How likely are English learners to graduate from high school? New study shows it depends on race, gender, and income
2024-05-06
English learners are, on average, less likely to graduate high school in four years than students who never needed to learn English in school. But social identities like race and gender make a difference, and some groups of English learners are actually more likely to graduate, according to a new study by a team of education researchers at NYU and the University of Houston.
For instance, young women who ever learned English in school are more likely to graduate in four years than young men who did not. Similarly, Black English learners tend to have better four-year graduation rates than Black peers who never needed to learn English ...
SwRI’s Herron named 2024 ASSP Safety Professional of the Year
2024-05-06
SAN ANTONIO — May 6, 2024 —The American Society of Safety Professionals (ASSP) has named Southwest Research Institute’s Matthew Herron, M.S., P.E., CSP, CPE, its 2024 Safety Professional of the Year. The award is presented annually to an ASSP member who demonstrates outstanding achievement in the occupational safety and health (OSH) field while also advancing the OSH profession overall.
“It’s a great honor to be recognized by the ASSP as Safety Professional of the Year,” said Herron, a lead safety engineer in SwRI’s Mechanical Engineering Division. “I firmly ...
Long-term cardiovascular outcomes in children and adolescents with hypertension
2024-05-06
About The Study: Children diagnosed with hypertension had a higher associated long-term risk of major adverse cardiac events compared with controls without hypertension. Improved detection, follow-up, and control of pediatric hypertension may reduce the risk of adult cardiovascular disease.
Authors: Rahul Chanchlani, M.B.B.S., M.D., M.Sc., of McMaster University in Hamilton, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2024.1543)
Editor’s ...
CRIPSR gene editing leads to improvements in vision for people with inherited blindness, clinical trial shows
2024-05-06
KEY TAKEAWAYS
BRILLIANCE trial results showed 11 out of 14 treated participants experienced some improvements in vision and quality of life measures.
CRISPR-based therapy was found safe with no dose-limiting toxicities reported.
Mass Eye and Ear researchers say their findings support continued research and clinical trials of CRISPR therapies for inherited retinal disorders.
BOSTON- (MAY 6, 2024) Results from a groundbreaking clinical trial of CRISPR gene editing in 14 individuals ...
Improvement seen in most participants of pioneering CRISPR gene editing trial
2024-05-06
PORTLAND, Oregon – About 79% of clinical trial participants experienced measurable improvement after receiving experimental, CRISPR-based gene editing that is designed to fix a rare form of blindness, according to a paper published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“This trial shows CRISPR gene editing has exciting potential to treat inherited retinal degeneration,” said Mark Pennesi, M.D., Ph.D., a corresponding author on the paper, an ophthalmologist and Oregon Health & Science University’s lead scientist for the Phase ...
Cybersecurity education varies widely in US
2024-05-06
PULLMAN, Wash. -- Cybersecurity programs vary dramatically across the country, a review has found. The authors argue that program leaders should work with professional societies to make sure graduates are well trained to meet industry needs in a fast-changing field.
In the review, published in the Proceedings of the Association for Computing Machinery’s Technical Symposium on Computer Science Education, a Washington State University-led research team found a shortage of research in evaluating the instructional approaches being used to teach cybersecurity. The authors also contend that programs ...
New vaccine effective against coronaviruses that haven’t even emerged yet
2024-05-06
Researchers have developed a new vaccine technology that has been shown in mice to provide protection against a broad range of coronaviruses with potential for future disease outbreaks - including ones we don’t even know about.
This is a new approach to vaccine development called ‘proactive vaccinology’, where scientists build a vaccine before the disease-causing pathogen even emerges.
The new vaccine works by training the body’s immune system to recognise specific regions of eight different coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-1, SARS-CoV-2, and several that are ...
Simulated chemistry: New AI platform designs tomorrow’s cancer drugs
2024-05-06
Scientists at UC San Diego have developed a machine learning algorithm to simulate the time-consuming chemistry involved in the earliest phases of drug discovery, which could significantly streamline the process and open doors for never-before-seen treatments. Identifying candidate drugs for further optimization typically involves thousands of individual experiments, but the new artificial intelligence (AI) platform could potentially give the same results in a fraction of the time. The researchers used the new tool, described in Nature Communications, to synthesize 32 new drug candidates for cancer.
The technology is part of a new but growing trend ...
Human ‘neural compass’ pinpointed in new study
2024-05-06
A pattern of brain activity that helps prevent us from getting lost has been identified in a new study, published in Nature Human Behaviour.
Researchers at the University of Birmingham and Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich have for the first time been able to pinpoint the location of an internal neural compass which the human brain uses to orientate itself in space and navigate through the environment.
The research identifies finely tuned head direction signals within the brain. The results are comparable to neural codes identified in ...
Personalized screening early in pregnancy may improve preeclampsia detection
2024-05-06
Research Highlights:
A personalized screening algorithm for preeclampsia in the first trimester of pregnancy may help clinicians better predict who is at risk for developing the condition and who may benefit from treatment with a daily, low-dose aspirin.
In this study of more than 7,000 women, the new screening method, which combined maternal history, biomarker tests and ultrasound tests, was better at identifying preeclampsia risk in than current risk factor-based guidelines.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Monday, May 6, 2024
DALLAS, May 6, 2024 — A new screening algorithm for preeclampsia combining maternal history, ...
Expanding a lymph node, boosting a vaccine
2024-05-06
Expanding a lymph node, boosting a vaccine
A biomaterial vaccine enhances and sustains lymph node expansion following vaccination, boosting anti-tumor immunity in an animal model.
By Benjamin Boettner
(BOSTON) — Each one of us has around 600 lymph nodes (LNs) – small, bean-shaped organs that house various types of blood cells and filter lymph fluid – scattered throughout our bodies. Many of us have also experienced some of our LNs to temporarily swelling during infections with viruses or other pathogens. This LN expansion and subsequent contraction can also result from vaccines injected nearby, and in fact ...
GIST-MIT CSAIL researchers develop a biomechanical dataset for badminton performance analysis
2024-05-06
In sports training, practice is the key, but being able to emulate the techniques of professional athletes can take a player’s performance to the next level. AI-based personalized sports coaching assistants can make this a reality by utilizing published datasets. With cameras and sensors strategically placed on the athlete's body, these systems can track everything, including joint movement patterns, muscle activation levels, and gaze movements.
Using this data, personalized feedback is provided on player technique, along with improvement recommendations. Athletes can access this feedback anytime, and anywhere, making these systems versatile for athletes at ...
Study sheds light on 11th century Arab-Muslim optical scientist whose work laid ground for modern-day physics
2024-05-06
Scientists from the University of Sharjah and the Warburg Institute are poring over the writings of an 11th century Arab-Muslim polymath to demonstrate their impact on the development of optical sciences and how they have fundamentally transformed the history of physics from the Middle Ages up to modern times in Europe.
Their research focuses on the legacy of al-Ḥasan Ibn al-Haytham known in Latin as “Alhazen” and particularly his most influential work titled Book of Optics, reputed in Arabic as Kitab al-Manazir and first circulated in Europe via its Latin translation dubbed ‘Perspectiva’. Ibn ...
Rethinking “socially admitted” patients
2024-05-06
Labelling vulnerable patients in hospital as “socially admitted” may prevent treatment of medical issues, according to new research in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231430.
Emergency departments are the last resort for some socially vulnerable people who may not have an acute or new medical issue. They may be seeking care because of a breakdown of supports or the inability of the patient, or their family, to cope with living at home. These people are known colloquially as “social admissions,” and other labels such as “orphan patient,” “failure ...
A better way to ride a motorcycle
2024-05-06
Motorcycles are designed to accommodate the average-sized rider, leaving taller and shorter riders vulnerable to discomfort.
A new study from the University of Waterloo used software that predicted realistic motorcycle riding behaviours, considering human factors and ergonomic trade-offs. It found that shorter and taller statures require joint adjustments to achieve their preferred riding posture.
Taller riders are required to flex their ankles, knees, hips and elbows more to interact with the motorcycle properly, ...
Survey of US parents highlights need for more awareness about newborn screening, cystic fibrosis and what to do if results are abnormal
2024-05-05
A national survey led by Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago found that parents have insufficient knowledge of newborn screening in general and of cystic fibrosis (CF) in particular. Researchers asked specific questions about CF based on studies showing that initial CF follow-up visits after a positive newborn screening often occur after 4 weeks of age, which is later than the recommended timeframe for best outcomes. Later follow-up is associated with worse nutrition in childhood, a predictor of long-term health in CF. Parents ...
Outcomes of children admitted to a pediatric observation unit with a psychiatric comanagement model
2024-05-05
About The Study: The findings of this study show a significantly lower pediatric emergency department length of stay and inpatient psychiatric admission rate following pediatric observation unit care and potential savings in inpatient psychiatric resources without contributing to 30-day readmission rates.
Authors: Rachel G. Kasdin, M.S., of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2024.1123)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...
SCAI announces 2024-25 SCAI-WIN CHIP Fellowship Recipient
2024-05-05
LONG BEACH (May 4, 2024) Mariem A. Sawan, MBBS, chief interventional cardiology fellow at Emory University, has been selected as the recipient of the SCAI-Women in Innovations (SCAI-WIN) CHIP Fellowship, the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions announced today.
The $115,000 fellowship opportunity was made possible by support from Abiomed (founding supporter), Boston Scientific, Medtronic, and Shockwave Medical, Inc., and is offered to interventional cardiology (IC) fellows or practicing interventional cardiologists ...
SCAI’s 30 in Their 30’s Award recognizes the contributions of early career interventional cardiologists
2024-05-05
LONG BEACH (May 4, 2024) During SCAI 2024 Scientific Sessions, the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) presented its "30 in Their 30’s" award to thirty early-career interventional cardiologists.
This award program recognizes the excellence of these members for their outstanding leadership and demonstration of SCAI's core values and is designed to encourage and support young interventional cardiologists who have already made a significant impact in the field.
Recipients include:
Aakash Garg, MD, FSCAI
Adnan Khalif, MD, FSCAI
Alejandro ...
SCAI Emerging Leaders Mentorship Program welcomes a new class of interventional cardiology leaders
2024-05-05
LONG BEACH (May 4, 2024) The Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) is pleased to announce the selection of 12 new early-career interventional cardiologists to participate in the 2024-2026 Emerging Leader Mentorship (ELM) Program.
The ELM Fellows program is a two-year training and mentorship program designed to help participants enhance their skills and prepare for leadership positions in medicine. The program is offered in collaboration with the American College of Cardiology and the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
The ELM Selection Committee chose 12 individuals based on their leadership ...
SCAI bestows highest designation ranking to leading interventional cardiologists
2024-05-05
LONG BEACH (May 4, 2024) Today, the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) announced its 2025 Master Interventionalists of SCAI (MSCAI) designation recipients during the SCAI 2025 Scientific Sessions in Long Beach.
The MSCAI designation is awarded to individuals who have demonstrated excellence in invasive/interventional cardiology over the course of their career and for their commitment to the highest levels of clinical care, innovation, publication, and teaching.
This year’s MSCAI ...
SCAI names James B. Hermiller, MD, MSCAI, President for 2024-25
2024-05-05
LONG BEACH (May 4, 2024) James B. Hermiller, MD, MSCAI, director of the Interventional Cardiology Fellowship and the Structural Heart Program at St. Vincent Ascension Heart Center in Indianapolis, IN, assumed the office of president of the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) today during the closing ceremonies at the SCAI 2024 Scientific Sessions in Long Beach, CA.
An interventional cardiologist, researcher, and teacher, Hermiller has been an author, leading enroller, primary investigator, and steering committee member in many transcatheter therapy studies, including multiple pivotal trials of structural heart disease. ...
Racial and ethnic disparities in all-cause and cause-specific mortality among US youth
2024-05-04
About The Study: Racial and ethnic disparities were observed for almost all leading causes of injury and disease that were associated with recent increases in youth mortality rates. Addressing the increasing disparities affecting American Indian or Alaska Native and Black youth will require efforts to prevent homicide and suicide, especially those events involving firearms.
Authors: Elizabeth R. Wolf, M.D., M.P.H., of the Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine in Richmond, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.3908)
Editor’s ...
Ready to launch program introduces medical students to interventional cardiology field
2024-05-04
LONG BEACH (May 4, 2024) Interventional cardiology's future success relies on a diverse workforce that will help to positively impact patient outcomes. Now in its second year, SCAI’s Ready to Launch program introduces the interventional cardiology field to a diverse group of medical students at all levels, providing hands-on experience and mentorship opportunities. The program is hosted annually during SCAI Scientific Sessions with participation from local medical schools.
“This ...
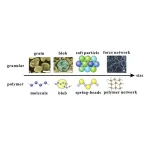
Variety in building block softness makes for softer amorphous materials
2024-05-04
Tokyo, Japan – Scientists from Tokyo Metropolitan University have created a new model for disordered materials to study how amorphous materials resist stress. They treated groups of atoms and molecules as squishy spheres with varying softness. Putting their model under a load, they discovered unexpected disparities between harder regions and where forces were concentrated, with areas in between such regions “hardening” to produce elongated “force chains”. Their findings promise new insights into designing better materials.
When it comes to building hard materials, using hard ingredients is not enough. For example, when concrete fails during ...
[1] ... [1202]
[1203]
[1204]
[1205]
[1206]
[1207]
[1208]
[1209]
1210
[1211]
[1212]
[1213]
[1214]
[1215]
[1216]
[1217]
[1218]
... [8831]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.