New gene delivery vehicle shows promise for human brain gene therapy
2024-05-16
In an important step toward more effective gene therapies for brain diseases, researchers from the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard have engineered a gene-delivery vehicle that uses a human protein to efficiently cross the blood-brain barrier and deliver a disease-relevant gene to the brain in mice expressing the human protein. Because the vehicle binds to a well-studied protein in the blood-brain barrier, the scientists say it has a good chance at working in patients.
Gene therapy could potentially treat a range of severe genetic brain disorders, which currently ...
Finding quantum order in chaos
2024-05-16
If you zoom in on a chemical reaction to the quantum level, you’ll notice that particles behave like waves that can ripple and collide. Scientists have long sought to understand quantum coherence, the ability of particles to maintain phase relationships and exist in multiple states simultaneously; this is akin to all parts of a wave being synchronized. It has been an open question whether quantum coherence can persist through a chemical reaction where bonds dynamically break and form.
Now, for the first time, a team of Harvard scientists has demonstrated the survival of quantum coherence in a chemical reaction involving ultracold molecules. These findings highlight the potential of ...
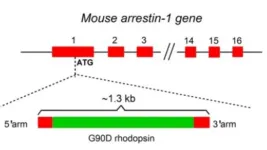
Study suggests high-frequency electrical ‘noise’ results in congenital night blindness
2024-05-16
In what they believe is a solution to a 30-year biological mystery, neuroscientists at Johns Hopkins Medicine say they have used genetically engineered mice to address how one mutation in the gene for the light-sensing protein rhodopsin results in congenital stationary night blindness.
The condition, present from birth, causes poor vision in low-light settings.
The findings, published May 14 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, demonstrate that the rhodopsin gene mutation, called ...
TeltoHeart wristband, developed by Lithuanians, receives important medical device certification
2024-05-16
Teltonika’s TeltoHeart, a multifunctional smart wristband system developed in cooperation between Lithuanian industry and universities has been given the CE MDR (Class IIa) medical device certification. This approval confirms that the product meets the comprehensive quality standards for medical devices and opens up new markets worldwide for this innovative product.
"This is an important recognition that we have been working towards since the start of this project in 2020. The CE MDR certification proves that TeltoHeart is a safe ...
Unique brain circuit is linked to Body Mass Index
2024-05-16
· One region is related to olfaction and reward, the other to negative feelings like pain · When the connection between these brain regions is weak, people have higher BMI
· Food may continue to be rewarding, even when these individuals are full
CHICAGO --- Why can some people easily stop eating when they are full and others can’t, which can lead to obesity?
A Northwestern Medicine study has found one reason may be a newly discovered structural connection ...
Noise survey highlights need for new direction at Canadian airports #ASA186
2024-05-16
OTTAWA, Ontario, May 16, 2024 – The COVID-19 pandemic changed life in many ways, including stopping nearly all commercial flights. At the Toronto Pearson International Airport, airplane traffic dropped by 80% in the first few months of lockdown. For a nearby group of researchers, this presented a unique opportunity.
Julia Jovanovic will present the results of a survey conducted on aircraft noise and annoyance during the pandemic era Thursday, May 16, at 11:10 a.m. EDT as part of a joint meeting of the Acoustical Society of America and ...
COSPAR partners with LASP for 1st COSPAR Center of Excellence
2024-05-16
Partnering with LASP was an obvious decision for COSPAR. LASP stands out with its distinguished track record in space science research, having deployed scientific instruments to every planet in our solar system, the Sun and numerous moons. In particular, LASP has been at the forefront of pioneering Cube-Sat missions, consistently achieving remarkable success in gathering scientific data. With seven completed CubeSat missions and nine more in active development or orbit, LASP has demonstrated unparalleled expertise in this field. ...
Building a better sarcasm detector #ASA186
2024-05-16
OTTAWA, Ontario, May 16, 2024 – Oscar Wilde once said that sarcasm was the lowest form of wit, but the highest form of intelligence. Perhaps that is due to how difficult it is to use and understand. Sarcasm is notoriously tricky to convey through text — even in person, it can be easily misinterpreted. The subtle changes in tone that convey sarcasm often confuse computer algorithms as well, limiting virtual assistants and content analysis tools.
Xiyuan Gao, Shekhar Nayak, and Matt Coler of Speech Technology Lab at the University of Groningen, Campus Fryslân developed a multimodal algorithm ...
Natural toxins in food: Many people are not aware of the health risks
2024-05-16
Many people are concerned about residues of chemicals, contaminants or microplastics in their food. However, it is less well known that many foods also contain toxins of completely natural origin. These are often chemical compounds that plants use to ward off predators such as insects or microorganisms. These substances are found in beans and potatoes, for example, and can pose potential health risks. However, according to a recent representative survey by the German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR), only just under half of the respondents (47 per cent) were even aware of plant toxic substances. The BfR Consumer Monitor Special on naturally occurring plant toxins ...
Archaeology: Egyptian pyramids built along long-lost Ahramat branch of the Nile
2024-05-16
31 pyramids in Egypt, including the Giza pyramid complex, may originally have been built along a 64-km-long branch of the river Nile which has long since been buried beneath farmland and desert. The findings, reported in a paper in Communications Earth & Environment, could explain why these pyramids are concentrated in what is now a narrow, inhospitable desert strip.
The Egyptian pyramid fields between Giza and Lisht, built over a nearly 1,000-year period starting approximately 4,700 years ago, now sit on the edge of the inhospitable Western Desert, part of the Sahara. ...
Effectiveness of a web-based cognitive behavioral self-help intervention for binge eating disorder
2024-05-16
About The Study: In this randomized clinical trial of a web-based self-help intervention for patients with binge eating disorder, the findings confirmed its effectiveness in reducing binge eating episodes and improving various mental health outcomes, highlighting a scalable solution to bridge the treatment gap for this condition.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Luise Pruessner, M.S., email luise.pruessner@psychologie.uni-heidelberg.de.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
Physician and AI chatbot responses to cancer questions from social media
2024-05-16
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that chatbots can generate quality, empathetic, and readable responses to patient questions comparable to physician responses sourced from an online forum. Further research is required to assess the scope, process integration, and patient and physician outcomes of chatbot-facilitated interactions.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Srinivas Raman, M.D., M.A.Sc., email srinivas.raman@rmp.uhn.ca.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
How did sabre-toothed tigers acquire their long upper canine teeth?
2024-05-16
In a groundbreaking study, an international team led by scientists from the University of Liège has investigated the evolutionary patterns behind the development of sabre teeth, with some unexpected results along the way. A study that enriches our understanding of the Earth's past, but also documents the mechanisms leading to evolutionary convergence.
Sabre teeth, those iconic elongated upper canine teeth, have long fascinated both scientists and the general public, notably because they have appeared several times in the fossil record, including two particularly well-known lineages of sabre-toothed tigers: the felids (the family of ...
End-of-life systemic treatment for patients with advanced cancers does not improve survival
2024-05-16
Patients with very advanced solid tumors saw no significant improvement in overall survival after receiving systemic therapy, according to a study published today in JAMA Oncology by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and Yale Cancer Center.
The findings provide further evidence to help oncologists counsel patients that additional cancer-directed therapy is not likely to benefit them, allowing them to focus instead on palliative and supportive care options that have been demonstrated ...
To optimize guide-dog robots, first listen to the visually impaired
2024-05-16
May 16, 2024
To Optimize Guide-Dog Robots, First Listen to the Visually Impaired
Award-winning research led by UMass Amherst shows to be successful, Guide-dog users and trainers need to provide insight into features that make robotic helpers useful in the real world
AMHERST, Mass. — What features does a robotic guide dog need? Ask the blind, say the authors of an award-winning paper. Led by researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, a study identifying how to develop robot guide dogs with insights from guide dog users and trainers won a Best Paper Award at ...
Imaging fibrous structure abnormalities of the white of the eye in myopathic patients
2024-05-16
Researchers provide an innovative approach to understanding ocular pathologies by visualizing the fiber structure of the sclera, the outermost eye layer
Tokyo, Japan – Eye diseases are extremely prevalent worldwide, with recent estimates suggesting that one-third of the global population suffers from some type of vision impairment. Given the high complexity of the human eye, the precise origin and nature of many eye diseases remain unclear, leaving affected people with limited diagnostic and treatment options.
Now, in a study made available online on March 7, 2024 and published in Volume 142, Number 4 of JAMA Ophthalmology on ...
Loneliness and mental health problems are interconnected
2024-05-16
“We have found a correlation between loneliness and several mental health problems,” says Associate Professor Rubén Rodríguez-Cano at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU’s) Department of Psychology.
In a new study, researchers are looking at whether lonely people are more prone to problems such as depression and psychosis. Based on medication use, the correlation is clear.
“The risk of a lonely person also struggling with mental health problems is greater than for people who ...
Dr. Daniel Geynisman named new Editor-in-Chief for JNCCN—Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network
2024-05-16
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [May 16, 2024] — Daniel M. Geynisman, MD, is being announced as the new Editor-in-Chief for JNCCN—Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Dr. Geynisman has a long history of working with NCCN in a variety of roles and served as medical oncology section editor for Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations since 2018 and authored more than 130 peer-reviewed publications. He is an Associate Professor in the Department of Hematology/Medical Oncology and Chief of the Division of Genitourinary Medical Oncology at Fox Chase Cancer Center.
“We are thrilled to welcome Dr. Geynisman into this ...
A new and better way to detect media censorship
2024-05-16
Worldwide news media are facing increasing pressure from autocrats to report favourably about their leaders and party politics. Political scientists launch a new computational method that can detect such media censorship by states while it is happening. This method provides valuable insights for communicating regime-driven media capture to the public. It is now described in detail in the scientific journal ‘Democratization’.
One of the first steps of would-be autocrats is to control the ...
Listening to muscles
2024-05-16
Spinal muscular atrophy or “SMA” for short is a terrible disease in which a genetic mutation causes certain nerves responsible for sending signals to muscles to degenerate. This leads to muscles wasting away, and many patients have died a painful death due to this rare condition. Genetic treatments have only been available for a few years. Now, a team led by Emmanuel Nedoschill, Ferdinand Knieling and Adrian Regensburger from the “Translational Pediatrics” working group at the Department of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine at Uniklinikum Erlangen have devised ...
Spider silk sound system #ASA186
2024-05-16
OTTAWA, Ontario, May 16, 2024 – The best microphone in the world might have an unexpected source: spider silk. Spiders weave webs to trap their insect snacks, but the sticky strands also help spiders hear. Unlike human eardrums and conventional microphones that detect sound pressure waves, spider silk responds to changes in the velocities of air particles as they are thrust about by a sound field. This sound velocity detection method remains largely underexplored compared to pressure sensing, but it holds great potential for high-sensitivity, long-distance sound detection.
Researchers ...
Equitable opportunity for transplants: Experts provide disparity-sensitive measures for transplant centers
2024-05-16
INDIANAPOLIS – An Expert Insight, published in the journal Transplantation, highlights health equity, disparity and inequality in organ transplantation along the continuum of care and across organ types. The authors provide a guide to transplant centers for the use of disparity-sensitive measures to monitor and address health disparities in transplantation and to redress long-standing inequities and inequalities in this vital arena.
“Our goal is to ensure that all patients who need a transplant have ...
Gene therapy relieves back pain, repairs damaged disc in mice
2024-05-16
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Disc-related back pain may one day meet its therapeutic match: gene therapy delivered by naturally derived nanocarriers that, a new study shows, repairs damaged discs in the spine and lowers pain symptoms in mice.
Scientists engineered nanocarriers using mouse connective-tissue cells called fibroblasts as a model of skin cells and loaded them with genetic material for a protein key to tissue development. The team injected a solution containing the carriers into damaged discs in mice at the same time the back injury ...
To sound like a hockey player, speak like a Canadian #ASA186
2024-05-16
OTTAWA, Ontario, May 16, 2024 – As a hockey player, Andrew Bray was familiar with the slang thrown around the “barn” (hockey arena). As a linguist, he wanted to understand how sport-specific jargon evolved and permeated across teams, regions, and countries. In pursuit of the sociolinguistic “biscuit” (puck), he faced an unexpected question.
“It was while conducting this initial study that I was asked a question that has since shaped the direction of my subsequent research,” said Bray. “‘Are you trying to figure out why the Americans sound like fake Canadians?’”
Canadian ...
Why do we overindulge?
2024-05-16
If you tend to do other things or get distracted while eating dinner, you may be running the risk of over-consuming everyday pleasures later, possibly because the distraction caused you to enjoy yourself less, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
The study looked at how distraction affects “hedonic consumption,” or buying and using products and experiences because they make us feel good and not necessarily because we need them.
“On any given day, a person may take great pleasure from one or more of these activities, yet people often consume more hedonic ...
[1] ... [1184]
[1185]
[1186]
[1187]
[1188]
[1189]
[1190]
[1191]
1192
[1193]
[1194]
[1195]
[1196]
[1197]
[1198]
[1199]
[1200]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.