Two new studies by Mount Sinai researchers in science offer key insights into the origins and potential treatment of mental health disorders
2024-05-23
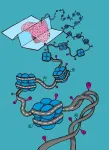
Working under the umbrella of the PsychENCODE Consortium, the mental health research project established in 2015 by the National Institutes of Health, a team of Mount Sinai scientists has uncovered important new insights into the molecular biology of neuropsychiatric disease through two new studies published in a special issue of Science on Friday, May 24. These investigations, conducted with colleagues from other major research centers, involve the largest single-cell analysis to date of the brains of people with schizophrenia, and a first-of-its-kind ...
Sequencing of the developing human brain uncovers hundreds of thousands of new gene transcripts
2024-05-23
A team led by researchers at UCLA and the University of Pennsylvania has produced a first-of-its kind catalog of gene-isoform variation in the developing human brain. This novel dataset provides crucial insights into the molecular basis of neurodevelopmental and psychiatric brain disorders and paves the way for targeted therapies.
The research, published in Science, also details how transcript expression varies by cell type and maturity, finding that changing gene-isoform expression levels can help ...
Carnegie Mellon University researchers to tackle carbon use, sustainability through NSF expeditions in computing awards
2024-05-23
Researchers from Carnegie Mellon University's School of Computer Science will contribute to two multi-institution research initiatives aimed at reducing the use of carbon and creating sustainable computing.
The projects recently received funding through the U.S. National Science Foundation's (NSF) Expeditions in Computing Awards program, which is providing $36 million to three projects selected for their potential to revolutionize computing and make significant impacts toward reducing the carbon footprint of the lifecycle of computers. The ...
USDA-NIFA grant supports microwave tech to zap weed seeds
2024-05-23
By John Lovett
University of Arkansas System Division of Agriculture
FAYETTEVILLE, Ark. — It’s not just for burritos and popcorn. Microwave technology is also being tested as a new tool to destroy weed seeds and decrease herbicide use.
Scientists and engineers with the Arkansas Agricultural Experiment Station are investigating the use of 915 MHz microwaves to neutralize a variety of weed seeds underground. The study is supported by a nearly $300,000 Agriculture and Food Research Initiative grant from the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s National Institute of Food and Agriculture, with additional support ...
Research spotlight: AI enabled body composition analysis predicts outcomes for patients with lung cancer treated with immunotherapy
2024-05-23
Tafadzwa Chaunzwa, MD, a researcher in the Artificial Intelligence in Medicine (AIM) Program at Mass General Brigham and a senior resident physician at the Harvard Radiation Oncology Program, is the lead author of a paper published in JAMA Oncology. Chaunzwa and senior author Hugo Aerts, PhD, director of the AIM Program, and associate professor at Harvard University, shared highlights from their paper.
How would you summarize your study for a lay audience?
As treatments like immunotherapy improve cancer survival rates, there is a growing need for clinical decision-support tools that predict treatment response ...
Silky shark makes record breaking migration
2024-05-23
In a recent study, researchers from the Charles Darwin Foundation (CDF), in collaboration with the Guy Harvey Research Institute (GHRI) and Save Our Seas Foundation Shark Research Center (SOSF-SRC) at Nova Southeastern University in Florida, and the Galapagos National Park Directorate (GNPD) have documented the most extensive migration ever recorded for a silky shark (Carcharhinus falciformis), revealing critical insights into the behavior of this severely overfished species and emphasizing the urgent need for cooperative international management measures to prevent further population declines.
The ...
Sexual parasitism helped anglerfish invade the deep sea during a time of global warming
2024-05-23
Members of the vertebrate group including anglerfishes are unique in possessing a characteristic known as sexual parasitism, in which males temporarily attach or permanently fuse with females to mate. Now, researchers reporting in the journal Current Biology on May 23 show that sexual parasitism arose during a time of major global warming and rapid transition for anglerfishes from the ocean floor to the deep, open sea.
The findings have implications for understanding evolution and the effects that global warming may have in the deep sea, according to the researchers.
“Our results show how the ...
Archaeology: Differences in Neanderthal and Palaeolithic human childhood stress
2024-05-23
Neanderthal children (who lived between 400,000 and 40,000 years ago) and modern human children living during the Upper Palaeolithic era (between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago) may have faced similar levels of childhood stress but at different developmental stages, according to a study published in Scientific Reports. The authors suggest that these findings could reflect differences in childcare and other behavioural strategies between the two species.
Laura Limmer, Sireen El Zaatari and colleagues analysed the dental enamel of 423 Neanderthal teeth (from 74 Homo neanderthalensis individuals) and 444 Upper Palaeolithic humans (from 102 Homo sapiens ...
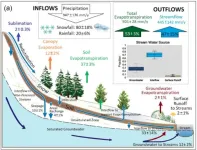
Rising temperatures will significantly reduce streamflow in the upper Colorado river basin as groundwater levels fall, new research shows
2024-05-23
The Colorado River makes life possible in many Western cities and supports agriculture that sustains people throughout the country. Most of the river’s water begins as snowmelt from the mountainous watersheds of Colorado, Utah, and Wyoming, and a warming climate will drastically reduce these streamflows, new research finds.
Researchers from Desert Research Institute (DRI), USGS, and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory teamed up for the new study, published May 23 in Nature Water. By applying warming to historical conditions for the East River in Colorado and using computer simulations to observe the impact on streamflow and groundwater ...
Prenatal exposure to chemical mixtures and metabolic syndrome risk in children
2024-05-23
About The Study: The findings of this cohort study suggest that prenatal exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemical mixtures may be associated with adverse metabolic health in children. Given the pervasive nature of endocrine-disrupting chemicals and the increase in metabolic syndrome, these findings hold substantial public health implications.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Martine Vrijheid, Ph.D., email martine.vrijheid@isglobal.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
Effectiveness of a school- and primary care–based HPV vaccination intervention
2024-05-23
About The Study: In this cluster randomized trial, within the context of the late COVID-19 pandemic period and limited school and general practitioner participation, at-school human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination significantly increased vaccination coverage. The trial did not show a significant effect for training general practitioners and education and motivation, although it may be observed after more time has elapsed after the intervention.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Morgane Michel, Ph.D., email morgane.michel@aphp.fr.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.11938)
Editor’s ...
Exposure to mixtures of endocrine-disrupting chemicals during pregnancy is associated with higher odds of metabolic syndrome in children
2024-05-23
The term ‘metabolic syndrome’ (MetS) encompasses a group of factors, such as abdominal obesity, hypertension and insulin resistance, that together increase the risk of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. A new study suggests that prenatal exposure to a combination of endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) is associated with a poorer metabolic health in childhood, which in turn may contribute to an increased risk of metabolic syndrome in adulthood. The research, led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, has been published in JAMA Network Open.
EDCs ...
Sea of love: Behind the unusual sexual parasitism of deep-water anglerfishes
2024-05-23
New Haven, Conn. – As the planet’s most expansive ecosystem, the deep sea can be a tough place to find a mate. Though, scientists say, some deep-sea anglerfishes evolved a unique method of reproduction that ensures that once they land a partner in the vast open waters, they remain latched for life.
These anglerfishes, called ceratioids, reproduce through sexual parasitism, in which the tiny males attach to their much larger female counterparts to mate. In some species, the males bite the females ...
USTC proposes therapeutic approach for inflammatory bowel disease
2024-05-23
In a study published in Cell Host & Microbe, a research team led by Prof. PAN Wen from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with research teams led by Prof. ZHU Shu and Prof. SONG Xinyang, demonstrated the causal link between microbial factors and dysfunction of intestinal stem cells (ISCs) in colitis. On the basis of this mechanism, they proposed a possible approach to restore ISC function in colitis.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic disease characterized by the microbial ...
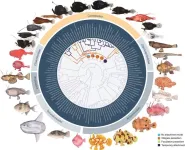
International planet hunters unveil massive catalog of strange worlds
2024-05-23
While thousands of planets have been discovered around other stars, relatively little is known about them. A NASA catalog featuring 126 exotic, newly discovered worlds includes detailed measurements that allow for comparisons with our own solar system.
The catalog details a fascinating mix of planet types beyond our solar system, from rare worlds with extreme environments to ones that could possibly support life.
The planets were analyzed by a large, international team of scientists using NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) in collaboration with the W.M. Keck Observatory on Maunakea, Hawai’i. They are described in today’s edition of The Astrophysical ...
Innovative techniques open new avenues in drug discovery for brain diseases
2024-05-23
Oak Brook, IL – Volume 29, Issue 2 of SLAS Discovery features two review articles, six original research articles covering phenotypic screening perspectives, medulloblastoma therapies and interventions for neurodegenerative diseases.
Reviews
Perspectives on phenotypic screening−Screen Design and Assay Technology Special Interest Group
The SLAS Screen Design and Assay Special Interest Group articulate the group’s discussion held at the SLAS2023 International Conference. Collectively, the group members’ perspectives highlight various challenges, progress and proposed solutions to ...
SLAS Technology presents: Advances in Synthetic Biology
2024-05-23
Oak Brook, IL – Volume 29, Issue 2 of SLAS Technology, includes three original research articles covering skin cutaneous melanoma, glycan-bead coupling and acoustic ejection mass spectrometry, and eight articles from the Advances in Synthetic Biology Special Issue.
Original Research
Validating core therapeutic targets for osteoporosis treatment based on integrating network pharmacology and informatics
This study recognizes metabolism-related lncRNAs associated with osteoporosis (OP) and constructed a prediction model for OP progression using these lncRNAs. The authors identify central therapeutic targets including CBFB, GLO1, NFKB2 ...
YouTubers cheer people up more than casual friends
2024-05-23
One-sided relationships with YouTubers are more emotionally fulfilling than talking to casual friends, a new study suggests.
The University of Essex research discovered people feel watching online stars like Zoella, KSI and PewDiePie can cheer them up more than weak-tie acquaintances – like neighbours or co-workers.
Dr Veronica Lamarche, from the Department of Psychology, also found people feel liked, respected and understood by fictional characters.
The study suggests watching online celebrities offer positive reinforcement - despite them not being able to respond.
Dr ...
Researchers advocate for structured framework to study the benefits of exercise training in multiple sclerosis rehabilitation
2024-05-23
East Hanover, NJ – May 22, 2024 – A team of experts in multiple sclerosis (MS) research recommends a structured approach to the study of mechanisms of exercise training for improving outcomes for multiple sclerosis (MS). In a review article, “Focusing on neural mechanisms of exercise training benefits in multiple sclerosis,” (doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2024.105633) published in Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders on April 16, 2024, they emphasize the value of adopting an experimental medicine framework to optimize ...
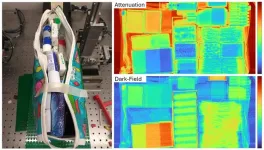
Researchers detect hidden threats with advanced x-ray imaging
2024-05-23
WASHINGTON — Researchers have combined various x-ray imaging technologies to create multi-contrast images that can be used to detect threatening materials such as explosives in thousands of complicated scenarios. The new approach, which also leverages readily available machine learning procedures for materials classification, could be useful for security screening as well as applications in the life and physical sciences.
“This method is particularly well suited to discriminating objects with very ...
Hypertension and kidney function after living kidney donation
2024-05-23
About The Study: In this cohort study of living kidney donors and nondonors with the same follow-up schedule, the risks of hypertension and albuminuria were not significantly different. After the initial drop in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) from nephrectomy, donors had a slower mean rate of eGFR decline than nondonors but were more likely to have an eGFR between 30 and 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 at least once in follow-up.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Amit X. Garg, M.D., Ph.D., email amit.garg@lhsc.on.ca.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
Kidney transplant outcomes from deceased donors who received dialysis
2024-05-23
About The Study: Compared with receiving a kidney from a deceased donor who did not undergo dialysis, receiving a kidney from a deceased donor who underwent dialysis prior to kidney donation was associated with a significantly higher incidence of delayed graft function, but no significant difference in graft failure or death at follow-up.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Chirag R. Parikh, M.D., Ph.D., email chirag.parikh@jhmi.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.8469)
Editor’s Note: Please see ...
Potentially habitable 'exo-Venus' with Earth-like temperature discovered
2024-05-23
Potentially habitable 'exo-Venus' with Earth-like temperature discovered
Royal Astronomical Society press release
RAS PR 24/12
Embargoed until 15:00 BST on Thursday 23 May 2024
Astronomers have made the rare and tantalising discovery of an Earth-like exoplanet 40 light-years away that may be just a little warmer than our own world.
The potentially-habitable planet, named Gliese 12 b, orbits its host star every 12.8 days, is comparable in size to Venus - so slightly smaller than ...
Earth twin or evil twin
2024-05-23
The discovery of a planet similar to Venus around a star in the neighborhood of the Solar System raises hopes that astronomers may someday unlock the secret to why life appeared on Earth.
The study of life in the Universe is difficult because we have only one example of a planet where life has been confirmed: Earth. It is difficult to say which characteristics of Earth are required for life to appear, and which are irrelevant. Until we find an “Earth twin” where the conditions for life also appeared, the best astronomers ...
Tracking down the genetic causes of lupus to personalize treatment
2024-05-23
Lupus is a lifelong, often painful and occasionally lethal autoimmune disease. Few treatments exist today beyond powerful steroids to knock down a patient's immune system — a therapy that has its own serious risks.
The good news is that new and promising treatments are in clinical trials. But the term lupus belies the fact that the disease has a variety of causes, which means that treatments will have to be highly personalized to guarantee that each patient is given the drug that targets the specific genetic mutation ...
[1] ... [1156]
[1157]
[1158]
[1159]
[1160]
[1161]
[1162]
[1163]
1164
[1165]
[1166]
[1167]
[1168]
[1169]
[1170]
[1171]
[1172]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.