Strong-field photoelectron holography in the subcycle limit
2024-05-10
Scientists Unveil Fundamental Electron-holograms for Ultrafast imaging of Atoms and Molecules
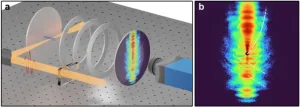
A team of scientists led by Professor Dong Eon Kim at the Pohang University of Science and Technology and Professor X. Lai at the Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology achieved a breakthrough in ultrafast imaging by separately and clearly observing two distinct holographic patterns, spider-leg- and fishbone-like, for the first time. They utilized near-single-cycle laser pulses not only ...
HKUST researchers throw new light on carboxysomes in key discovery that could boost photosynthesis
2024-05-10
A research team led by the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has discovered how carboxysomes, carbon-fixing structures found in some bacteria and algae, work. The breakthrough could help scientists redesign and repurpose the structures to enable plants to convert sunlight into more energy, paving the way for improved photosynthesis efficiency, potentially increasing the global food supply and mitigating global warming.
Carboxysomes are tiny compartments in certain bacteria and algae that encase particular enzymes in a shell made of proteins. They perform carbon fixation, which is ...
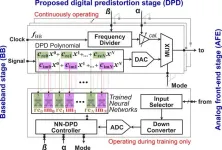
Learning the imperfections: a new approach to using neural networks for low-power digital pre-distortion (DPD) in mmWave systems
2024-05-10
In the world around us, a quiet but very important evolution has been taking place in engineering over the last decades. As technology evolves, it becomes increasingly clear that building devices that are physically as close as possible to being perfect is not always the right approach. That’s because it often leads to designs that are very expensive, complex to build, and power-hungry. Engineers, especially electronic engineers, have become very skilled in using highly imperfect devices in ways that allow ...
Worker rights are one of the least protected human rights, new research reveals
2024-05-10
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Worker rights are among the least protected human rights in the world, according to new research from faculty at Binghamton University, State University of New York.
The findings are part of a new report published by the CIRIGHTS Data Project, the largest human rights dataset in the world. Since 1981, the project has ranked countries around the world on their respect for human rights, providing an annual “report card” on 25 internationally recognized human rights. The project ...
Unveiling crucial virulent milRNAs implicated in the initial infection of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense
2024-05-10
Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense (Foc) is a typical soil-borne fungus that causes Fusarium wilt by infecting the roots and blocking the vascular tissues of host banana, and threatens the global banana production. Total four races have been reported in Foc, of which the tropical race 4 (TR4) is the most widespread race. In some severely affected banana plantations, the conventional ‘Cavendish’ variety had to be abandoned for other alternative crops due to the spread of TR4. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of the pathogenesis of FWB and the development ...
Developing an efficient host-vector system for a model archaeon by solving CRISPR-based host-plasmid conflict
2024-05-10
This study is led by Prof. Qunxin She (Shandong University) and Dr. Guanhua Yuan (Shandong University). The research group has constructed versatile genetic tools for Saccharolobus islandicus REY15A, one of the very few archaeal models for archaea biology and CRISPR biology research, and these include efficient genome editing, robust protein expression systems, interference plasmid assay, gene silencing and CRISPR-based gene editing. Nevertheless, plasmid vectors constructed for this crenarchaeon thus far are based solely on the pRN2 cryptic plasmid. “A dual host-vector system is required to enrich the genetic toolbox for this model archaeon.” the ...
Development of technology for producing bioplastics from agricultural and food byproducts by the World Institute of Kimchi
2024-05-10
As kimchi has been drawing attention as a global healthy food trend, cabbage is one of the representative vegetables used as a main ingredient for manufacturing kimchi overseas.
The annual global production of cabbage and other Brassica crops is reported to be 72 million tons, and more than 30% of them are estimated to be discarded during the manufacturing and distribution processes, causing environmental pollution as well as considerable waste disposal costs in the industry.
In connection with this problem, Hae Choon Chang, President of the World Institute of Kimchi (WiKim), a government-funded research institute under the Ministry of Science and ICT, announced on April 22 that ...
How the brain is flexible enough for a complex world (without being thrown into chaos)
2024-05-10
Every day our brains strive to optimize a trade-off: With lots of things happening around us even as we also harbor many internal drives and memories, somehow our thoughts must be flexible yet focused enough to guide everything we have to do. In a new paper in Neuron, a team of neuroscientists describes how the brain achieves the cognitive capacity to incorporate all the information that’s relevant without becoming overwhelmed by what’s not.
The authors argue that the flexibility arises from a key property observed in many neurons: “mixed selectivity.” While many neuroscientists used to think each cell had just one dedicated function, more recent evidence ...
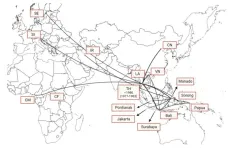
Tracing HIV in Indonesia
2024-05-10
The HIV variant dominant in Indonesia was introduced from Thailand over multiple events. The Kobe University study traces where it came from and how it spread from there, offering insights of possible value to the development of treatments against the disease.
HIV is the virus causing AIDS, but one of the things that make it so difficult to treat is that there are many variants of it. Kobe University virologist KAMEOKA Masanori says, “The diversity is increasing every day and the prevalent virus strains differ from region to ...
Metabolism of autism reveals developmental origins
2024-05-10
Researchers at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine have shed new light on the changes in metabolism that occur between birth and the presentation of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) later in childhood. The researchers discovered that a small number of biochemical pathways are responsible for the majority of these changes, which could help inform new early detection and prevention strategies for autism.
“At birth, the physical appearance and behavior of a child who will develop autism over the next few years are indistinguishable from that of a neurotypical child. Indeed, in most cases the fate of the child with regard to autism is not ...
Comparative analysis of robot-assisted language learning systems and human tutors in English conversation lessons
2024-05-10
Advancements in large language models, robotics, and software such as text-to-speech, have made it possible to develop robots that can understand language, interact physically, and communicate verbally. These breakthroughs have opened up possibilities for robots to be used for educational purposes. However, this raises the question of whether robots are as good as human tutors. While robots offer certain benefits, they cannot replicate the nuanced interactions and personalized feedback human tutors provide.
To determine the suitability of using ...
Under 4-minute milers’ longevity shows that extreme exercise doesn’t seem to curb lifespan
2024-05-10
Extreme exercise doesn’t seem to shorten the lifespan as is widely believed, suggest the findings of a study on the longevity of the first 200 athletes to run a mile in under 4 minutes, and published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
They outlive the general population by several years, shows the study, which marks the 70th anniversary of the seminal achievement of Roger Bannister, who was the first person to run a mile in under 4 minutes in May 1954.
While regular moderate exercise is considered a pillar of healthy ageing, ...
Journal retracts 6 further articles and corrects 2 others authored by former editor
2024-05-10
The British Journal of Sports Medicine has retracted six further articles authored by former editor, Dr Paul McCrory, and corrected another two, following an extensive investigation of his sole authored content in the journal.*
The retractions comprise four ‘warm up’ editorials and one book review due to plagiarism. A letter has also been retracted because of duplicate publication. And a research article and a review article have been corrected due to inappropriate reuse of content.
This latest tranche of retractions and corrections completes BMJ’s 2-year investigation ...
Running under a four-minute mile could be the key to a long and healthy life
2024-05-10
A new study released to mark the 70th anniversary of Sir Roger Bannister’s sub-four-minute mile record has revealed the first 200 runners to follow in his footsteps also share another remarkable trait.
The study from investigators in Australia and Canada found the 200 elite runners live on average almost five years longer than the general population.
Professor Mark Haykowsky, the Research Chair in Aging and Quality of Life in the Faculty of Nursing at the University of Alberta, says the findings published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine demonstrate the vital importance of aerobic fitness.
Professor Haykowsky says: “Breaking ...
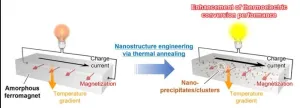
Transforming common soft magnets into a next-generation thermoelectric conversion materials by 3 minutes heat treatment
2024-05-10
1. A research team from NIMS and Nagoya University has demonstrated that an iron-based amorphous alloy, widely used as a soft magnetic material in transformers and motors, can be transformed into a "transverse" thermoelectric conversion material that converts electric and thermal currents in orthogonal directions, with just a short period of heat treatment. This is the first example that highlights the importance of microstructure engineering in the development of transverse thermoelectric conversion materials, and provides new design guidelines for materials development to realize environmentally friendly power generation and thermal management technologies ...
Good vibrations: New tech may lead to smaller, more powerful wireless devices
2024-05-09
What if your earbuds could do everything your smartphone can do already, except better? What sounds a bit like science fiction may actually not be so far off. A new class of synthetic materials could herald the next revolution of wireless technologies, enabling devices to be smaller, require less signal strength and use less power.
The key to these advances lies in what experts call phononics, which is similar to photonics. Both take advantage of similar physical laws and offer new ways to advance technology. While photonics takes advantage of photons – or light – phononics does the same with phonons, which are the physical particles that transmit mechanical vibrations ...
Revolutionizing nurse work environment research
2024-05-09
PHILADELPHIA (May 9, 2024) – New research from Penn Nursing’s Center for Health Outcomes and Policy Research (CHOPR) – recently published online in the journal Research in Nursing & Health – has successfully validated a new, streamlined version of the Practice Environment Scale of the Nursing Work Index (PES-NWI), originally authored in 2002 by Eileen T. Lake, PhD, RN, FAAN, Professor of Nursing, the Edith Clemmer Steinbright Professor in Gerontology, and Associate Director of CHOPR, who is also lead author on this publication. This innovative tool, known as the PES-5, is designed to revolutionize how nurse work environments are measured across ...
New ‘forever chemical’ cleanup strategy discovered
2024-05-09
As the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency cracks down on insidious “forever chemical” pollution in the environment, military and commercial aviation officials are seeking ways to clean up such pollution from decades of use of fire suppressant foams at military air bases and commercial airports.
Fire-suppression foams contain hundreds unhealthful forever chemicals, known by chemists as PFAS or poly- and per-fluoroalkyl substances. These compounds have stubbornly strong fluorine-to-carbon bonds, which allow them to persist indefinitely in the environment, hence the moniker “forever chemicals.” ...
Squeezed by neighbors, planet glows with molten lava
2024-05-09
UC Riverside astrophysicist Stephen Kane had to double check his calculations. He wasn’t sure the planet he was studying could be as extreme as it seemed.
Kane never expected to learn that a planet in this faraway star system is covered with so many active volcanoes that seen from a distance it would take on a fiery, glowing-red hue.
“It was one of those discovery moments that you think, ‘wow, it’s amazing this can actually exist,” Kane said. A paper detailing the discovery has been published in The Astronomical Journal.
Launched in 2018, NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey ...
GPS-like system shows promise as HIV vaccine strategy to elicit critical antibodies
2024-05-09
DURHAM, N.C. – A team led by the Duke Human Vaccine Institute (DHVI) has developed a vaccine approach that works like a GPS, guiding the immune system through the specific steps to make broadly neutralizing antibodies against HIV.
Publishing in the journal Cell Host & Microbe, the study describes an approach that provides step-by-step directions for the immune system to generate the elusive, yet necessary antibodies for a successful HIV vaccine.
“HIV is the fastest-evolving virus known. So it’s been a long-standing goal in HIV research to create ...
NSF awards $630,000 to study teeth of non-human primates
2024-05-09
The National Science Foundation awarded $630,444 to Kathleen Paul, an assistant professor of anthropology at the U of A, to provide a comprehensive outline of dental genetic architecture for two primate species of tamarins and macaques.
Paul's research team’s ultimate goal is to harness this information to advance bioanthropological practice, including the use of teeth for reconstructing evolutionary processes and experiences of stress and illness.
No live animals will be used in the research. Instead, skeletonized individuals from collections ...
Discrimination may accelerate aging
2024-05-09
Discrimination may speed up the biological processes of aging, according to a new study led by researchers at the NYU School of Global Public Health.
The research links interpersonal discrimination to changes at the molecular level, revealing a potential root cause of disparities in aging-related illness and death.
“Experiencing discrimination appears to hasten the process of aging, which may be contributing to disease and early mortality and fueling health disparities,” said Adolfo Cuevas, assistant professor in the Department of Social and Behavioral Sciences at NYU’s ...
New machine learning algorithm promises advances in computing
2024-05-09
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Systems controlled by next-generation computing algorithms could give rise to better and more efficient machine learning products, a new study suggests.
Using machine learning tools to create a digital twin, or a virtual copy, of an electronic circuit that exhibits chaotic behavior, researchers found that they were successful at predicting how it would behave and using that information to control it.
Many everyday devices, like thermostats and cruise control, utilize linear controllers – which use ...
How climate change will affect malaria transmission
2024-05-09
University of Leeds news release
Embargoed until 1900 BST, 9 May 2024
How climate change will affect malaria transmission
A new model for predicting the effects of climate change on malaria transmission in Africa could lead to more targeted interventions to control the disease according to a new study.
Previous methods have used rainfall totals to indicate the presence of surface water suitable for breeding mosquitoes, but the research led by the University of Leeds used several climatic and hydrological models to include real-world processes of evaporation, infiltration and flow through rivers.
This ...
Presenting a safer, low-cost, and low-energy whole-body magnetic resonance imaging device
2024-05-09
Machine learning enables cheaper and safer low-power magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) without sacrificing accuracy, according to a new study. According to the authors, these advances pave the way for affordable, patient-centric, and deep learning-powered ultra-low-field (ULF) MRI scanners, addressing unmet clinical needs in diverse healthcare settings worldwide. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has revolutionized healthcare, offering noninvasive and radiation-free imaging. It holds immense promise for advancing medical diagnoses through artificial intelligence. However, despite its five decades of development, MRI remains largely inaccessible, particularly ...
[1] ... [1185]
[1186]
[1187]
[1188]
[1189]
[1190]
[1191]
[1192]
1193
[1194]
[1195]
[1196]
[1197]
[1198]
[1199]
[1200]
[1201]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.