Polyamorous youth report facing stigma, heightened levels of depression
2024-04-29
PULLMAN, Wash. – While increasingly visible among adults, polyamory also exists among adolescents, and as a new study indicates, so does the stigma that can come with it.
A Washington State University study of 323 youth ages 12 to 17 at an LGBTQ+ summer camp found that 54, or about 16.7%, identified as polyamorous or ambiamorous, meaning they were open to either monogamous or polyamorous relationships. These “poly” and “ambi” youth reported higher levels of depressive symptoms than their LGBTQ+ peers.
The study, one of the first to investigate polyamorous relationships in youth, was published in the journal Psychology & Sexuality.
“It ...
Competition from “skinny label” generics saved Medicare billions
2024-04-29
IMPORTANT UPDATE:
The article referenced in Tip #4 on color ultrasound for suspected GCA will not be published on April 30. If you had planned to cover this topic, please hold your stories until further notice. In its place, Annals will publish the following:
Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors and the Risk for Dialysis and Cardiovascular Disease in Patients With Stage 5 Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-1874
Please contact Angela ...
Xavier Ochsner College of Medicine announces founding dean and location in downtown New Orleans at Benson Tower
2024-04-29
New Orleans, La. – Xavier University of Louisiana (Xavier), a leading undergraduate institution in preparing Black students to successfully complete medical school, has announced continued progress with Ochsner Health (Ochsner), the Gulf South’s leading academic medical center in training physicians, to launch their transformational Xavier Ochsner College of Medicine (XOCOM). This groundbreaking partnership marks a significant milestone in advancing medical education by addressing health disparities ...
Three Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute faculty members honored by AAAS
2024-04-29
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute’s Boleslaw Szymanski, Ph.D., and Chunyu Wang, M.D. Ph.D., have been elected fellows of the American Association for the Advancement Science (AAAS). Steven Cramer, Ph.D., who was elected AAAS Fellow in 2017, was elected Council Member of the Section on Engineering.
The mission of the AAAS is to “advance science, engineering, and innovation throughout the world for the benefit of all.” Each year, AAAS elects fellows whose “efforts… are scientifically or socially distinguished.”
Over RPI’s 200-year history, 70 RPI faculty members have been ...
STRONG STAR Consortium secures $17 million in DOD research funding for brain injuries, PTSD and more
2024-04-29
SAN ANTONIO, April 29, 2024 – In a recent round of grant awards, the STRONG STAR Consortium based at The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) was selected by the U.S. Department of Defense for a total of $17 million in funding to launch eight new research projects focused on traumatic brain injury and psychological health.
The combined projects will enable the consortium to take a big step forward in its mission to advance the care of military personnel and veterans recovering from war-related trauma ...
Scientists harness the wind as a tool to move objects
2024-04-29
Researchers have developed a technique to move objects around with a jet of wind. The new approach makes it possible to manipulate objects at a distance and could be integrated into robots to give machines ethereal fingers.
‘Airflow or wind is everywhere in our living environment, moving around objects like pollen, pathogens, droplets, seeds and leaves. Wind has also been actively used in industry and in our everyday lives – for example, in leaf blowers to clean leaves. But so far, we can’t control the direction the leaves move – we can only blow them together into a pile,’ says Professor Quan Zhou from Aalto University, who led the study.
The first ...
Long snouts protect foxes when diving headfirst in snow
2024-04-29
ITHACA, N.Y. – When hunting for mice in winter, red and arctic fox are known to plunge headfirst at speeds of 2-4 meters per second, but their sharp noses reduce the impact force in snow and protect them from injury, according to a new Cornell University study.
The fundamental research sheds light on the biomechanics of the unique hunting behavior (known as mousing), advances our understanding of animal adaptations and offers insights into snow injuries people experience during snowboarding or skiing.
The study published April 29 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
While ...
Laser imaging could offer early detection for at-risk artwork
2024-04-29
DURHAM, N.C. -- Look closely at Impressionist paintings in museums compared with photos of them taken 50 years ago, and you might notice something odd: some are losing their bright yellow hues.
Take the dramatic sunset in Edward Munch’s famous painting “The Scream.” Portions of the sky that were once a vivid orangish yellow have faded to off-white.
Likewise, some of the sunny yellow that Henri Matisse brushed between the reclining nudes in his painting “The Joy of Life” is now more of a drab beige.
Several other paintings from this period are facing ...
"BioBlitz" citizen science reveals urban biodiversity, guides management
2024-04-29
Citizen scientists are uncovering rare animal, plant, and fungi species in areas where they have never been seen before, increasing our knowledge of urban biodiversity and proving the existence of local species long thought extinct. The approach used is called a BioBlitz, a biological census in which citizen scientists contribute photographs or audio of living organisms they can see or hear in a designated area over a particular period, creating a snapshot of an area’s biodiversity.
In a recently published article in the journal BioScience, Dr. Esti Palma (University of Melbourne) ...
Haiti study suggests early-onset heart failure is prevalent form of heart disease in low-income countries
2024-04-29
Early-onset heart failure is alarmingly common in urban Haiti—over 15-fold higher than previously estimated—according to a study conducted by Weill Cornell Medicine researchers in partnership with the Haitian medical organization GHESKIO. Heart failure occurs when the heart muscle can no longer pump an adequate amount of blood throughout the body.
The study indicates that the nature of cardiovascular disease in Haiti, and perhaps other low- and middle-income nations, differs from wealthier countries where ischemic heart disease, also called coronary heart disease, is prevalent. This condition, ...
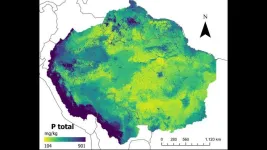
Maps developed with artificial intelligence confirm low levels of phosphorus in Amazonian soil
2024-04-29
As the impacts of climate change increasingly affect the daily lives of residents in several countries, including Brazil, the resilience of forests, especially tropical ones such as the Amazon, has become a frequent topic of research. In addition to studying various factors that influence the way vegetation reacts to global warming, scientists are seeking to improve vegetation models – tools that play a crucial role in understanding and managing ecosystems, contributing to biodiversity conservation and sustainable development.
And it is exactly this combination that is described in research published in the journal Earth System Science Data by a group associated ...
Uptick in NYC transit assault rate during COVID pandemic; has not returned to pre-pandemic levels despite subway safety plan
2024-04-29
April 29, 2024-- Has the New York City subway become less safe? This is the question Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health researchers sought to answer in their newest paper investigating rates of complaints to and arrests by the New York City Police Department Transit Bureau. The findings showed that anxieties related to crime on New York City transit rose following NYC’s COVID-19 pandemic state of emergency declaration in 2020, leading to declines in subway ridership. The results are published in the journal Injury Epidemiology.
The ...
Hongbo Chi, PhD named 2023 AAAS Fellow
2024-04-29
(MEMPHIS, Tenn., April 29, 2024)- Hongbo Chi, PhD, a faculty member and the Robert G. Webster Endowed Chair in Immunology at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, has been recognized as a fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS), the world’s largest general scientific society and publisher of the Science Family of Journals. Chi will be formally inducted Sept. 21, during the organization’s annual Fellows Forum in Washington D.C.
Chi is the most recent St. Jude faculty member selected as an AAAS Fellow. Other St. Jude honorees include: Thirumala-Devi Kanneganti, PhD, Victor Torres, PhD, Douglas Green, PhD, Charles Rock, ...
Study finds school entry requirements linked to increased HPV vaccination rates
2024-04-29
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – April 29, 2024 – A new study from researchers at Wake Forest University School of Medicine shows that school entry requirements are linked to an increase in human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccinations.
The findings appear online in Pediatrics.
HPV is a common sexually transmitted infection, which can cause health problems such as genital warts and certain cancers. To prevent infection, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend that 11- to 12-year-olds receive two doses of the HPV vaccine, given 6 to 12 months apart. However, CDC data from 2022 ...
Study reveals higher injury and assault rates among NYC food delivery gig workers dependent on the work
2024-04-29
A study published Monday in the Journal of Urban Health by a team of CUNY researchers finds that food delivery gig workers in New York City face a high risk of injury and assault, particularly those dependent on gig work as their main job. The study analyzes data from a survey of 1,650 delivery workers, collected between October and December 2021 by the New York City Department of Consumer and Worker Protection.
Alarmingly, about 22% reported experiencing injuries, and 21% reported assaults while on the job, with those using e-bikes or mopeds more than twice as likely to be injured or assaulted compared to those who deliver by car.
Of particular importance was the relationship ...
Kaposi sarcoma discovery could facilitate drug development
2024-04-29
Researchers at UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center, after decades of research efforts, have developed a mouse model of Kaposi sarcoma that could be key to the development of new drugs to treat the disease. Kaposi sarcoma is a cancer that is the most common cancer in people living with HIV.
The findings appeared in Cell Host & Microbe.
“This is an important development as we have created the first animal model ever of Kaposi sarcoma. Animal models are essential to move new drugs from the laboratory bench into clinical trials,” said UNC Lineberger’s Dirk Dittmer, PhD, senior corresponding author, co-leader of the UNC Lineberger Virology ...
Research shows link between pollution and heart risks in residents of the city of São Paulo, Brazil
2024-04-29
The relationship between living in a polluted city like São Paulo (Brazil) and lung disease or cancer is well known. But the problems go further. Unprecedented research shows that long-term exposure to air pollution is directly linked to increased heart risks in residents of the capital of the state of the same name. People with high blood pressure are at even greater risk.
The study, published in the journal Environmental Research, was conducted by researchers from the University of São Paulo (USP) with support from FAPESP (projects 13/21728-2, 16/23129-7 and 19/06435-5). The research shows ...
Rice’s Yousif Shamoo elected AAAS fellow
2024-04-29
Rice University bioscientist Yousif Shamoo has been elected a fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS), the world’s largest general scientific society and publisher of the journal Science.
The lifetime honor, one of the highest in the scientific community, is accorded to fewer than 1% of AAAS members each year. Shamoo, the Ralph and Dorothy Looney Professor in the Department of Biosciences, was recognized “for distinguished contributions to research on multidrug resistance, protein structure ...
Mazin to study electronic, transport & topological properties of frustrated magnets
2024-04-29
Igor Mazin, Professor of Practice for Advanced Studies in Theoretical Physics, Quantum Materials Center, Physics and Astronomy, is set to receive funding for the project: “Electronic, transport and topological properties of frustrated magnets.”
In this project, Mazin and his collaborators will examine frustrated magnetic systems.
Magnetic frustration lies at the core of the notion of skyrmions and quantum spin liquid.
Mazin will receive $258,480 from the National Science Foundation for this project. Funding will begin in May 2024 and will end in late April 2027.
###
ABOUT GEORGE MASON UNIVERSITY
George Mason University is Virginia’s largest ...
TCT 2024 Career Achievement Award to be presented to Robert A. Harrington, MD
2024-04-29
NEW YORK – April 25, 2024 – The TCT® 2024 Career Achievement Award will be presented to Robert A. Harrington, MD, during Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics® (TCT®), the annual scientific symposium of the Cardiovascular Research Foundation® (CRF®). TCT® will take place October 27-30 2024, in Washington, DC at the Walter E. Washington Convention Center. The award is given each year to an outstanding individual who has made extraordinary contributions to the field of interventional cardiology and has transformed ...
Tibetan plateau had broader social dimensions than previously thought
2024-04-29
The Tibetan plateau—the world’s highest and largest plateau—poses a challenge to the people who live there because of its extreme climate. In a new study, researchers have discovered stone artifacts that suggest that there were more cultural exchanges between those who lived on the plateau and those living on its perimeter.
“The Tibetan plateau has an average elevation of more than 4500 meters, which makes Colorado seem like it is at sea level. It’s amazing that people have been able to occupy this area on and off for at least the last 40,000 years,” said Stanley Ambrose (MME), a professor of anthropology. “Unfortunately, very little ...
Oncotarget sponsors 19th International p53 Workshop in Italy
2024-04-29
Oncotarget is a contributing sponsor at the 19th International p53 Workshop in Trieste, Italy, on May 13–16, 2024.
BUFFALO, NY- April 29, 2024 – Oncotarget is a contributing sponsor at the 19th International p53 Workshop, organized by the International Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (ICGEB), which takes place from May 13–16, 2024, in Trieste, Italy.
“Groundbreaking research and cutting-edge advancements in the field of the most studied human gene and most frequently mutated gene in cancer, will take center stage at the 19th ...
NYS solar work: Good for climate, but are they good jobs?
2024-04-29
ITHACA, N.Y. -- New York state solar construction workers – whose numbers are expected to grow rapidly to meet climate goals – are transient, may not receive benefits and are subject to racial disparities in pay, finds a new report from the Climate Jobs Institute (CJI) at Cornell University.
“Exploring the Conditions of the New York Solar Workforce” was funded by the New York State Department of Labor and surveyed more than 260 solar installation and maintenance workers. The exploratory study is the first to focus on workers’ experiences, seeking to bridge gaps in government and industry ...
New system boosts efficiency of quantum error correction
2024-04-29
The fragile qubits that make up quantum computers offer a powerful computational tool, yet also present a conundrum: How can engineers create practical, workable quantum systems out of bits that are so easily disturbed — and wiped of data — by tiny changes in their environment?
Engineers have long struggled with how to make quantum computers less error-prone, often by developing ways to detect and correct errors rather than prevent them in the first place. However, many such error-correction schemes involve duplicating information across hundreds or thousands of physical qubits at once, which quickly becomes hard to scale up in an efficient way.
Now, ...
Study suggests staying current with COVID-19 vaccinations helps combat emerging variants
2024-04-29
New research using live SARS-CoV-2 virus reveals an updated vaccine provides a strong immune response against previous strains and emerging variants.
The findings by researchers at Oregon Health & Science University, published in the journal Emerging Infectious Diseases, suggest a clear benefit in receiving updated vaccinations on a regular basis, especially among older people or those with underlying medical conditions.
“The virus is still circulating, it’s continuing to evolve, and it remains dangerous,” said co-senior author Fikadu Tafesse, Ph.D., associate professor of molecular ...
[1] ... [1209]
[1210]
[1211]
[1212]
[1213]
[1214]
[1215]
[1216]
1217
[1218]
[1219]
[1220]
[1221]
[1222]
[1223]
[1224]
[1225]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.