Place-based measures of inequity and vision difficulty and blindness
2024-05-09
About The Study: Residential measures of inequity through segregation, income inequality, or persistent poverty were associated with a greater number of residents living with vision difficulty and blindness in this cross-sectional study. It is essential to understand and address how neighborhood characteristics can impact rates of vision difficulty and blindness.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Patrice M. Hicks, Ph.D., M.P.H., email pmhicks@med.umich.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2024.1207)
Editor’s ...
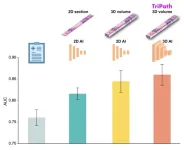
AI advancements make the leap into 3D pathology possible
2024-05-09
Researchers developed Tripath to bridge computational gaps to process 3D tissue and predict outcomes based on 3D morphological features
Cancer recurrence models trained on 3D tissue volumes outperformed models trained on 2D tissue images
Human tissue is intricate, complex and, of course, three dimensional. But the thin slices of tissue that pathologists most often use to diagnose disease are two dimensional, offering only a limited glimpse at the tissue’s true complexity. There is a growing push in the field of pathology toward examining tissue in its three-dimensional form. But 3D pathology datasets can contain hundreds of times more data than their 2D counterparts, ...
Net zero plans show limited climate ambition on ‘residual’ emissions
2024-05-09
New research by the University of East Anglia (UEA) reveals what countries think will be their most difficult to decarbonise sectors when they reach net zero, with agriculture expected to be responsible for the largest remaining emissions.
Once countries have taken the ‘easy’ steps to get to net zero - such as switching to more renewable electricity, electric cars, and heat pumps for homes - they are still left with some sources of emissions.
These ‘residual’ emissions continue to be emitted at the ...
New Rhizobia-diatom symbiosis solves long-standing marine mystery
2024-05-09
Nitrogen is an essential component of all living organisms. It is also the key element controlling the growth of crops on land, as well as the microscopic oceanic plants that produce half the oxygen on our planet. Atmospheric nitrogen gas is by far the largest pool of nitrogen, but plants cannot transform it into a usable form. Instead, crop plants like soybeans, peas and alfalfa (collectively known as legumes) have acquired Rhizobial bacterial partners that “fix” atmospheric nitrogen into ammonium. This partnership makes legumes one of the most important ...
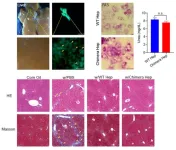
New stem cell research may have implications for liver transplantation
2024-05-09
Liver disease, due to viral infections, alcohol abuse, obesity, or cancer, accounts for 1 in every 25 deaths worldwide. A liver transplant can be life saving for people with end-stage liver disease. However, the procedure has limitations related to donor shortage, a technically challenging and invasive surgical procedure, and the requirement for lifelong immunosuppressive medication in the transplant recipients. An alternative to whole organ transplantation is the less invasive injection of dissociated human liver cells, but donor shortage is still an issue. Utilizing ...
New cells could be key to treating obesity
2024-05-09
Understanding how fat tissue forms and functions is crucial for addressing obesity and related metabolic diseases. However, adipose tissue, or body fat, behaves differently based on its location in the body.
Take, for example, the omentum: a large, apron-like fatty tissue hanging from the stomach that covers organs within the peritoneum, such as the stomach and intestines. It not only stores fat but also plays roles in immune regulation and tissue regeneration.
Omental adipose tissue is associated with ...
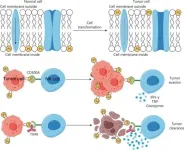
Supercharging immune cells to battle blood cancer: Breakthrough in cancer immunotherapy
2024-05-09
A new study reveals a groundbreaking approach to immunotherapy, demonstrating that blocking the interaction between the CD300A receptor and phosphatidylserine (PS) significantly enhances the ability of human natural killer (NK) cells to lyse hematologic malignancies (HMs).
Cancer has a profound impact on human life, and immune checkpoint therapy (ICT) has made remarkable strides in cancer treatment. However, ICT faces challenges such as low overall response rates and the emergence of immune-related adverse events. To overcome these hurdles, researchers are exploring new immune checkpoints. CD300A, a type-I transmembrane protein with immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory ...
Liberals and conservatives differ on climate change beliefs—but are relatively united in taking action
2024-05-09
The division between liberals and conservatives on both climate-change beliefs and related policy support is long-standing. However, the results of a newly released global experiment show that despite these differences, the two camps actually align when it comes to taking certain actions to combat climate change.
The study, led by researchers at New York University, finds that when given the opportunity, liberals and conservatives take action to address climate change at roughly the same levels—and that ...
Biogeographical evidence shows trickster animal folklore limited by environmental factors
2024-05-09
Humans have the capacity to imagine civilizations and creatures that have never existed, and our language reflects that ability. It would therefore be understandable if the stories we tell ourselves stretched beyond the bounds of local ecology. However, research has shown that many cultural artifacts and ideas are strongly affected by environmental factors.
Researchers in Japan wanted to know if the biogeography of a region could constrain motifs in animal folklore. To do this, they studied the distribution of animal trickster folklore against the distribution of the animal the folklore ...
Researchers harness blurred light to 3D print high quality optical components
2024-05-09
WASHINGTON — Canadian researchers have developed a new 3D printing method called blurred tomography that can rapidly produce microlenses with commercial-level optical quality. The new method may make it easier and faster to design and fabricate a variety of optical devices.
“We purposely added optical blurring to the beams of light used for this 3D printing method to manufacture precision optical components,” said Daniel Webber from the National Research Council of Canada. “This enables production of optically smooth surfaces.”
In Optica, Optica Publishing Group’s journal for high-impact research, these researchers demonstrate the new method by using ...
Older adults with aggressive blood cancer are responsive to treatment and show prolonged survival
2024-05-09
(WASHINGTON, May 9, 2024) – Standard of care treatment for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is safe and effective for adults over 80, according to a study published in Blood Neoplasia. For roughly a quarter of patients, this treatment can durably prolong survival.
AML is an aggressive and often deadly form of blood cancer that can be difficult to treat. For older adults with AML, the conventional treatment consists of a medication called venetoclax combined with a hypomethylating agent (HMA), also known as VEN-HMA. AML treatment is often intensive and can significantly suppress the immune system ...
Redesigning healthcare: Integrating social care into a safety net health system
2024-05-09
INDIANAPOLIS -- Neighborhoods of high need are where investment in social care offers the best opportunities to improve health. Screening for social determinants of health is comparatively easy, but building the infrastructure to meet needs occurring outside the formal healthcare system is quite difficult. Few health systems have achieved more than even partial integration of social care into routine patient care.
In a case study of pioneering social care provided by Eskenazi Health, a safety net health system located in Indianapolis, ...
Discovery made into which children will outgrow their peanut allergy
2024-05-09
Australian researchers have discovered how changes in antibody levels over time can predict which children are likely to outgrow their peanut allergy.
The research, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute (MCRI) in Melbourne and published in Allergy, found two thirds of children with a peanut allergy remain allergic by the age of 10. But for those who did naturally outgrow their allergy, the majority achieved this by six years old.
The study was the first to use antibodies as biomarkers to identify persistent or a resolved ...
Princeton physicists reveal the microscopic basis of a new form of quantum magnetism
2024-05-09
By Tom Garlinghouse for the Princeton University Department of Physics
Not all magnets are the same. When we think of magnetism, we often think of magnets that stick to a refrigerator’s door. For these types of magnets, the electronic interactions that give rise to magnetism have been understood for around a century, since the early days of quantum mechanics. But there are many different forms of magnetism in nature, and scientists are still discovering the mechanisms that drive them.
Now, physicists ...
Oikopleura who? Species identity crisis in the genome community
2024-05-09
When two animals look the same, eat the same, behave the same way, and live in similar environments, one might expect that they belong to the same species.
However, a tiny zooplankton skimming the ocean surfaces of microscopic food particles challenges this assumption. Researchers from Osaka University, University of Barcelona and the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) have analyzed the genome of Oikopleura dioica from the Seto Inland Sea, the Mediterranean, and the Pacific Ocean around the Okinawa Islands, and in doing so, they have raised numerous questions about speciation and the role of gene location in ...
Developed compiler acceleration technology for quantum computers
2024-05-09
[Highlights]
- Developed a new compilation method to generate optimal sequences to be executed on quantum computers
- The new method is based on a probabilistic approach and reduces the time to search for the optimal sequence by several orders of magnitude.
- Expected to contribute to quantum information processing at quantum nodes that support the quantum internet
[Abstract]
The National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT, President: TOKUDA Hideyuki, Ph.D.), RIKEN (President: GONOKAMI Makoto, Ph.D.), Tokyo University of Science (President: Dr. ISHIKAWA Masatoshi), and the University of Tokyo (President: FUJII Teruo, Ph.D.) succeeded ...
Report: Governments falling short on promises of effective biodiversity protection
2024-05-09
WASHINGTON— A new analysis of the world’s largest 100 marine protected areas (MPAs) published today in Conservation Letters suggests that governments are falling short on delivering the promise of effective biodiversity protection due to slow implementation of management strategies and failure to restrict the most impactful activities.
The assessment, titled “Ocean protection quality is lagging behind quantity: Applying a scientific framework to assess real marine protected area progress ...
Study shows how night shift work can raise risk of diabetes, obesity
2024-05-09
Just a few days on a night shift schedule throws off protein rhythms related to blood glucose regulation, energy metabolism and inflammation, processes that can influence the development of chronic metabolic conditions.
The finding, from a study led by scientists at Washington State University and the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, provides new clues as to why night shift workers are more prone to diabetes, obesity and other metabolic disorders.
“There are processes tied to the master biological clock in our brain that are saying that day ...
Eleventh Nano Research Award goes to Louis E. Brus and Moungi Bawendi
2024-05-09
Recently, Nano Research announced awardees of the 11th Nano Research Award. Two outstanding scientists, Professor Louis E. Brus of Columbia University and Professor Moungi Bawendi of Massachusetts Institute of Technology, have been awarded this honor.
The Nano Research Award, established by the journal Nano Research together with Tsinghua University Press (TUP) and Springer Nature in 2013, aims to recognize outstanding contributions to nano research by an individual scientist. The winner is selected by the Award Committee ...
Traffic injuries to low-income NYC residents fell 30% in first five years of ‘vision zero’ road safety program, NYU study finds
2024-05-09
Among New Yorkers with low incomes, the “Vision Zero” initiative to stem roadway crashes resulted in a marked, 30% reduction in traffic injuries of varying severity from early 2014 – when the city government launched the program – until 2019, according to a new study conducted at New York University.
The study, scheduled for publication May 8 at 4:00 p.m. (ET) in the American Journal of Public Health, revealed this trend of improved safety by comparing Medicaid-covered injury ...
AI tool instantly assesses self-harm risk
2024-05-09
Suicidality hit new record high in U.S. in 2022
New tool was 92% effective at predicting four variables related to self-harm
AI uses a small set of judgment and contextual variables as opposed to big data, and strongly supports the hypothesis of a standard model of mind
EVANSTON, Ill. --- A new assessment tool that leverages powerful artificial intelligence was able to predict whether participants exhibited suicidal thoughts and behaviors using a quick and simple combination of variables.
Developed by researchers at Northwestern University, the University of Cincinnati (UC), Aristotle ...
An epigenome editing toolkit to dissect the mechanisms of gene regulation
2024-05-09
Understanding how genes are regulated at the molecular level is a central challenge in modern biology. This complex mechanism is mainly driven by the interaction between proteins called transcription factors, DNA regulatory regions, and epigenetic modifications – chemical alterations that change chromatin structure. The set of epigenetic modifications of a cell’s genome is referred to as the epigenome.
In a study just published in Nature Genetics, scientists from the Hackett Group at EMBL Rome have developed a modular epigenome editing platform – a system to program epigenetic modifications at any location in the genome. The system allows scientists to study the impact ...
How aging clocks tick
2024-05-09
Aging clocks can measure the biological age of humans with high precision. Biological age can be influenced by environmental factors such as smoking or diet, thus deviating from the chronological age that is calculated using the date of birth. The precision of these aging clocks suggests that the aging process follows a programme. Scientists David Meyer and Professor Dr Björn Schumacher at CECAD, the Cluster of Excellence Cellular Stress Responses in Aging-Associated Diseases of the University of Cologne, have now discovered that aging clocks actually measure the increase in stochastic changes in cells. The study ‘Aging clocks based on accumulating stochastic variation’ ...
miR-146a rs2910164 C>G Polymorphism and Wilms tumor susceptibility in Eastern Chinese children
2024-05-09
Background and objectives
Wilms tumor is the most common renal malignancy in children. miR-146a, a highly conserved small noncoding RNA, plays a critical role in various human diseases. Increasing studies have suggested that rs2910164 C>G polymorphism in miR-146a is associated with susceptibility to cancers. However, miR-146a rs2910164 C>G polymorphism influence on Wilms tumor remains unknown. The aim of this study was to evaluate the relationship between miR-146a rs2910164 C>G polymorphism and Wilms ...
Simple “swish-and-spit” oral rinse could provide early screening for gastric cancer
2024-05-09
BETHESDA, MD. (May 9, 2024) — A simple oral rinse could provide early detection of gastric cancer, the fourth-leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide, according to a study scheduled for presentation at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2024.
“In the cancer world, if you find patients after they've developed cancer, it's a little too late,” said Shruthi Reddy Perati, MD, author and general surgery resident at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson School of Medicine. “The ideal time to try to prevent ...
[1] ... [1187]
[1188]
[1189]
[1190]
[1191]
[1192]
[1193]
[1194]
1195
[1196]
[1197]
[1198]
[1199]
[1200]
[1201]
[1202]
[1203]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.