Study supports lower BMI threshold for obesity in the over 40s
2024-05-15
Changes in body composition with ageing—increases in body fat and declines in muscle—mean that BMI is not accurate in predicting obesity in middle-aged and older adults.
BMI identified half as many over 40s with obesity as predicted by body fat percentage.
A new lower BMI cut-off for obesity based on body fat percentage (27kg/m²) in the over 40s may be more appropriate than the existing WHO BMI threshold (30 kg/m²).
The authors say establishing this new lower BMI cut-off point for the over 40s in clinical settings and obesity guidelines potentially ...
Text messages with financial incentives can help men who are living with obesity lose weight, UK study finds (JAMA)
2024-05-15
Men in England, Scotland and Northern Ireland offered up to £400 for hitting weight loss targets lost more weight than those not given cash incentive
Win-win strategy could pay for itself, say researchers
*Note: this paper is being presented at the European Congress on Obesity (ECO) and is being published in JAMA. Please credit both the congress and the journal in your stories.*
A new study presented at the European Congress on Obesity (ECO) in Venice, Italy (12-15 May), and published simultaneously in JAMA, has concluded that text messages with financial incentives can help men who are living with obesity lose weight and could be a valuable alternative ...
Scientists develop an affordable sensor for lead contamination
2024-05-14
Engineers at MIT, Nanytang Technological University, and several companies have developed a compact and inexpensive technology for detecting and measuring lead concentrations in water, potentially enabling a significant advance in tackling this persistent global health issue.
The World Health Organization estimates that 240 million people worldwide are exposed to drinking water that contains unsafe amounts of toxic lead, which can affect brain development in children, cause birth defects, and produce a variety of neurological, cardiac, ...
UC Irvine-led study links sleep apnea severity during REM stage to verbal memory decline
2024-05-14
Irvine, Calif., May 14, 2024 — A research team led by the University of California, Irvine has revealed the link between the frequency of sleep apnea events during the rapid-eye-movement stage and the severity of verbal memory impairment in older adults at risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Verbal memory refers to the cognitive ability to retain and recall information presented through spoken words or written text and is particularly vulnerable to Alzheimer’s.
The study, recently published online in the journal Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy, discovered a specific correlation between the severity of sleep apnea – when breathing pauses while ...
What’s actually in your supplements? Chapman University researchers detect hidden ingredients and questionable claims in supplements
2024-05-14
A recent study published in Analytical Science Journal conducted by Schmid College of Science and Technology Professor Rosalee Hellberg and students Calin Harris, Diane Kim, Miranda Miranda and Chevon Jordan, reveal that some supplement companies may mislead customers with unproven health claims and undeclared ingredients.
The researchers focused on supplements that have been associated with the purported treatment or prevention of COVID-19 and other respiratory illnesses. During the pandemic, the use of dietary supplements skyrocketed throughout the world. “There was a big spike in purchase and use of these types ...
STRIVE project to study ozone, atmospheric layers among finalists for next-generation NASA satellite
2024-05-14
A project led by the University of Washington to better understand our atmosphere’s complexity is a finalist for NASA’s next generation of Earth-observing satellites. The space agency this week announced the projects that will each receive $5 million to advance to the next stage and conduct a one-year concept study.
STRIVE seeks to better understand the troposphere that we inhabit and the stratosphere above it, where the ozone layer is, as well as the interface where these two layers meet. That interface, about 6 miles (10 kilometers) above the surface, is where important ...
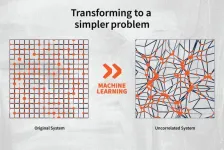
Simulating diffusion using 'kinosons' and machine learning
2024-05-14
Researchers from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have recast diffusion in multicomponent alloys as a sum of individual contributions, called “kinosons.” Using machine learning to compute the statistical distribution of the individual contributions, they were able to model the alloy and calculate its diffusivity orders of magnitude more efficiently than computing whole trajectories. This work was recently published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
“We found a much more efficient way to calculate diffusion in solids, and at the same time, we learned more ...
Far from toxic, lactate rivals glucose as body's major fuel after a carbohydrate meal
2024-05-14
As a student competing in track and field at his Parlier high school, Robert Leija was obsessed with how to improve his performance and, in particular, prevent the buildup of lactic acid in his muscles during training. Like many athletes, he blamed it for the performance fatigue and muscle soreness he experienced after intense workouts.
But as a kinesiology student at Fresno State, he was handed an out-of-print textbook that told him he had it all wrong. Lactate wasn't a danger sign that athletes had depleted their body's supply of oxygen, but likely a normal product of the metabolic activity required to fuel the muscles during sustained exercise.
Now, as a graduate student ...
AI for more caring institutions
2024-05-14
More and more public services — such as affordable housing, public school matching and child welfare — are relying on algorithms to make decisions and allocate resources. So far, much of the work that has gone into designing these systems has focused on workers’ experiences using them or communities’ perceptions of them.
But what about the actual impact of these programs have on people, especially when the decisions the systems make lead to denial of services? Can you design algorithms to help people make sense of and ...
Astronomers spot a giant planet that is as light as cotton candy
2024-05-14
Astronomers at MIT, the University of Liège in Belgium, and elsewhere have discovered a huge, fluffy oddball of a planet orbiting a distant star in our Milky Way galaxy. The discovery, reported today in the journal Nature Astronomy, is a promising key to the mystery of how such giant, super-light planets form.
The new planet, named WASP-193b, appears to dwarf Jupiter in size, yet it is a fraction of its density. The scientists found that the gas giant is 50 percent bigger than Jupiter, and about a tenth as dense — an extremely low density, comparable to that of cotton candy.
WASP-193b is the second lightest planet discovered to date, ...
Sleep experts to convene in Houston for SLEEP 2024 annual meeting
2024-05-14
DARIEN, IL – Leading sleep and circadian scientists, sleep clinicians, and industry innovators will gather June 2-5 in Houston at SLEEP 2024, the 38th annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies, LLC. Thousands of sleep professionals will connect, explore, and grow at the world’s premier clinical and scientific sleep meeting, held jointly by the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and the Sleep Research Society.
“Every year, SLEEP brings together the world’s ...
Rice’s Mamouras wins NSF CAREER Award
2024-05-14
HOUSTON – (May 14, 2024) – As the Internet of Things (IoT) grows larger and more complex, it becomes increasingly difficult to develop applications.
“A common approach to this problem is to move data from the sensing devices to a central location, such as the cloud, for processing,” said Konstantinos Mamouras, assistant professor of computer science at Rice University. “But this centralized approach underutilizes the small IoT devices at the edge of the network and can overwhelm it due to the large movement of data.”
With his five-year, $547,555 National Science Foundation CAREER Award, Mamouras aims to decentralize the IoT, relieve network congestion and ...
ISS National Lab announces up to $750,000 in funding for technology development in low Earth orbit
2024-05-14
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER (FL), May 14, 2024 – The International Space Station (ISS) National Laboratory is soliciting flight concepts for technology development that would utilize the space-based environment of the orbiting laboratory. This solicitation, “Technology Development and Applied Research Leveraging the ISS National Lab,” is open to a broad range of technology areas, including chemical and material synthesis in space, translational medicine, in-space edge computing, and ISAM (in-space servicing, assembly, and manufacturing). ...
Counterfeit coins can be detected more easily thanks to a novel approach developed at Concordia
2024-05-14
Metal coins may be just about the oldest medium of exchange still in use today, but ensuring their worth requires some of the most state-of-the-art technology available. Counterfeit coins remain a threat to global currencies, with malicious actors flooding markets with fakes. European police broke up a Spain-based criminal ring in late April, demonstrating the issue’s ongoing urgency.
However, no counterfeit is completely detection-proof, no matter how genuine it appears. There are always some tell-tale signals of forgery, even if they are not ...
Professors elected to Academy of Distinguished Scholars
2024-05-14
The University of Texas at Arlington has elected two longtime professors to the Academy of Distinguished Scholars, considered the University’s most prestigious research and scholarship honor.
Ramon Lopez, professor of physics, and Michael D. Nelson, associate professor of kinesiology, are being recognized for their sustained and significant contributions to research and creativity.
“Members of the Academy of Distinguished Scholars exemplify UTA’s commitment to quality research and creative activity,” said Kate C. Miller, vice president of research and innovation. “Mike and Ramon have both ...
UTA biology students receive awards for excellence
2024-05-14
Thirteen undergraduate and graduate students at The University of Texas at Arlington are being honored for excellence in academics, research, mentoring and/or teaching with awards. The awards are a mix of direct applications from students and others where they were nominated by faculty advisors. A committee of biology faculty then voted on the competitive awards.c
“It’s so rewarding to be able to honor the next generation of biologists,” said Melissa Walsh, who chaired the selection committee ...
Making every hair appointment a sound experience #ASA186
2024-05-14
OTTAWA, Ontario, May 14, 2024 – Walking out of a hair salon can have customers feeling brand new, but the noisy environment may have negative effects at the cost of a new “do.” At Image Creators salon in Maryland, owner Silvia Campana along with her employees and customers noticed they had to work hard to understand each other’s words while in the salon, but they couldn’t put their finger on exactly why. In addition to difficulties understanding speech, Campana experienced increased ear pain and tinnitus after long-term exposure to ...
Tennessee teen uses national platform to advocate for CPR and heart health
2024-05-14
DALLAS, May 13, 2024 — The American Heart Association’s National Teen of Impact title offers Gen Z changemakers an influential platform to fight against heart disease to improve health and well-being in communities across the country. This year, Aniston Barnette, a 16-year-old volunteer advocate from Bristol, Tenn., is the 2024 national winner. As a prominent student-athlete, Barnette is supporting the lifesaving mission of the American Heart Association – celebrating one hundred years of lifesaving service – by promoting cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) awareness and education.
After watching family members suffer and die from ...
Study explores role of epigenetics, environment in differing Alzheimer’s risk between Black and white communities
2024-05-14
A study from North Carolina State University has found that environmentally caused alterations to specific areas of the genome – known as imprint control regions – during early development may contribute to the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease, and that Black people may be more affected than white people. The work adds to our understanding of the ways in which environmental factors can contribute to genetic alterations and disease susceptibility.
“In terms of genetics and disease, ...
Aston University researcher’s project selected as part of government support package to rebuild Ukraine’s energy system
2024-05-14
Aston University researcher’s work highlighted by the British government
Dr Muhammed Imran and his collaborators to develop and commercialise cascade heat pumps
Part of programme designed by British and Ukraine governments over the last 12 months.
An Aston University researcher’s project has been selected as part of a package of support to help rebuild Ukraine’s energy system, phase out fossil fuels and support post-war recovery.
In November 2023 it was announced that senior lecturer in engineering and technology Dr Muhammed Imran and his collaborators were to receive almost £1 ...
Researchers uncover what makes some chickens more water efficient than others
2024-05-14
FAYETTEVILLE, Ark. — In the first scientific report of its kind, researchers in Arkansas showed that chickens bred for water conservation continued to put on weight despite heat stress that would normally slow growth.
Research by the Arkansas Agricultural Experiment Station indicates the specially bred line of chickens developed by Sara Orlowski could save growers thousands of gallons of water and thousands of pounds of food each month without sacrificing poultry health. Orlowski is an associate professor of poultry science with the University of Arkansas System Division of Agriculture.
As global population increases ...
Looking inside battery cells
2024-05-14
Lithium-Ion batteries presently are the ubiquitous source of electrical energy in mobile devices, and the key technology for e-mobility and energy storage. Massive interdisciplinary research efforts are underway both to develop practical alternatives that are more sustainable and environmentally friendly, and to develop batteries that are safer, more performing, and longer-lasting – particularly for applications demanding high capacity and very dense energy storage. Understanding degradations and failure mechanisms in detail opens opportunities to better predict and mitigate them.
In the study, a team of researchers led by the CEA, the ILL and the ESRF in collaboration examined Li-ion ...
Gene expression of a tropical starfish fluctuates between the seasons
2024-05-14
Gene expression of a tropical starfish fluctuates between the seasons
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002620
Article Title: Seasonal tissue-specific gene expression in wild crown-of-thorns starfish reveals reproductive and stress-related transcriptional systems
Author Countries: Australia
Funding: This research was supported by a Linkage Project grant (LP170101049) from the Australian Research Council to BMD, ...
150,000+ people died in three decades to 2019 due to heatwaves according to first global mapping of heat-triggered mortality
2024-05-14
A Monash-led study - the first to globally map heatwave-related mortality over a three-decade period from 1990 to 2019 – has found that an additional 153,000+ deaths per warm season were associated with heatwaves, with nearly half of those deaths in Asia.
In comparison to 1850–1990, the global surface temperature has increased by 1.14℃ in 2013–2022 and is expected to increase by another 0.41-3.41℃ by 2081–2100. With the increasing impacts of climate change, heatwaves are increasing not only in frequency but also in severity and magnitude.
The study, published today in PLOS Medicine and led by Monash University’s Professor Yuming Guo, ...
Study tallies heatwave deaths over recent decades
2024-05-14
Between 1990 and 2019, more than 150,000 deaths around the globe were associated with heatwaves each year, according to a new study published May 14th in PLOS Medicine by Yuming Guo of Monash University, Australia, and colleagues.
Heatwaves, periods of extremely high ambient temperature that last for a few days, can impose overwhelming thermal stress on the human body. Studies have previously quantified the effect of individual heatwaves on excess deaths in local areas, but have not compared these statistics around the globe over such ...
[1] ... [1177]
[1178]
[1179]
[1180]
[1181]
[1182]
[1183]
[1184]
1185
[1186]
[1187]
[1188]
[1189]
[1190]
[1191]
[1192]
[1193]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.