may expect them to
2024-07-23
CAMBRIDGE, MA – One thing that makes large language models (LLMs) so powerful is the diversity of tasks to which they can be applied. The same machine-learning model that can help a graduate student draft an email could also aid a clinician in diagnosing cancer.
However, the wide applicability of these models also makes them challenging to evaluate in a systematic way. It would be impossible to create a benchmark dataset to test a model on every type of question it can be asked.
In a new paper, MIT researchers took a different approach. They ...
[1] ... [1045]
[1046]
[1047]
[1048]
[1049]
[1050]
[1051]
[1052]
1053
[1054]
[1055]
[1056]
[1057]
[1058]
[1059]
[1060]
[1061]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.