UNC Greensboro researcher approved for NCInnovation grant funding for lithium refining research
2024-05-17
UNC Greensboro researcher Hemali Rathnayake, Ph.D., has been approved for grant funding from NCInnovation to continue her work in developing a cost-effective and efficient lithium refining process for converting lithium into battery-grade lithium carbonate.
The grant approval is conditioned on standard next steps, including executed grant agreements and formal notification to government partners. This funding is part of NCInnovation’s larger mission to unlock the innovative potential of North Carolina’s world-class universities.
“From ...
Plants restrict use of “Tipp-Ex proteins”
2024-05-17
Plants have special corrective molecules at their disposal that can make retrospective modifications to copies of genes. However, it would appear that these “Tipp-Ex proteins” do not have permission to work in all areas of the cell, only being used in chloroplasts and mitochondria. A study by the University of Bonn has now explained why this is the case. It suggests that the correction mechanism would otherwise modify copies that have nothing wrong with them, with fatal consequences for the cell. The findings have now been ...
New AI tool to help beat brain tumors
2024-05-17
A new AI tool to more quickly and accurately classify brain tumours has been developed by researchers at The Australian National University (ANU).
According to Dr Danh-Tai Hoang, precision in diagnosing and categorising tumours is crucial for effective patient treatment.
“The current gold standard for identifying different kinds of brain tumours is DNA methylation-based profiling,” Dr Hoang said.
“DNA methylation acts like a switch to control gene activity, and ...
Antioxidant Dietary Supplement “Twendee X®” can help counter systemic sclerosis
2024-05-17
Autoimmune diseases occur when the body’s immune system attacks healthy cells instead of protecting them. Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is one such autoimmune condition characterized by faulty circulatory and immune systems, leading to the occurrence of fibrosis (hardening and scarring of healthy tissue) of the skin and internal organs. SSc is known to affect patients throughout their lives, thereby, impairing their quality of life. Although precise mechanisms underlying SSc development and progression are not clearly understood, a complex interplay of immune, hormonal, environmental, and genetic factors is often implicated.
Moreover, ...
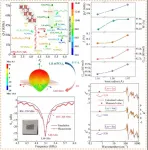
Low-permittivity LiLn(PO3)4 (Ln = La, Sm, Eu) dielectric ceramics for microwave/millimeter-wave communication
2024-05-17
Microwave dielectric ceramics are the cornerstone of wireless communication devices, widely utilized in mobile communications, satellite radar, GPS, Bluetooth, and WLAN applications. Components made from these ceramic materials, such as filters, resonators, and dielectric antennas, are extensively used in wireless communication networks. As wireless communication frequencies extend into higher bands, signal delay issues become increasingly prominent. Low dielectric constants (εr) can reduce electromagnetic coupling effects, effectively minimizing signal delays. Consequently, developing new ceramic materials with ...
Online dashboard to help save children from dangerous diarrheal diseases
2024-05-17
University of Virginia researchers are developing a flexible online tool for navigating information used in the fight to save children from deadly diarrheal diseases by identifying transmission hotspots and accelerating the deployment of treatments and new vaccines.
Diarrhea not only kills hundreds of thousands of children around the world every year, it contributes to malnutrition that can prevent kids from growing and developing to their full potential both physically and mentally, trapping them in poverty. While significant progress has been made against ...
Anti-diabetic treatment associated with reduced risk of developing blood cancer
2024-05-17
(WASHINGTON, May 17, 2024) – People who use metformin are less likely to develop a myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN) over time, indicating that the treatment may help prevent the development of certain types of cancers, according to a study published in Blood Advances.
Metformin is a therapy used to treat high blood sugar in people with type 2 diabetes that increases the effect of insulin, reduces how much glucose is released from the liver and helps the body absorb glucose. A meta-analysis of previous studies connected the therapy with ...
Pickleball courts in a legal pickle #ASA186
2024-05-17
OTTAWA, Ontario, May 17, 2024 – Pickleball Legal Consultant is a job title that likely did not exist a decade ago, but as pickleball courts infiltrate neighborhoods to satiate an appetite for a sport whose namesake is a snack, communities take issue with the resulting influx of noise. Now homeowners’ associations and city councils face litigation by those whose lives are disrupted by pickleball’s din.
Charles Leahy, an attorney, retired mechanical engineer, and former HOA board member became ...
Ancient arachnid from coal forests of America stands out for its spiny legs
2024-05-17
LAWRENCE — More than 300 million years ago, all sorts of arachnids crawled around the Carboniferous coal forests of North America and Europe. These included familiar ones we’d recognize, such as spiders, harvestmen and scorpions — as well exotic animals that now occur in warmer regions like whip spiders and whip scorpions.
But there were also quite bizarre arachnids in these habitats belonging to now extinct groups. Even among these stranger species now lost to time, one might have stood out for its up-armored legs.
The ancient critter recently was described in a new paper published ...
Model disgorgement: the key to fixing AI bias and copyright infringement?
2024-05-17
By Ian Scheffler
By now, the challenges posed by generative AI are no secret. Models like OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Anthropic’s Claude and Meta’s Llama have been known to “hallucinate,” inventing potentially misleading responses, as well as divulge sensitive information, like copyrighted materials.
One potential solution to some of these issues is “model disgorgement,” a set of techniques that force models to purge themselves of content that leads to copyright infringement or biased responses.
In ...
Researchers develop “game-changing” blood test for stroke detection
2024-05-17
Stroke is the leading cause of disability worldwide and the second leading cause of death, but the right early intervention can prevent severe consequences. A new study led by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, and collaborators developed a new test by combining blood-based biomarkers with a clinical score to identify patients experiencing large vessel occlusion (LVO) stroke with high accuracy. Their results are published in the journal Stroke: Vascular and Interventional Neurology.
“We have developed a game-changing, accessible tool that could help ensure that more people suffering from ...
New guideline: Barrett’s esophagus can precede esophageal cancer, but not all patients need a procedure to remove abnormal cells
2024-05-17
Bethesda, MD (May 17, 2024) — The American Gastroenterological Association’s (AGA) new evidence-based Clinical Practice Guideline on Endoscopic Eradication Therapy of Barrett's Esophagus and Related Neoplasia, published today in Gastroenterology, establishes updated guidance for Barrett’s esophagus patients.
A precursor to esophageal cancer, Barrett’s esophagus is a condition in which the cells in the esophagus have been replaced with non-cancerous abnormal cells. These cells can progress to a condition called dysplasia, which may in turn become cancer. Dysplasia is considered low-grade or ...
Researchers in Portugal develop an image analysis AI platform to boost worldwide research
2024-05-17
A team of researchers from the Instituto Gulbenkian de Ciência (IGC) in Portugal, together with Åbo Akademi University in Finland, the AI4Life consortium, and other collaborators, have developed an innovative open-source platform called DL4MicEverywhere published today in the journal Nature Methods*. This platform provides life scientists with easy access to advanced artificial intelligence (AI) for the analysis of microscopy images. Itenables other researchers, ...
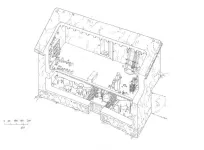
A devastating fire 2,200 years ago preserved a moment of life and war in Iron Age Spain — right down to a single gold earring
2024-05-17
A ruined building in the middle of the Pyrenees records a tragedy for the people who lived there — a devastating fire which burned a settlement to the ground, destroying everything down to a hidden gold earring. Now archaeologists’ excavation of Building G, in the strategically placed Iron Age site of Tossal de Baltarga, reveals a way of life derailed by violence: potentially, a forgotten episode of the war between Carthage and Rome.
“The destruction was dated around the end of the third century BCE, the moment where the Pyrenees were involved in the Second Punic War and the passage of Hannibal’s troops,” ...
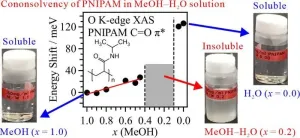
Exploration of polymer cononsolvency mechanism through soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy
2024-05-17
This study investigates the cononsolvency mechanism of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM), which is soluble in pure methanol (MeOH) and water but insoluble in aqueous MeOH solutions. Combining oxygen K-edge X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) with theoretical calculations executed in molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and inner-shell calculations, it was found that hydrophobic interactions between PNIPAM and MeOH clusters play a key role in PNIPAM aggregation and cononsolvency emergence.
PNIPAM is ...
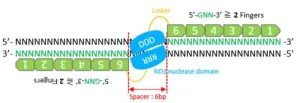
Researchers use machine-learning modeling tools to improve zinc-finger nuclease editing technology
2024-05-17
Genome editing is making inroads into biomedical research and medicine. By employing biomolecule modeling tools, a Japanese research team is accelerating the pace and cutting the cost of zinc finger nuclease (ZFN) technology, a primary gene editing tool.
In a recently published study, researchers from Hiroshima University and the Japanese National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology demonstrated how machine learning-driven modular assembly systems can improve gene editing.
The study was published on April 10 in the journal Advanced Science.
“Genome editing is ...
USC researcher awarded $3.1 million to study early brain development of babies born to mothers with diabetes in pregnancy
2024-05-17
It has long been understood that pregnant women with diabetes are more likely to have children with obesity than women who do not have diabetes during pregnancy. But scientists have not fully understood the cause or why babies born to mothers with diabetes are also more likely to develop obesity and associated metabolic disorders later in life.
To help find answers, Keck School of Medicine of USC researcher Shan Luo, PhD, has been awarded $3.1 million in funding from the National Institutes of Health and the National Institute of Diabetes ...
Men at greater risk of major health effects of diabetes than women
2024-05-17
Men are at greater risk than women of the major health effects of diabetes (types 1 and 2), suggests a long term study published online in the Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health.
Rates of cardiovascular disease, leg, foot, and kidney complications, and the sight-threatening eye disease diabetic retinopathy are all higher in men, regardless of whether they had diabetes for more or less than 10 years, the findings show.
The global prevalence of diabetes is similar in men and women, and is projected to rise to 783 million by 2045, note the researchers.
But ...
Likelihood of kids and young people smoking and vaping linked to social media use
2024-05-17
The more time spent on social media, the greater the likelihood that children and young people will both smoke and/or vape, suggests research published online in the respiratory journal Thorax.
Clocking up a weekday tally of 7 or more hours was associated with a more than a doubling in risk among 10 to 25 year olds, the findings indicate, reinforcing concerns about the marketing clout of these platforms, say the researchers.
The existing body of research on social media use and smoking and ...
Global life expectancy to increase by nearly 5 years by 2050 despite geopolitical, metabolic, and environmental threats, reports new global study
2024-05-17
**Embargo: 23.30 [UK time], 6:30 p.m. [EDT] May 16, 2024**
Global Burden of Disease
The latest findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study (GBD) 2021, published today in The Lancet, forecast that global life expectancy will increase by 4.9 years in males and 4.2 years in females between 2022 and 2050.
Increases are expected to be largest in countries where life expectancy is lower, contributing to a convergence of increased life expectancy across geographies. The trend is largely driven by public health measures that ...
High primary health coverage significantly reduces child mortality in Latin America
2024-05-17
The implementation of primary health care (PHC) over the last two decades has prevented more than 300,000 child deaths in four Latin American countries, and could prevent more than 140,000 by 2030 in a scenario of economic crisis. This is the main conclusion of a study coordinated by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by “la Caixa” Foundation, published in The Lancet Global Health.
The 2018 Astana Declaration highlighted the critical role of PHC in ensuring that everyone enjoys the highest possible standard of health, and in achieving universal health coverage. The Declaration also stressed the ...
Ubiquitin trailblazer elected Fellow of prestigious Royal Society
2024-05-17
WEHI division head and pioneer of ubiquitination Professor David Komander has been elected a Fellow of the esteemed Royal Society, the UK’s national science academy.
Prof Komander was recognised for his significant research contributions towards understanding ubiquitin, the ‘kiss of death’ protein which tells our cells which proteins to break down or recycle – a vital process that helps cells stay healthy and function correctly. Prof Komander’s work has helped unravel the ‘ubiquitin code’ that enables ubiquitin to perform many ...
A new ‘rule of biology’ may have come to light, expanding insight into evolution and aging
2024-05-17
By Darrin S. Joy
A molecular biologist at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences may have found a new “rule of biology.”
A rule of biology, sometimes called a biological law, describes a recognized pattern or truism among living organisms. Allen’s rule, for example, states that among warm-blooded animals, those found in colder areas have shorter, thicker limbs (to conserve body heat) than those in hotter regions, which need more body surface area to dissipate heat.
Zoologist Joel Allen formulated this idea in 1877, and though he wasn’t the first or the last to present a rule of biology, his ...
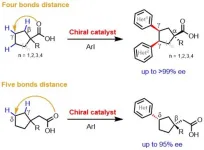
Scripps Research chemists develop new method for making gamma chiral centers on simple carboxylic acids
2024-05-17
LA JOLLA, CA—Scripps Research chemists have accomplished a long elusive feat in synthetic chemistry: the invention of a broadly useful method for constructing “gamma chiral centers” on simple starting compounds called carboxylic acids. The method, published on May 16, 2024 in Science, significantly extends the ability of chemists to build and modify complex pharmaceutical molecules and other valuable chemical products.
The term chiral refers to a type of asymmetry that allows some chemical compounds to exist in left-handed and right-handed forms. Often, only one of these forms has the ...
2024 SIAM Annual Meeting (AN24) with online component including SIAM Conference on Discrete Mathematics (DM24) and the SIAM Conference on Applied Mathematics in Education (ED24)
2024-05-16
The SIAM Annual Meeting provides a broad view of the state of the art in applied mathematics, computational and data science, and their applications through invited presentations, prize lectures, minitutorials, minisymposia, contributed presentations, and posters. END ...
[1] ... [1168]
[1169]
[1170]
[1171]
[1172]
[1173]
[1174]
[1175]
1176
[1177]
[1178]
[1179]
[1180]
[1181]
[1182]
[1183]
[1184]
... [8822]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.