It’s all in the smile: Aston University-led research finds politicians can influence voters with facial expressions
2024-04-29
Dr Carl Senior identified two types of smile – affiliative and reward – given by political leaders during the last UK general election in 2019
The eventual winner, Boris Johnson, was found to display the affiliative smile, which acts to align voter behaviour
The study is the first to look at how supporters of election losers react to the eventual winner.
New research led by Aston University’s Dr Carl Senior has found that the type of smile used by a political leader can influence voters to support them and their political agenda.
There are many different types of smile, and the ...
Possible alternative to antibiotics produced by bacteria
2024-04-29
Many bacteria produce substances to gain an advantage over competitors in their highly competitive natural environment. Researchers at the University Hospital Bonn (UKB), the University of Bonn and the German Center for Infection Research (DZIF) have discovered a new so-called lantibiotic, namely epilancin A37. It is produced by staphylococci that colonize the skin and acts specifically against their main competitors there, the corynebacteria. This specificity is presumably mediated by a very special mechanism of action, which the researchers were able to decipher in detail. ...
Quantitative study assesses how gender and race impact young athletes’ perceptions of their coaches
2024-04-29
Quantitative study assesses how gender and race impact young athletes’ perceptions of their coaches
Across the U.S., there are over 8 million student-athletes in high school and college. Engaging in sports can contribute to physical, mental, and social benefits, and coaches can play a key role in student-athletes’ continued participation in sports.
A recent study led by UNC Greensboro’s Dr. Tsz Lun (Alan) Chu, published in Sport, Exercise, and Performance Psychology, examines how multiple aspects of a young athlete’s ...
Enzymes open new path to universal donor blood
2024-04-29
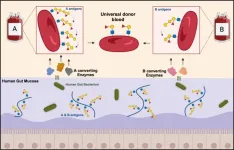
The quest to develop universal donor blood has taken a decisive step forward. Researchers at DTU and Lund University have discovered enzymes that, when mixed with red blood cells, are able to remove specific sugars that make up the A and B antigens in the human ABO blood groups. The results have been published in the scientific journal Nature Microbiology.
"For the first time, the new enzyme cocktails not only remove the well-described A and B antigens, but also extended variants previously not recognized as problematic for transfusion safety. We are close to being able to produce universal blood from group B donors, while there is still work to be done to convert ...
Gemini south reveals origin of unexpected differences in giant binary stars
2024-04-29
It is estimated that up to 85% of stars exist in binary star systems, some even in systems with three or more stars. These stellar pairs are born together out of the same molecular cloud from a shared abundance of chemical building blocks, so astronomers would expect to find that they have nearly identical compositions and planetary systems. However, for many binaries that isn’t the case. While some proposed explanations attribute these dissimilarities to events occurring after the stars evolved, a team of astronomers have confirmed for the first time that they can actually originate ...
Hornets found to be primary pollinators of two Angelica species
2024-04-29
Researcher Ko Mochizuki of the University of Tokyo discovered that two species in the genus Angelica are pollinated primarily by hornets. This overturns the conventional belief that Angelica species are “generalists,” meaning that there is not one primary pollinator but a variety of species. As hornets are rarely primary pollinators, the discovery also impacts future ecological research and conservation efforts. The findings were published in the journal Ecology.
White, small, open, secretes nectar and produces pollen: these are the kinds of flowers that many types of insects can reach ...
Aspirin vs placebo as adjuvant therapy for breast cancer
2024-04-29
About The Study: In this randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial that included 3,020 patients with high-risk nonmetastatic breast cancer, daily aspirin therapy did not improve risk of breast cancer recurrence or survival in early follow-up. Despite its promise and wide availability, aspirin should not be recommended as an adjuvant breast cancer treatment.
Authors: Wendy Y. Chen, M.D., of the Dana Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
Association of new-onset seizures with SARS-CoV-2 vaccines
2024-04-29
About The Study: This systematic review and meta-analysis showed that the incidence proportion of new-onset seizures after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination was not statistically different between vaccine recipients and placebo recipients or unvaccinated participants in the pooled analyses of more than 118,000 participants in randomized clinical trials.
Authors: Churl-Su Kwon, M.D., M.P.H., of Columbia University in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2024.0967)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including ...
How can forests be reforested in a climate-friendly way?
2024-04-29
Europe's forests have already been severely affected by climate change. Thousands of hectares of trees have already died due to drought and bark beetles. Scientists from the University of Vienna and the Technical University of Munich TUM have now investigated which trees can be used for reforestation. Their findings: only a few tree species are fit for the future, such as English oak in the UK. However, mixed forests are important for the survival of forests, otherwise the forest ecosystem as a whole could be weakened. The results of the study were recently published in the renowned journal Nature Ecology and Evolution.
Although European forests are naturally home to a ...
More plants on the menu of ancient hunter-gatherers
2024-04-29
Conducted by an international team of scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology (Leipzig, Germany), Géoscience et Environnement Toulouse (Toulouse, France), and the Institut National des Sciences de l’Archéologie et du Patrimoine (Rabat, Morocco), the study examines the diet of individuals associated with the Iberomaurusian culture discovered in the cave of Taforalt, Morocco. Using a comprehensive multi-isotopic approach, including zinc and strontium isotope analysis in dental enamel, carbon, nitrogen, ...
The aspirin conundrum: navigating negative results, age, aging dynamics and equity
2024-04-29
WASHINGTON – A new study examining the role of aspirin in breast cancer treatment reveals critical issues related to health equity and aging that have broad implications for cancer and other disease intervention trials, say researchers from Georgetown University’s Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center. They outline their concerns in an editorial accompanying the study’s findings published April 29 in the JAMA (“The Aspirin Conundrum: Navigating Negative Results, Age, Aging Dynamics and Equity”).
The ...
Cancer screening rates are significantly lower in US federally qualified health centers
2024-04-29
HOUSTON and ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. ― A national study led by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and The University of New Mexico (UNM) Comprehensive Cancer Center found major gaps in breast, cervical and colorectal cancer screening use in Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHCs) in the U.S., relative to overall screening rates in the country.
The findings, published today in JAMA Internal Medicine, revealed screening use in FQHCs was 45.4% for breast cancer, 51% for cervical cancer and 40.2% for colorectal cancer, compared to cancer screening rates in the general American population of 78.2%, 82.9% and 72.3%, respectively.
“FQHCs ...
Nature's nudge: Study shows green views lead to healthier food choices
2024-04-29
Natural scenery typically conjures up positive emotions and a sense of wellbeing for most individuals. A new study by INSEAD shows that verdant views can also nudge people to pick healthier food.
Published in Communications Psychology, a new journal by Nature, the study suggests that spending time in a natural setting, such as walking in a park (vs. on city streets), or simply viewing greenery outside the window (vs. an urban view), leads people to make healthier food choices afterward.
“Our ...
AI algorithms can determine how well newborns nurse, study shows
2024-04-29
A modified pacifier and AI algorithms to analyze the data it produces could determine if newborns are learning the proper mechanics of nursing, a recent study shows.
Specifically, the researchers from the University of California San Diego measured if babies are generating enough suckling strength to breastfeed and whether they are suckling in a regular pattern based on eight independent parameters.
The results, published in the April 18 online edition of IEEE Journal of Translational Engineering ...
Scientists develop new organoid model to study thymus function
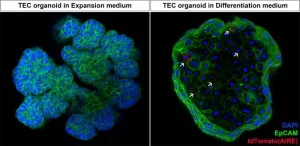
2024-04-29
Researchers from the Organoid group have developed a new organoid model that can be used to study the thymus. The organoids, derived from mouse thymus tissue, specifically model thymic epithelial cells (TECs). These cells are responsible for training the T cells of the immune system to properly respond to pathogens. It is the first laboratory model that enables long-term culture of TECs, which presents new opportunities to study their function. Ultimately, this could also bring new insights into the treatment ...
A revised classification of primary iron overload syndromes
2024-04-29
Background and Aims
The clinical introduction of hepcidin25 (Hep25) has led to a more detailed understanding of its relationship with ferroportin (FP) and divalent metal transporter1 in primary iron overload syndromes (PIOSs). In 2012, we proposed a classification of PIOSs based on the Hep25/FP system, which consists of prehepatic aceruloplasminemia, hepatic hemochromatosis (HC), and posthepatic FP disease (FP-D). However, in consideration of accumulated evidence on PIOSs, we aimed to renew the classification.
Methods
We ...
Expanding health equity by including nursing home residents in clinical trials
2024-04-29
INDIANAPOLIS – Clinical trials are constantly being designed and study participants enrolled to determine if medical treatments and therapies are safe and effective. Much has been written about the importance of including diverse populations in these trials.
However, the nearly 1.4 million individuals who live in the 15,600 nursing homes across the U.S. have been largely left out of clinical trials, despite the prevalence of such common conditions as hypertension, depression, diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease in this population.
A commentary by faculty of Regenstrief Institute, Indiana University, UCLA ...
Identification and exploration of transcripts involved in antibiotic resistance mechanism of two critical superbugs
2024-04-29
Background and objectives
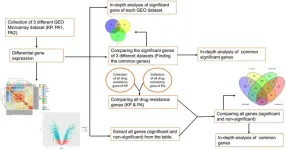
Infectious diseases caused by pathogenic strains of bacteria are a global cause of morbidity and mortality. Hospital-acquired infections caused by Klebsiella pneumonia and Pseudomonas aeruginosa were found vulnerable during the COVID-19 pandemic. They are also responsible for the onset of certain life-threatening infectious diseases such as cystic fibrosis, endocarditis, bacteremia, and sepsis. Looking into the importance of these two superbugs there is a strong need for extensive comparative differential gene expression analysis ...
Quantum fiber optics in the brain enhance processing, may protect against degenerative diseases
2024-04-29
WASHINGTON, DC – (April 26, 2024) The effects of quantum mechanics—the laws of physics that apply at exceedingly small scales—are extremely sensitive to disturbances. This is why quantum computers must be held at temperatures colder than outer space, and only very, very small objects, such as atoms and molecules, generally display quantum properties. By quantum standards, biological systems are quite hostile environments: they’re warm and chaotic, and even their fundamental components—such as cells—are considered very large.
But ...
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai names Miriam Merad, MD, PhD, as Dean for Translational Research and Therapeutic Innovation
2024-04-29
New York, NY [April 29, 2024]—Miriam Merad, MD, PhD, a world-renowned immunologist, has been appointed Dean for Translational Research and Therapeutic Innovation of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. The appointment reaffirms Icahn Mount Sinai’s commitment to pioneering medical progress and catalyzing the rapid advancement of research innovation.
Dr. Merad, the Mount Sinai Professor in Cancer Immunology, will also continue to serve as the founding Chair of the Department of Immunology and Immunotherapy, Director of the Marc and Jennifer Lipschultz Precision Immunology Institute, and Director ...
Details of hurricane Ian’s aftermath captured with new remote sensing method
2024-04-29
Category 4 Hurricane Ian made landfall in Florida’s Lee County on Sept. 28, 2022, battering the region with wind speeds of 155 miles per hour and storm surge up to 13 feet – the highest storm surge documented in Southwest Florida in the past 150 years.
In the aftermath of a disaster, rapidly assessing damage is critical for rescue, recovery and emergency planning. Damage assessments are typically conducted through field reconnaissance deployments, which can be labor-intensive, costly and risky. Moreover, field-based emergency response ...
Robots can’t outrun animals. A new study explores why
2024-04-29
The question may be the 21st century’s version of the fable of the tortoise and the hare: Who would win in a foot race between a robot and an animal?
In a new perspective article, a team of engineers from the United States and Canada, including University of Colorado Boulder roboticist Kaushik Jayaram, set out to answer that riddle. The group analyzed data from dozens of studies and came to a resounding “no.” In almost all cases, biological organisms, such as cheetahs, cockroaches and even humans, seem to be able to outrun their robot counterparts.
The researchers, led by Samuel Burden at the University of Washington and ...
The Human Immunome Project unveils scientific plan to decode and model the immune system
2024-04-29
NEW YORK, April 29, 2024 – The Human Immunome Project (HIP), a global nonprofit scientific initiative, released its Scientific Plan today, on World Immunology Day, the organization announced. The plan provides a detailed roadmap of how the Human Immunome Project and its network of global study sites will generate the world’s largest and most diverse immunological dataset and use these data to power publicly available AI models of the immune system.
“The immune system is the epicenter of human health, and our newly released ...
New research funding awarded to assess the role of race in predicting heart disease
2024-04-29
Highlights:
The American Heart Association awarded four new scientific research grants to evaluate the role of race in measuring heart disease risk.
The funded studies are focused on multi-ethnic groups and studying how race, considered a social rather than biological construct, affects health risk prediction when it is incorporated as a variable in algorithms.
This research is funded by a grant from the Doris Duke Foundation to study the complex issue of how race and ethnicity, when factored into cardiovascular clinical care algorithms ...
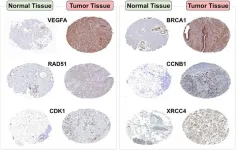
Exploring the role of seven key genes in breast cancer: insights from in silico and in vitro analyses
2024-04-29
Background and objectives
Breast cancer remains a significant global health concern, warranting further exploration into its genetic basis and potential therapeutic targets. This study aimed to elucidate the genetic associations of seven pivotal genes with breast cancer and discern their potential role in disease prognosis.
Methods
The genes VEGFA, BRCA1, RAD51, CCNB1, CHEK1, CDK1, and XRCC4 were curated from over 30 articles. Their association with breast cancer was analyzed using both in silico and in vitro techniques. The in silico assessment ...
[1] ... [1210]
[1211]
[1212]
[1213]
[1214]
[1215]
[1216]
[1217]
1218
[1219]
[1220]
[1221]
[1222]
[1223]
[1224]
[1225]
[1226]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.