TTUHSC’s Ahmed investigating cardiac cell regeneration
2024-05-16
When a patient is experiencing heart failure, a leading cause of death worldwide, they begin to lose healthy and functioning cardiac cells. Heart failure causes these once-flexible cells to develop into fibrotic cells that are no longer able to contract and relax. This stiffening of the cardiac cells compromises their ability to carry blood efficiently to the rest of the organs in the human system. Because humans cannot regenerate these cardiac cells, the patient faces a long road to recovery marked by preventative or symptomatic treatments.
However, some ...
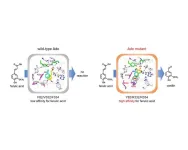
Bioengineered enzyme creates natural vanillin from plants in one step
2024-05-16
Vanilla extract is one of the most widely used flavoring compounds in food products and cosmetics. The pleasant and sweet smell of this classic flavor is imparted by the chemical compound ‘vanillin’ found in the seed pods of vanilla plants belonging to the orchid family. In plants, vanillin is synthesized by the conversion of ferulic acid by the enzyme - VpVAN. However, laboratory biosynthesis of vanillin from plant-derived VpVAN yields only very small quantities of vanillin, and is, therefore, commercially impractical. Further, although chemically derived ...
How does the brain turn waves of light into experiences of color?
2024-05-16
NEW YORK, NY — Perceiving something – anything – in your surroundings is to become aware of what your senses are detecting. Today, Columbia University neuroscientists identify, for the first time, brain-cell circuitry in fruit flies that converts raw sensory signals into color perceptions that can guide behavior.
Their findings were pulbished in the journal Nature Neuroscience.
“Many of us take for granted the rich colors we see every day – the red of a ripe strawberry ...
Wind farms can offset their emissions within two years, new study shows
2024-05-16
After spinning for under two years, a wind farm can offset the carbon emissions generated across its entire 30-year lifespan, when compared to thermal power plants.
That’s according to a new peer-reviewed study published in the Journal of the Royal Society of New Zealand – which also shows within six months a turbine can generate all the energy consumed across its life-cycle.
The research uses data from the Harapaki onshore wind farm in Hawke’s Bay, New Zealand – however the authors of the paper explain that their findings would be replicated across most, if not all, wind farms internationally.
“The wind turbine technology employed in New Zealand ...
One in three people die due to atherosclerosis: A new initiative aims to find new ways to prevent it
2024-05-16
One in three people around the world die from cardiovascular disease, which is mainly caused by atherosclerosis. This makes atherosclerosis the leading cause of death globally. Additionally, many people live with serious manifestations of atherosclerosis, for example, following a heart attack or a stroke.
Atherosclerosis not only represents a significant burden for these individuals, but also a heavy burden on healthcare systems and societies in all parts of the world.
“Atherosclerosis may develop from an early age and often remains 'silent’, that is, without symptoms, ...
More efficient bioethanol production might be possible using persimmon tannin to help yeast thrive
2024-05-16
While ethanol in alcoholic beverages impairs drinkers’ motor functions, it is that same substance that can power motor vehicles in a cleaner, more sustainable manner. What is necessary for the production of ethanol is yeast, but ethanol is among the environmental factors that add stress to yeasts, hindering their growth. To promote efficient bioethanol production, scientists have been searching for substances that can help yeasts better withstand ethanol, but few effective ones have been found.
An Osaka Metropolitan ...
What is the carbon footprint of a house in Japan?
2024-05-16
Fukuoka, Japan—Researchers at Kyushu University have published a comprehensive analysis on the carbon footprint of constructing a wooden house in Japan. The study covered the total amount of emissions produced, taking into consideration the entire supply chain including the processing and transport of the raw materials that go into building a house.
The team hopes that by identifying emission hot spots in the supply chain that go into building a house, policy makers can implement strategies to reduce its climate impact. Their analysis was published in the Journal of Environmental ...
University of Oregon researchers uncover how jelly sea creatures might shape modern robotics
2024-05-16
Scientists at the University of Oregon have discovered that colonies of gelatinous sea animals swim through the ocean in giant corkscrew shapes using coordinated jet propulsion, an unusual kind of locomotion that could inspire new designs for efficient underwater vehicles.
The research involves salps, small creatures that look similar to jellyfish that take a nightly journey from the depths of the ocean to the surface. Observing that migration with special cameras helped UO researchers and their colleagues capture the macroplankton’s graceful, coordinated swimming behavior.
“The largest migration on the planet ...
Link between COVID-19 vaccine complication and rare ‘common cold’ blood disease
2024-05-16
New research led by Flinders University and international experts is expanding understanding of vaccine-induced immune thrombocytopenia and thrombosis (known as VITT).
At the height of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2021,VITT emerged as a new disease following adenovirus vector-based vaccines – notably the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine.
VITT was found to be caused by an unusually dangerous blood autoantibody directed against a protein termed platelet factor 4 (or PF4).
In separate research in 2023, ...
Ochsner Baton Rouge opens new outpatient infusion pharmacy
2024-05-16
BATON ROUGE – Ochsner Baton Rouge has opened the new Ochsner Outpatient and Home Infusion Pharmacy – Baton Rouge at 4730 Bluebonnet Blvd., Suite 401. This advanced facility provides treatment for chronic, specialty and acute home infusions.
The pharmacy is conveniently located and designed with patient comfort and accessibility in mind. Each of its six patient rooms offers a spa-like environment, providing patient care in a peaceful, supportive setting that promotes healing. Ochsner’s pharmacists work closely with patients’ healthcare providers to create customized treatment plans, ensuring personalized and effective ...
When saying “please” is more strategic than magic
2024-05-16
Key takeaways
A new study by UCLA sociologists found that using the word “please” does not always indicate respect or politeness.
In the study, “please” was used only 7% of the time, mostly when there was an inhospitable interactional environment to overcome.
Findings will help researchers in their understanding of politeness in the flow of social behavior and norms.
By kindergarten age, most children have been taught that “please” is a magic word. “Please” is an expression of politeness that shows courtesy and respect, turning a potential demand into a request that will – ...
Nature Conferences, Davos Alzheimer’s Collaborative, Aga Khan University launch Africa’s first-ever dementia conference to advance lifespan brain health innovations across diverse communities
2024-05-16
The Davos Alzheimer’s Collaborative (DAC), the organization leading an unprecedented global response to Alzheimer’s, today announced the first-ever brain health and dementia conference in Africa, held in Nairobi, Kenya from September 11-12 in partnership with Nature Conferences and the Aga Khan University’s Brain & Mind Institute. The conference, “The Future of Dementia in Africa: Advancing Global Partnerships,” focuses on scientific advancements in understanding the impact of dementia, risk ...
Climate change likely to aggravate brain conditions
2024-05-16
Climate change, and its effects on weather patterns and adverse weather events, is likely to negatively affect the health of people with brain conditions, argue a UCL-led team of researchers.
In a Personal View article, published in The Lancet Neurology, the team emphasise the urgent need to understand the impact of climate change on people with neurological conditions – in order to preserve their health and prevent worsening inequalities.
Following a review of 332 papers published across the world between 1968 and 2023, the team, led by Professor Sanjay Sisodiya (UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology), said they expect the scale of the potential ...
Updated medical guidance on “excited delirium” brought forward
2024-05-16
Updated medical guidance on excited delirium, the controversial term accused of covering up deaths in police custody, including that of George Floyd, is being brought forward before its scheduled date of October 2025, reports The BMJ today.
The move comes as attitudes towards the use of the term appear to be changing, explains journalist Chris Stokel-Walker. For instance, last month Colorado joined California in banning police, medical staff and coroners from using the term, and the UK Independent ...
New study shows continued high effectiveness of HPV vaccination in England
2024-05-16
The human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination programme in England has not only been associated with a substantial reduction in cervical disease, but has done so in all socioeconomic groups, finds a study published by The BMJ today.
Although women living in the most deprived areas are still at higher risk of cervical disease than those in less deprived areas, the results show that well planned and executed public health interventions can both improve health and reduce health inequalities.
HPV ...
HPV vaccine prevents most cervical cancer cases in more deprived groups, major study shows
2024-05-16
Strict embargo: 23.30 hrs BST
Wednesday, 15 May, 2024
Peer-reviewed
Observational
People
The human papillomavirus, or HPV, vaccine is cutting cases of cervical cancer right across the socio-economic spectrum, with most cases being prevented in more deprived groups, according to a major study funded by Cancer Research UK.
Until now, there had been concerns that the HPV vaccine could have an unequal impact across society. After carrying out the longest follow-up on the effectiveness of the HPV vaccine, researchers at Queen Mary University of London concluded the HPV vaccination programme in England is helping to close some inequalities ...
Radiation-based immunogenic vaccine combined with a macrophage “checkpoint inhibitor” for boosting innate and adaptive immunity against metastatic colon cancers
2024-05-15
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2024.02.015
This new article publication from Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, discusses how the use of a radiation-based immunogenic vaccine combined with a macrophage “checkpoint inhibitor” can boost innate and adaptive immunity against metastatic colon cancers.
Immunogenic dying tumor cells hold promising prospects as cancer vaccines to activate systemic immunity against both primary and metastatic tumors. Especially, X-ray- induced dying tumor cells are rich in highly immunogenic tumor-associated antigens ...
Branched glycopolymer prodrug-derived nanoassembly combined with a STING agonist activates an immuno-supportive status to boost anti-PD-L1 antibody therapy
2024-05-15
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2024.02.006
This new article publication from Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, discusses how branched glycopolymer prodrug-derived nanoassembly combined with a STING agonist activates an immuno-supportive status to boost anti-PD-L1 antibody therapy.
Despite the great potential of anti-PD-L1 antibodies for immunotherapy, their low response rate due to an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment has hampered their application.
To address this issue, the authors of this article constructed a cell membrane-coated nanosystem (mB4S) to reverse an immunosuppressive microenvironment to an immuno-supportive ...
5S-Heudelotinone alleviates experimental colitis by shaping the immune system and enhancing the intestinal barrier in a gut microbiota-dependent manner
2024-05-15
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2024.02.020
This new article publication from Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, discusses how 5S-Heudelotinone alleviates experimental colitis by shaping the immune system and enhancing the intestinal barrier in a gut microbiota-dependent manner.
Aberrant changes in the gut microbiota are implicated in many diseases, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Gut microbes produce diverse metabolites that can shape the immune system and impact the intestinal barrier integrity, indicating that microbe-mediated modulation may be a promising strategy for preventing and treating IBD.
Although ...
ALS-linked C9orf72 dipeptide repeats inhibit starvation-induced autophagy through modulating BCL2–BECN1 interaction
2024-05-15
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2024.02.004
This new article publication from Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, discusses how ALS-linked C9orf72 dipeptide repeats inhibit starvation-induced autophagy through modulating BCL2–BECN1 interaction.
Growing evidence indicate that dysfunction of autophagy contributes to the disease pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD), two neurodegenerative disorders. The GGGGCC·GGCCCC repeat RNA expansion in chromosome 9 open reading frame 72 (C9orf72) ...
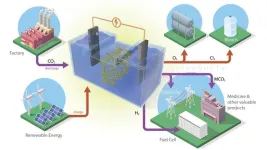
Carbon-capture batteries developed to store renewable energy, help climate
2024-05-15
Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory are developing battery technologies to fight climate change in two ways, by expanding the use of renewable energy and capturing airborne carbon dioxide.
This type of battery stores the renewable energy generated by solar panels or wind turbines. Utilizing this energy when wind and sunlight are unavailable requires an electrochemical reaction that, in ORNL’s new battery formulation, captures carbon dioxide from industrial emissions and converts it to value-added products.
ORNL researchers recently created and tested two different formulations for batteries that ...
From roots to resilience: investigating the vital role of microbes in coastal plant health
2024-05-15
Georgia’s saltwater marshes — living where the land meets the ocean — stretch along the state’s entire 100-mile coastline. These rich ecosystems are largely dominated by just one plant: grass.
Known as cordgrass, the plant is an ecosystem engineer, providing habitats for wildlife, naturally cleaning water as it moves from inland to the sea, and holding the shoreline together so it doesn’t collapse. Cordgrass even protects human communities from tidal surges.
Understanding how these ...
Q&A: How did the COVID-19 pandemic affect older adults’ technology use?
2024-05-15
The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic changed how nearly everyone mediated their social interactions through technology. Some moved happy hours into video chats. Others delved deeper into social media, or took a step back from it. Millions of people worked or learned through computers.
University of Washington researchers took particular interest in how this tech shift affected older adults’ social relationships. The team interviewed 16 older adults in Washington and Oregon, ages 65 to 80, about how their technology ...
Blood pressure drugs more than double bone-fracture risk in nursing home patients
2024-05-15
Records from nearly 30,000 nursing home residents indicate that blood pressure medications more than double the risk of life-threatening bone fractures, according to Rutgers Health research.
The authors of the study, which appears in JAMA Internal Medicine, said the increased risk stems from the medications’ tendency to impair balance, particularly when patients first stand up and temporarily experience low blood pressure that deprives the brain of oxygen. Interactions with other drugs and low baseline balance in many nursing home patients compound the problem.
“Bone fractures often start nursing home patients on a downward spiral,” ...
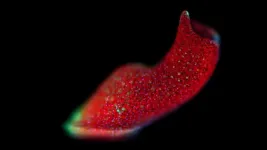
Regenerating worms have genetic control over their algal partners
2024-05-15
Many organisms are far more complex than just a single species. Humans, for example, are full of a variety of microbes. Some creatures have even more special connections, though. Acoels, unique marine worms that regenerate their bodies after injury, can form symbiotic relationships with photosynthetic algae that live inside them. These collections of symbiotic organisms are called a holobiont, and the ways that they “talk” to each other are something scientists are trying to understand – especially ...
[1] ... [1171]
[1172]
[1173]
[1174]
[1175]
[1176]
[1177]
[1178]
1179
[1180]
[1181]
[1182]
[1183]
[1184]
[1185]
[1186]
[1187]
... [8822]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.