Low testosterone in men associated with higher risk for death
2024-05-13
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 13 May 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not ...
Chatbots tell people what they want to hear
2024-05-13
Chatbots share limited information, reinforce ideologies, and, as a result, can lead to more polarized thinking when it comes to controversial issues, according to new Johns Hopkins University–led research.
The study challenges perceptions that chatbots are impartial and provides insight into how using conversational search systems could widen the public divide on hot-button issues and leave people vulnerable to manipulation.
“Because people are reading a summary paragraph generated by AI, they think they’re getting unbiased, fact-based answers,” said lead author Ziang Xiao, an assistant professor of computer ...
Herpes cure with gene editing makes progress in laboratory studies
2024-05-13
SEATTLE — May 13, 2024 — Researchers at Fred Hutch Cancer Center have found in pre-clinical studies that an experimental gene therapy for genital and oral herpes removed 90% or more of the infection and suppressed how much virus can be released from an infected individual, which suggests that the therapy would also reduce the spread of the virus.
“Herpes is very sneaky. It hides out among nerve cells and then reawakens and causes painful skin blisters,” said Keith Jerome, MD, PhD, professor ...
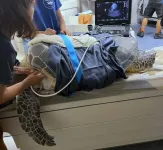
Catch and release can give sea turtles the bends #ASA186
2024-05-13
OTTAWA, Ontario, May 13, 2024 – Six out of seven sea turtle species are endangered, and humans are primarily responsible. Commercial fishing activities are the largest human-caused disturbance to sea turtles due to accidental capture.
Fishers are typically unaware if a sea turtle is caught in their net until it’s completely pulled out of the water. However, releasing sea turtles without veterinary evaluations can be harmful. When accidentally caught, the turtles’ normal diving processes are interrupted, ...
Researchers unveil unique tidal disruption event with unprecedented early optical bump
2024-05-13
A research team from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) presented a detailed analysis of a tidal disruption event (TDE) with unique characteristics, providing new insights into the behavior of TDEs and their multiwavelength emissions. The study was published online in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
When a star ventures too close to a supermassive black hole at the center of a galaxy, it gets torn apart by the black hole's immense tidal forces, resulting ...
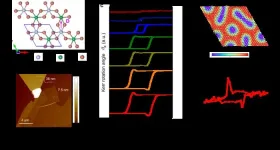
Researchers discover "topological hall effect" in two-dimensional quantum magnets
2024-05-13
In a recent study published in Nature Physics, researchers from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, together with researchers of University of Science and Technology of China, have introduced the concept of the "Topological Kerr Effect" by using the low-temperature magnetic field microscopy system and the magnetic force microscopy imaging system supported by the steady-state high magnetic field experimental facility.
The study holds great promise for advancing our understanding of topological magnetic ...
Like dad and like mum…all in one plant
2024-05-13
In a new study, led by Charles Underwood from the Max Planck Institute for Plant Breeding Research (MPIPZ) in Cologne, Germany, scientists established a system to generate clonal sex cells in tomato plants and used them to design the genomes of offspring. The fertilization of a clonal egg from one parent by a clonal sperm from another parent led to plants containing the complete genetic information of both parents. The study is now published in Nature Genetics.
Hybrid seeds, combining two different parent lines with specific favorable traits, are popular in agriculture as they give rise to robust crops with enhanced productivity, and have been utilized by farmers ...
New molecule mimics the anti-clotting action of blood-sucking organisms
2024-05-13
DURHAM, N.C. – Nature gave ticks, mosquitos and leaches a quick-acting way to keep blood from clotting while they extract their meal from a host.
Now the key to that method has been harnessed by a team of Duke researchers as a potential anti-clotting agent that could be used as an alternative to heparin during angioplasty, dialysis care, surgeries and other procedures.
Publishing in the journal Nature Communications, the researchers describe a synthetic molecule that mimics the effects of compounds in the saliva of blood-sucking critters. Importantly, the new molecule can also ...
Transgender preteens report 13 hours of daily screen time
2024-05-13
Toronto, ON - A new national study found that transgender preteens, 12 and13 years old, reported 13 hours of daily recreational screen time, which was 4.5 hours more than their cisgender peers. Data were collected from 2019 to 2021, overlapping with the COVID-19 pandemic, and the study was published in Annals of Epidemiology.
“Transgender adolescents are more likely to experience school-based bullying and exclusion from peer groups due to their gender identity, leading them to spend less time in traditional school activities and more time on screens,” says lead author, Jason Nagata, MD, associate professor of pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco. ...
World's largest hummingbird is actually two species
2024-05-13
For release: May 13, 2024
Ithaca, NY—The Giant Hummingbird of western South America is not one species but two, according to an international group of researchers. The northern population stays in the high Andes year-round while the southern population migrates from sea level up to 14,000 feet for the nonbreeding months. The two species appear identical. But looks deceive—their genomes and behaviors tell a different story. The paper announcing the find was published this week in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“These ...
New findings released from US 2020 Facebook and Instagram election study
2024-05-13
In the weeks before and after the 2020 presidential election, researchers ran a number of tests to try to understand how much Facebook and its corporate cousin, Instagram, may be contributing to the nation's political divide.
One of those experiments — led by Matthew Gentzkow and Hunt Allcott, economics professors at Stanford University — centered on more than 35,000 Facebook and Instagram users who were paid to stay off the platforms in the run-up to Election Day. There’s a lot that researchers could glean from the social media hiatus, including whether people’s political attitudes shifted and in what ways. If views changed dramatically, that ...
How miniature backpacks led to the discovery of the world’s largest hummingbird species
2024-05-13
Researchers from UNM’s Museum of Southwestern Biology (MSB) have uncovered the giant hummingbird’s extreme long-distance migration for the first time. Their eight-year study, Extreme elevational migration spurred cryptic speciation in giant hummingbirds published this week in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, led them to another important discovery: The world’s largest hummingbird is a new species.
The team, led by Jessie Williamson, UNM Ph.D., 2022, included the Museum of Southwestern Biology at UNM, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile in Chile, and Centro de Ornitología ...
New synthetic biomarker technology differentiates between prior Zika and dengue infections
2024-05-13
A newly discovered Zika virus-specific synthetic molecule is capable of differentiating Zika-immune patient samples from samples of patients previously infected with the related dengue virus. The technology may lead to the development of better diagnostics and vaccine candidates, scientists announced today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The study, led by researchers at the University of Pittsburgh School of Public Health and The Herbert Wertheim UF Scripps Institute for Biomedical Innovation & Technology, is the first to apply an innovative “epitope surrogate” technology to Zika. Until now, researchers and clinicians have lacked diagnostic ...
Fruit fly testes offer potential tool against harmful insects
2024-05-13
A way to curb nagging insects has been flying under our radar—an enzyme from fruit fly testes.
The compound could control bugs that carry disease and harm crops by stunting their ability to procreate, Johns Hopkins University researchers found.
“We have a toe in the door to control fruit fly populations with this enzyme,” said Steven Rokita, a professor of chemistry at Johns Hopkins who led the research. “It could offer a good way to control fertility of all kinds of biological and agricultural pests, starting with mosquito populations.”
The findings are set to publish ...
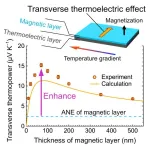
Exceptionally large transverse thermoelectric effect produced by combining thermoelectric and magnetic materials
2024-05-13
1. A NIMS research team has demonstrated for the first time ever that a simple stack of thermoelectric and magnetic material layers can exhibit a substantially larger transverse thermoelectric effect—energy conversion between electric and heat currents that flow orthogonally to each other within it—than existing magnetic materials capable of exhibiting the anomalous Nernst effect. This mechanism may be used to develop new types of thermoelectric devices useful in energy harvesting and heat flux sensing.
2. Seebeck effect-based ...
Researchers identify fastest rate of natural carbon dioxide rise over the last 50,000 years
2024-05-13
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Today’s rate of atmospheric carbon dioxide increase is 10 times faster than at any other point in the past 50,000 years, researchers have found through a detailed chemical analysis of ancient Antarctic ice.
The findings, just published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, provide important new understanding of abrupt climate change periods in Earth’s past and offer new insight into the potential impacts of climate change today.
“Studying the ...
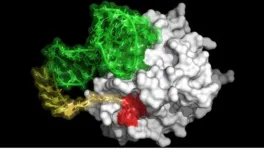
Research on centromere structure yields new insights into the mechanisms of chromosome segregation errors
2024-05-13
Researchers from the Kops group in collaboration with researchers from the University of Edinburgh, made a surprising new discovery in the structure of the centromere, a structure that is involved in ensuring that chromosomes are segregated properly when a cell divides. Mistakes in chromosome segregation can lead to cell death and cancer development. The researchers discovered that the centromere consists of two subdomains. This fundamental finding has important implications for the process of chromosome segregation and provides new mechanisms underlying erroneous divisions in cancer cells. The research was published in Cell on May 13th 2024.
Our bodies consist of trillions of ...
Ochsner Medical Center-Baton Rouge earns Acute Stroke Ready Certification from Joint Commission
2024-05-13
BATON ROUGE, La. – Ochsner Medical Center - Baton Rouge has earned The Joint Commission’s Gold Seal of Approval® and the American Stroke Association’s Heart-Check mark for Acute Stroke Ready Certification.
The designation means OMC-Baton Rouge meets The Joint Commission's designation for readiness to treat patients who experience severe stroke.
To achieve certification, OMC-Baton Rouge underwent a rigorous, unannounced onsite. During the visit, a team of Joint Commission reviewers evaluated compliance with numerous certification standards, including ...
CEHD researchers studying family-led early childhood systems change for educational equity
2024-05-13
CEHD Researchers Studying Family-Led Early Childhood Systems Change For Educational Equity
Colleen Vesely, Associate Professor, College of Education and Human Development (CEHD); Bethany Letiecq, Associate Professor, Research Methods, CEHD; Rochelle Davidson Mhonde, Assistant Professor, Global and Community Health; and Jung Yeon Park, Assistant Professor of Quantitative Research Methods, School of Education, received funding for the project: “Family-Led Early Childhood Systems Change ...
Raz receives funding for Intent-Based Orchestration In Distributed Command & Control (IBODC2) software
2024-05-13
Raz Receives Funding For Intent-Based Orchestration In Distributed Command & Control (IBODC2) Software
Ali ...
Kelly receives funding for civil war graffiti preservation
2024-05-13
Kelly Receives Funding For Civil War Graffiti Preservation
Mills Kelly, Senior Scholar and Former Director, Roy Rosenzweig Center for History and New Media (RRCHNM); Professor, History, has received funding from the National Endowment for the Humanities for: “Off the Wall: Digital Preservation of Civil War Graffiti Houses.”
Kelly will use the funding to support the building and publishing of a digital archive focused on soldiers’ graffiti found in Civil War-era structures located in the ...
New viruses on the horizon
2024-05-13
Suddenly they appear and - like the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus - can trigger major epidemics: Viruses that nobody had on their radar. They are not really new, but they have changed genetically. In particular, the exchange of genetic material between different virus species can lead to the sudden emergence of threatening pathogens with significantly altered characteristics. This is suggested by current genetic analyses carried out by an international team of researchers. Virologists from the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) were in charge of the large-scale study.
“Using a new computer-assisted analysis method, we discovered 40 previously ...
SIAM Conference on Mathematics of Planet Earth (MPE24)
2024-05-13
Climate change, biodiversity, infectious diseases, sustainability, and the associated socio-economic impacts are among the areas of greatest global concern. The SIAM Conference on Mathematics of Planet Earth (MPE24) provides a forum for interdisciplinary researchers to discuss mathematical, statistical, and computational strategies for addressing these problems. The discussion at MPE24 will range from the development of quantitative techniques and algorithms to providing policy makers with tools for qualitative decision support.
This year, MPE24 is especially interested in sessions and presentations that address fundamental ...
SIAM Conference on Nonlinear Waves and Coherent Structures (NWCS24)
2024-05-13
Theoretical and computational aspects of applied mathematical research on nonlinear waves and coherent structures are relevant to subjects as diverse as general relativity, high-energy particle and plasma physics, fluid and solid mechanics, nonlinear electrical circuits, materials science (including metamaterials), Bose-Einstein condensation, nonlinear optics, random media, atmosphere and ocean dynamics, chemical reactions, and biology. Relevant predictions are often tested against physical experiments and open avenues for collaborations and interactions ...
Zampieri receives funding for doctoral consortium
2024-05-13
Marcos Zampieri, Assistant Professor, Information Sciences and Technology, received funding for: “Doctoral Consortium at Student Research Workshop at the Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (NAACL).”
Zampieri will use this funding to subsidize travel, conference, and housing expenses of students selected to participate in the NAACL 2024 Student Research Workshop, which will take place during the main NAACL conference on June 16-21, 2024 in Mexico City, Mexico.
The student research workshop welcomes contributions in two categories: 1) thesis proposals, for advanced students who have ...
[1] ... [1193]
[1194]
[1195]
[1196]
[1197]
[1198]
[1199]
[1200]
1201
[1202]
[1203]
[1204]
[1205]
[1206]
[1207]
[1208]
[1209]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.