Ohio State survey finds half of Americans feel unprepared to help in a life-threatening emergency
2024-05-22
COLUMBUS, Ohio – If someone collapsed after going into cardiac arrest, would you be prepared to help? For nearly half of Americans, the answer is no.
A new survey from The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center finds many Americans are ill-prepared to help in emergency situations.
The national poll of 1,005 people found only 51% of Americans feel they would be able to perform hands-only CPR in an emergency. When it comes to serious bleeding, 49% said they could step in to help. And 56% of survey ...
HPV testing for cervical cancer may be safe at longer intervals than what current guidelines recommend
2024-05-22
Bottom Line: The risk of detecting cervical precancer eight years after a negative human papillomavirus (HPV) screening was found to be similar to the risk after three years (the commonly recommended screening interval) after a negative cytology screening.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR)
Authors: Anna Gottschlich, PhD, MPH, assistant professor at Wayne State School of Medicine and the Barbara Ann Karmanos Cancer Institute
Background: ...
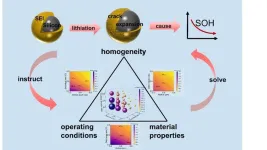
Investigating failure mechanisms of solid electrolyte interphase in silicon particles
2024-05-22
Lithium-ion batteries are widely used in new energy vehicles due to their low self-discharge rate and long cycle life. Currently, the anode material of commercial lithium-ion batteries mainly adopts graphite, with a theoretical capacity of only 372 mAh g-1 — which has gradually failed to meet the increasing demand for energy density.
Silicon has been widely studied by virtue of its high theoretical capacity of 4200 mAh g-1. However, silicon produces volume changes of up to 300% during lithiation and delithiation, and the ensuing mechanical degradation and capacity loss hinder applications. To reduce the adverse effects caused by mechanical deformation, silicon structure optimization ...
Legacy of Indigenous stewardship of camas dates back more than 3,500 years, OSU study finds
2024-05-22
An Oregon State University study found evidence that Indigenous groups in the Pacific Northwest were intentionally harvesting edible camas bulbs at optimal stages of the plant’s maturation as far back as 3,500 years ago.
The findings contribute to the growing body of research around Traditional Ecological Knowledge and practices, demonstrating the care and specificity with which Indigenous groups have been stewarding and cultivating natural resources for millennia.
Camas is an ecological and cultural keystone, meaning it is a species that many other organisms depend on and that features prominently within many cultural practices.
“If you think about salmon as being a charismatic ...
Regular fish oil supplement use might boost first time heart disease and stroke risk
2024-05-22
Regular use of fish oil supplements might increase, rather than lessen, the risk of first time heart disease and stroke among those in good cardiovascular health, but may slow progression of existing poor cardiovascular health and lower the risk of death, suggest the results of a large long term study, published in the open access journal BMJ Medicine.
Fish oil is a rich source of omega 3 fatty acids, and as such, is recommended as a dietary preventive to ward off the development of cardiovascular disease. But the evidence on how much protection it affords is inconclusive, explain the researchers.
To strengthen the evidence base, they set out to estimate the associations ...
Some teen girls clocking up close to 6 smartphone hours/day, Finnish study finds
2024-05-22
Some teenage girls are clocking up close to 6 hours a day on their smartphones, with a significant proportion of them likely addicted to social media, finds research published online in the journal Archives of Disease in Childhood.
Social media addiction was associated with poorer health and wellbeing, the findings indicate.
Recent research has linked increasing levels of anxiety among teen girls with social media use, note the researchers. This may involve several factors, one of which is addiction, with estimated international prevalence ranging from 5% to 31%, they add.
Because both anxiety and social media use are more common among girls, the researchers wanted to: measure ...
Pedestrians may be twice as likely to be hit by electric/hybrid cars as petrol/diesel ones
2024-05-22
Pedestrians may be twice as likely to be hit by an electric or hybrid car as those powered by petrol or diesel, finds a study of 2013-17 casualty rates in Great Britain, and published online in the Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health.
The risk is greater in urban areas, and governments must take steps to mitigate this safety hazard as they proceed to phase out fossil fuelled vehicles to improve air quality and curb climate change, urge the researchers.
Road traffic injuries are the leading cause of death for children and young people, and 1 in 4 road traffic deaths are of pedestrians, they note.
Amid ...
Scientists create tailored drug for aggressive breast cancer
2024-05-22
Scientists have used breast cancer cells’ weakness against themselves by linking a tumour-selective antibody with a cell-killing drug to destroy hard-to-treat tumours.
The research, published today in Clinical Cancer Research by a team from King’s College London and funded by Breast Cancer Now, marks a new method in cancer treatment.
The discovery is particular to triple negative breast cancer, which makes up 15% of all diagnosed breast cancer. This type of breast cancer is typically aggressive, resistant to chemotherapy, has a lower survival rate and is more common in women under 40.
Usual treatment involves surgery, chemotherapy ...
Language change harms our ability to communicate and understand
2024-05-22
EMBARGO: WEDNESDAY 22 MAY, 00:01 BST (TUESDAY 21 MAY, 19:01 ET).
Changes to the definitions of conceptual words like ‘woke’ and ‘gaslighting’ are harming our ability to communicate and understand our experiences, a Leeds academic argues.
In a new paper published in The Philosophical Quarterly journal, an ethicist at the University of Leeds has coined a term for the harm caused when language change leaves us lost for words.
Words such as ‘woke’, ‘depression’, ...
Jamestown Colony residents ate dogs with Indigenous ancestry
2024-05-22
Dogs with Indigenous ancestry were eaten during a period of starvation at Jamestown, the first English settlement in North America in the 17th century, according to new research in American Antiquity, published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of the Society for American Archaeology.
This discovery changes historians’ understanding of how Indigenous communities negotiated their relationship with rising colonial powers during this period. It also suggests that early European colonists depended on local Indigenous communities for their very survival, especially during the initial settlement period.
Researchers analysed ancient mitochondrial DNA from archaeological dogs from Jamestown ...
Australian study proves ‘humans are planet’s most frightening predator’
2024-05-22
Australia lacks fearsome large carnivores like lions and wolves, and the relative lack of fear that marsupials like kangaroos and wallabies show to dogs (and other introduced carnivores) has been attributed to a lack of evolutionary experience with large mammalian predators. This, however, overlooks the 50,000-year-long presence in Australia of the world’s most fearsome predator – the human ‘super predator.’
A new study conducted by Western University biology professor Liana Zanette, in collaboration with Calum ...
New York Valves 2024 late-breaking clinical trials and science announced
2024-05-22
NEW YORK – May 21, 2024 – The Cardiovascular Research Foundation® (CRF®) has announced New York Valves: The Structural Heart Summit will feature 12 Late-Breaking Clinical Trials and Science presentations. New York Valves 2024, the expanded iteration of our renowned annual Transcatheter Valve Therapy (TVT®) conference, will take place June 5-7, 2024, at the Jacob K. Javits Convention Center, North in New York City.
For nearly two decades, CRF® has led the way in pioneering transcatheter therapies for structural heart ...
Few moderate or severe asthma patients prescribed recommended inhaler regimen
2024-05-22
EMBARGOED UNTIL: 2:15 p.m. PT, May 21, 2024
Session: C94 - Asthma Quality Improvement, Health Services Research, and Disparities
Utilization of Single Maintenance and Reliever Therapy (SMART) for Moderate and Severe Asthma
Date and Time: Tuesday, May 21, 2024, 2:15 p.m.
Location: San Diego Convention Center, Room 28A-B (Upper Level)
ATS 2024, San Diego – Only 14.5 percent of adult patients with moderate or severe asthma are prescribed the recommended SMART combination inhaler regimen and over 40 percent of academic pulmonary and allergy clinicians have not adopted this optimal therapy, according to research published ...
A new way to fight an aggressive cancer in dogs
2024-05-22
Hemangiosarcoma is a common and aggressive type of cancer in dogs that arises from blood vessel cells and spreads very quickly, throughout the body, frequently affecting the spleen, liver, heart and muscles, among other organs.
“Because this type of cancer comes from blood vessels, it is common for these tumors to suddenly cause massive bleeding into the abdomen or chest,” says Heather Gardner, D.V.M., Ph.D., DACVIM (Oncology), GBS20. “Often when a dog is diagnosed, it is an emergency due to the blood loss associated with tumor rupture. They can have other problems related to hemangiosarcoma, such as lethargy, weakness, and ...
Jaboticaba peel reduces inflammation and controls blood sugar in people with metabolic syndrome
2024-05-21
The skin or peel of the Jaboticaba berry (Plinia jaboticaba), a native of the Brazilian Atlantic Rainforest, is usually thrown away because of its astringency (due to an abundance of mouth-puckering tannins), yet it can be a powerful ally in the treatment of obesity and metabolic syndrome, according to an article published in the journal Nutrition Research.
Conducted by researchers at the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP) in São Paulo state (Brazil), the study showed that inflammation and blood sugar levels improved in volunteers with obesity and metabolic syndrome who took 15 g per day of powdered jaboticaba peel as a dietary supplement for five weeks.
“The ...
Acute pseudoaneurysms following head gunshot wounds
2024-05-21
New Rochelle, NY, May 21, 2024—A new study in the peer-reviewed Journal of Neurotrauma contends that a significant fraction of traumatic intracranial aneurysms (TICAs) is missed on initial contrasted scans of patients suffering a civilian gunshot wound to the head (cGSWH). The study was designed to characterize acute TICAs using admission CT angiography (aCTA). Click here to read the article now.
The study showed that the presence of an intracerebral hematoma was the main predictor of TICA in cGSWH. Larger intracerebral hematomas in patients with cGSWH suggest hidden TICAs.
“When CTA was performed acutely, TICAs were ...
Misinformation swirled during Taiwan's 2024 elections
2024-05-21
With more than 70 countries hosting national elections, 2024 is the biggest election year in history, according to The Economist.
But how misinformation impacts elections, especially with the rise in content generated by artificial intelligence, continues to be of concern.
A research team examined misinformation narratives on social media in 2023 regarding the Taiwanese presidential election on January 13, 2024. They were especially interested in how narratives targeted relations between Taiwan and the United States.
Misinformation targeted mistrust and skepticism toward the U.S. rather ...
New report highlights many unknowns in green hydrogen plans across California
2024-05-21
OAKLAND, CA – Officials throughout the state of California have developed plans to start deploying green hydrogen at scale in the coming decade in order to reach California’s 2045 climate neutrality targets. A new analysis, published by scientists at PSE Healthy Energy, finds that while certain applications of green hydrogen may present opportunities to lower greenhouse gas emissions, many challenges remain and misalignments between current proposals could undermine progress toward state climate goals.
“Many state and local agencies are counting on massive build outs of green hydrogen infrastructure in the coming decades to achieve their climate targets,” ...
Adding obesity experts to primary care clinics improves patients’ weight loss outcomes
2024-05-21
Giving high-risk patients access to an obesity specialist through their regular primary care clinic increased their chances of receiving at least one evidence-based weight-management treatment, and led to more weight lost in just a year, a new University of Michigan study finds.
Primary care clinicians commonly struggle to help patients develop an individualized weight-management treatment plan during short clinic visits. Previous U-M research showed that most primary care patients with obesity do not lose at least 5% of their body weight, a goal that’s been shown to reduce obesity-related ...
Detecting odors on the edge: Researchers decipher how insects smell more with less
2024-05-21
Whether it’s the wafting aroma of our favorite meal or the dangerous fumes seeping from a toxic chemical, the human sense of smell has evolved into a sophisticated system that processes scents through several intricate stages. The brains of mammals have billions of neurons at their disposal to recognize odors they are exposed to, from pleasant to pungent.
Insects such as fruit flies, on the other hand, have a mere 100,000 neurons to work with. Yet their survival is dependent upon their ability to decipher the meaning of complex odor mixtures around them to locate food, seek potential mates and avoid predators. Scientists have pondered how insects are able to smell, or extract ...
Recycling carbon dioxide into household chemicals
2024-05-21
A low-cost, tin-based catalyst can selectively convert carbon dioxide to three widely produced chemicals — ethanol, acetic acid and formic acid.
Lurking within the emissions from many industrial operations is an untapped resource — carbon dioxide (CO2). A contributor of greenhouse gas and global warming, it could instead be captured and converted to value-added chemicals.
In a collaborative project involving the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory, Northern Illinois University and Valparaiso University, ...
Wayne State faculty member named president of the International Association for Great Lakes Research board
2024-05-21
DETROIT —
The International Association for Great Lakes Research today announced its new board of directors and has named Donna Kashian, Ph.D., professor of biological sciences and director of environmental sciences in the College of Liberal Arts and Sciences at Wayne State University, as president. Kashian previously served as vice president of the board.
Founded in 1967, the International Association for Great Lakes Research is a scientific organization made up of researchers studying the Laurentian Great Lakes, other large lakes of the world and their watersheds, as well as those ...
Consultative support to pediatric primary care providers in providing gender-affirming care
2024-05-21
New Rochelle, NY, May 21, 2024—A new study in the peer-reviewed journal Telemedicine and e-Health found that access to consultative support can increase pediatric primary care provider comfort providing gender-affirming care. Click here to read the article now.
The literature suggests that access to gender-affirming medical care is associated with improved medical outcomes among adolescents who identify as gender diverse or endorse a gender identity that differs from their sex assigned at birth. An increasing number of gender diverse youth seek guidance and support from their pediatric primary care providers (PPCPs), who often lack adequate training in this ...
Alaska’s rusting waters: Pristine rivers and streams turning orange
2024-05-21
Dozens of Alaska’s most remote streams and rivers are turning from a crystal clear blue into a cloudy orange, and the staining could be the result of minerals exposed by thawing permafrost, new research in the Nature journal Communications: Earth and Environment finds.
For the first time, a team of researchers from the National Park Service, U.S. Geological Survey, the University of California, Davis, and other institutions have documented and sampled some of the impaired waters, pinpointing ...
Jefferson Lab director named to 2024 Hampton Roads Power List
2024-05-21
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – Stuart Henderson, director of the U.S. Department of Energy's Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility, has been named to the Hampton Roads Power List by Inside Business. The list recognizes the major players in Hampton Roads’ economy. According to Inside Business, the 2024 list considered milestones and current events, and it features “the talk of Hampton Roads and the change that’s coming.”
“I am honored to be included in this list of people who are moving Hampton ...
[1] ... [1161]
[1162]
[1163]
[1164]
[1165]
[1166]
[1167]
[1168]
1169
[1170]
[1171]
[1172]
[1173]
[1174]
[1175]
[1176]
[1177]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.