The Clues for Cleaner Water
2024-05-06
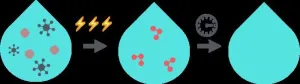
Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh and Drexel University in Philadelphia, along with Brookhaven National Laboratory, are working to solve a multipart mystery to make water disinfection treatments more sustainable.
Scalable electrochemical ozone production (EOP) technologies to disinfect dirty water may someday replace centralized chlorine treatments used today, whether in modern cities or remote villages. However, little is understood about EOP at the molecular level and how technologies that make it possible can be made to be efficient, economical, and sustainable.
Their research, “Interplay between Catalyst Corrosion and Homogeneous Reactive Oxygen Species ...
New $14.5 million center to help US Navy overcome emerging challenges
2024-05-06
Images
The U.S. Office of Naval Research is tapping academic expertise at the University of Michigan to solve current and future problems, Secretary of the Navy Carlos Del Toro announced during his visit to campus over graduation weekend.
The $14.5M Center for Naval Research and Education will also help train an engineering research community familiar with naval and marine applications.
"I am incredibly proud of the partnership between the University of Michigan and the Department of the Navy. Michigan is a key teammate in rebuilding our shipbuilding industry and restoring the comprehensive—commercial ...
Now available from Penn Nursing: innovative, online psychedelic course
2024-05-06
PHILADELPHIA (May 6, 2024) – Penn Nursing is proud to launch a groundbreaking new online course – Educating Nurses in Psychedelic Assisted Therapy – via Open Canvas. This free comprehensive course is designed to prepare nursing professionals for the pioneering field of psychedelic assisted therapy (PAT), aligning with the latest advancements in mental health treatment and Penn Nursing's commitment to social justice in healthcare.
With this new modality of care on the horizon, the need for well-educated, ...
Greet receives funding for Abstraction in the Andes, 1950 - 1970
2024-05-06
Michele Greet, Director, Art History Program, received funding for: “Abstraction in the Andes, 1950-1970.”
She will examine the emergence of abstract painting in Andean countries (Peru, Ecuador, and Bolivia) in the 1950s and 1960s. She will explore artists’ newfound interest in pre-Columbian art as source material as well as the circulation of ideas from Europe and the United States.
Although abstract art rapidly gained acceptance throughout Latin America after World War II, until recently, studies of abstract painting in the region have focused on the geometric styles that emerged in Brazil, Argentina, and Venezuela. Different variants of abstraction ...
Mindfulness training enhances opioid addiction treatment
2024-05-06
Supplementing standard opioid addiction treatment with Mindfulness Oriented Recovery Enhancement (MORE) — an intervention that incorporates mindfulness training, savoring skills, and cognitive reappraisal — cuts program dropout rates by 59 percent and relapses by 42 percent, according to Rutgers-led research.
These trial results come from Rutgers Health amid unprecedented opioid abuse. An estimated 10 million Americans misuse opioids or have opioid use disorder, while annual overdose deaths have exceeded 80,000.
Treatment with methadone or buprenorphine – alone or in combination with cognitive behavioral therapy – is imperfect. Half ...
Using advanced genetic techniques, scientists create mice with traits of Tourette disorder
2024-05-06
In research that may be a step forward toward finding personalized treatments for Tourette disorder, scientists at Rutgers University–New Brunswick have bred mice that exhibit some of the same behaviors and brain abnormalities seen in humans with the disorder.
As reported in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the researchers, using a technique known as CRISPR/Cas9 DNA editing that selectively modifies the DNA of living organisms, inserted the same genetic mutations found in humans with Tourette disorder into the corresponding genes in mouse embryos. After the mice were born, the scientists observed their behavior compared with littermates without the ...
3D video conferencing tool lets remote user control the view
2024-05-06
ITHACA, N.Y. -- Collaborating on a physical object when two people aren’t in the same room can be extremely challenging, but a new remote conferencing system allows the remote user to manipulate a view of the scene in 3D, to assist in complex tasks like debugging complicated hardware.
The system, called SharedNeRF, combines two graphics rendering techniques – one that is slow and photorealistic, and another that is instantaneous but less precise – to help the remote user experience ...
The Ottawa Hospital is expanding life-saving biotherapeutics research and manufacturing to its new campus thanks to $59 million grant
2024-05-06
The Ottawa Hospital is receiving $59 million to boost Canada’s capacity to develop and manufacture life-saving biotherapeutics, including vaccines, gene therapies and cell therapies. Most of the funding ($47 million) will support the construction and operation of a world-class biomanufacturing facility at The Ottawa Hospital’s new campus, while the remainder will enable harmonization and cooperation across six Canadian biomanufacturing facilities.
The funding is part of a $115 million investment from the Government of Canada in the Canadian Pandemic ...
Early neurodevelopmental assessments for predicting long-term outcomes in infants at high risk of cerebral palsy
2024-05-06
About The Study: The results of this study support the potential to identify cerebral palsy and its severity as early as corrected age 3 to 4 months through early neurodevelopmental assessments, but the role of these tests is limited in identifying cognitive and neurodevelopmental impairments.
Authors: Abdul Razak, M.D., of Monash University in Melbourne, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.9053)
Editor’s ...
Snowfall and drought: $4.8 million field campaign will improve forecasts in western US, led by U-M
2024-05-06
Images
A new science expedition in Yampa Valley, Colorado, will improve forecasts of snowfall and estimates of how climate change will impact snowpack and water availability in the western U.S. mountains, funded with $4.8M from the National Science Foundation.
The field campaign, led by the University of Michigan, brings together scientists from the University of Washington, University of Wisconsin, University of Utah, Colorado State University and Stony Brook University. The team will use an extensive suite of radars and snow-sampling instruments to measure the size and shape of snowflakes and aerosols. ...
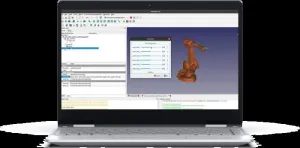
SwRI Workbench for Offline Robotics Development™ (SWORD™) launched at Automate 2024
2024-05-06
SAN ANTONIO — May 6, 2024 – Southwest Research Institute is simplifying robotics programming with a new toolkit that embeds computer-aided design (CAD) into robotics motion planning, modeling and execution. The SwRI Workbench for Offline Robotics Development™ (SWORD™) features a user-friendly graphical interface to demystify the fundamental coding required in robot operating system (ROS) application development.
Informed by the Institute’s role in supporting the ROS-Industrial community, SwRI developed ...
Science doesn't understand how ice forms (video)
2024-05-06
WASHINGTON, May 6, 2024 — This video contains incredible macro footage of supercooled water droplets nucleating ice. All George wanted to do was make a crystal-clear ice cube. Instead, he ended up rediscovering dendritic crystal growth, a beautiful phenomenon first described in the 17th century. You’ll never look at your freezer the same way again. https://youtu.be/24TB1vPuzIU?feature=shared
Reactions is a video series produced by the American Chemical Society and PBS Digital Studios. Subscribe to Reactions at http://bit.ly/ACSReactions and ...
Study reveals APOE4 gene duplication as a new genetic form of Alzheimer's disease
2024-05-06
Researchers from the Research Area on Neurological Diseases, Neuroscience, and Mental Health at the Sant Pau Research Institute, led by Dr. Juan Fortea, Director of the Memory Unit of the Neurology Service at the same hospital, have found that over 95% of individuals over 65 years old who have two copies of the APOE4 gene -APOE4 homozygotes- show biological characteristics of Alzheimer's pathology in the brain or biomarkers of this disease in cerebrospinal fluid and PET scans.
The study, published today in Nature Medicine, also concludes that those individuals homozygous for APOE4 also develop ...
Study highlights key predictors of adolescent substance use; special issue of the American Journal of Psychiatry focuses on substance use disorders
2024-05-06
NEW YORK, May 6, 2024 – New research, published online today in the American Journal of Psychiatry, examined a broad range of potential predictors of substance use among adolescents and found sociodemographic variables were the most robust predictors of substance use initiation.
The study is part of a special issue of the journal highlighting advances in understanding the neurobiology and sociodemographic underpinnings of substance use disorders and how this understanding has advanced recognition and treatment. Several authors discussed this work today at a special briefing during the 2024 Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric ...
Racial and ethnic disparities in initiation of direct oral anticoagulants among Medicare beneficiaries
2024-05-06
About The Study: In this cohort study of Medicare patients with atrial fibrillation, Black and Hispanic patients were less likely to initiate direct oral anticoagulants for atrial fibrillation, although these differences diminished over time. Identifying the factors behind these early disparities is crucial for ensuring equitable access to novel therapies as they emerge for Black and Hispanic populations.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Kamika R. Reynolds, M.S., Ph.D. (kreynolds@ifh.rutgers.edu) and Chintan ...
Behavioral interventions to improve breast cancer screening outreach
2024-05-06
About The Study: These findings show that text messaging women after initial breast cancer screening outreach via either electronic portal or mailings, as well as bulk ordering with or without text messaging, can increase mammogram completion rates.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author Shivan J. Mehta, M.D., M.B.A., M.S.H.P., email shivan.mehta@pennmedicine.upenn.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2024.0507)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
Venus has almost no water. A new study may reveal why
2024-05-06
Planetary scientists at the University of Colorado Boulder have discovered how Venus, Earth’s scalding and uninhabitable neighbor, became so dry.
The new study fills in a big gap in what the researchers call “the water story on Venus.” Using computer simulations, the team found that hydrogen atoms in the planet’s atmosphere go whizzing into space through a process known as “dissociative recombination”—causing Venus to lose roughly twice as much water every day compared to previous estimates.
The team will publish their findings May 6 in ...
DDT pollutants found in deep sea fish off Los Angeles coast
2024-05-06
In the 1940s and 1950s, the ocean off the coast of Los Angeles was a dumping ground for the nation’s largest manufacturer of the pesticide DDT – a chemical now known to harm humans and wildlife. Due to the stubborn chemistry of DDT and its toxic breakdown products, this pollution continues to plague L.A.’s coastal waters more than half a century later. While legal at the time, details of this industrial-scale pollution of the marine environment at a dump site some 15 miles offshore near Catalina Island ...
Turbid waters keep the coast healthy
2024-05-06
Turbid waters keep the coast healthy
To preserve the important intertidal areas and salt marshes off our coasts for the future, we need more turbid water. That is one of the striking conclusions from a new study conducted by a Dutch-Chinese team of researchers and published today in Nature Geoscience."These natural areas outside our dikes are essential for nature and coastal defense. But because how we are now building in the Delta and the hinterland, coastal defense is endangered in the long term," warns NIOZ researcher Tim Grandjean.
Satellite measurements
For his research, Grandjean linked decades of satellite measurements ...
Microscopic heart vessels imaged in super-resolution for first time at Imperial
2024-05-06
A new imaging technique tested in patients could improve the evaluation of cardiac conditions and undiagnosed chest pain.
Researchers from Imperial College London’s Department of Bioengineering and Faculty of Medicine worked alongside academics from UCL to produce sub-millimetre resolution images of cardiac micro-vessels. The non-invasive new imaging technique was tested on four human patients.
Existing imaging technologies can visualise large vessels on the heart’s surface. However, this new technique could allow scientists to study the physiology of the heart in more detail by imaging smaller micro-vessels within the heart muscle.
This research, ...
Clinical trial shows that cytisinicline can help people quit vaping
2024-05-06
BOSTON–Eleven million U.S. adults use e-cigarettes to vape nicotine, and about half of them say that they want to stop, but many have trouble doing so because nicotine is an addictive drug.
A plant-based medication called cytisinicline may be an effective therapy to help them stop vaping, according to the results of a new clinical trial co-led by an investigator from Massachusetts General Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system. The trial’s findings are published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
In the double-blind randomized clinical trial, 160 adults who vaped nicotine ...
Groundbreaking microcapacitors could power chips of the future
2024-05-06
– By Alison Hatt
In the ongoing quest to make electronic devices ever smaller and more energy efficient, researchers want to bring energy storage directly onto microchips, reducing the losses incurred when power is transported between various device components. To be effective, on-chip energy storage must be able to store a large amount of energy in a very small space and deliver it quickly when needed – requirements that can’t be met with existing technologies.
Addressing this challenge, scientists ...
Machine learning for maternal health: University of Oklahoma engineer receives NSF Career Award for preeclampsia study
2024-05-06
Norman, OK – Talayeh Razzaghi, an assistant professor of industrial and systems engineering at the University of Oklahoma, has been awarded a Faculty Early Career Development Program award from the National Science Foundation for her work titled “Personalized Maternal Care Decision Support System for Underserved Populations.”
Known as a CAREER award, Razzaghi was awarded $496,732 to research machine learning-based clinical decision support tools for early preeclampsia detection in maternal ...
Unraveling isopods' culinary secrets and why it matters for ecosystems
2024-05-06
New research on desert isopods' dietary preferences is the revelation of the complex factors influencing their food choices. By understanding how these animals meticulously regulate their nutrient intake and prefer biological soil crusts over plant litter, the study highlights the intricate dynamics of trophic interactions. Understanding the dietary preferences of desert isopods sheds light on the intricate interplay between organisms and their environment, informing ecosystem management and conservation strategies.
New study sheds light on the intricate nutritional and functional ...
Beyond therapy: Virtual reality shows promise in fighting depression
2024-05-06
(Toronto, May 6, 2024) A new study published in JMIR Mental Health sheds light on the promising role of virtual reality (VR) in treating major depressive disorder (MDD). Titled "Examining the Efficacy of Extended Reality–Enhanced Behavioral Activation for Adults With Major Depressive Disorder: Randomized Controlled Trial," the research, led by Dr Margot Paul and team from Stanford University, unveiled the effectiveness of extended reality (XR)–enhanced behavioral activation (XR-BA) in easing symptoms of depression.
MDD affects millions worldwide, and access to evidence-based psychotherapies remains a challenge for many. Traditional treatments ...
[1] ... [1201]
[1202]
[1203]
[1204]
[1205]
[1206]
[1207]
[1208]
1209
[1210]
[1211]
[1212]
[1213]
[1214]
[1215]
[1216]
[1217]
... [8831]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.