U of T researchers target neurogenesis in new approach to treat Parkinson’s disease
2024-04-30
Researchers at the University of Toronto have found a way to better control the preclinical generation of key neurons depleted in Parkinson’s disease, pointing toward a new approach for a disease with no cure and few effective treatments.
The researchers used an antibody to selectively activate a receptor in a molecular signaling pathway to develop dopaminergic neurons. These neurons produce dopamine, a neurotransmitter critical to brain health.
Researchers around the world have been working to coax stem cells to differentiate into dopaminergic ...
Microbiome researchers challenge the state of the art in colon cancer biomarker discovery
2024-04-30
Leuven (Belgium) 30/04/2024 - For the first time, researchers from VIB-KU Leuven, UZ Leuven, Janssen Pharmaceutica and multiple international collaborators have introduced quantitative methods and extensive confounder control to discover microbiome biomarkers in colorectal cancer development. While multiple microbial taxa have been put forward as potential cancer-associated biomarkers in the past, this new study uncovers obscured contributions that may have resulted in incorrect associations. The results have been published in Nature Medicine.
Cancer ...
Unveiling nature's custodians: groundbreaking study highlights crucial role of scavengers in wetlands
2024-04-30
A pioneering study highlights the importance of carrion and scavengers in wetlands on a global scale. A study by researchers from the Ecology area of the Miguel Hernández University of Elche (UMH) and the Ecology department of the University of Alicante (UA) reveals the fundamental importance of scavengers and carrion in wetlands. The article, published in Biological Reviews, emphasizes that the benefits provided by scavengers far outweigh the potential drawbacks. Among their essential functions are the recycling and transportation of nutrients and the regulation of water quality, benefiting the entire ecosystem, from soil and plants to birds and mammals.
Historically, ...
Data scarcity challenges identification of endocrine disruptors
2024-04-30
As a result, the researchers recommend updating the information requirements in the EU legislation, REACH. They also propose various approaches for evaluating chemical substances to ensure that all available information is fully utilized.
Researchers from DTU National Food Institute and the University of Southern Denmark have screened the scientific literature for the Danish Environmental Protection Agency to find substances showing signs of endocrine disrupting properties and thus being potentially harmful to humans and ...
A significant portion of the world’s population continues to trust vaccines, says survey in 23 countries
2024-04-30
A substantial proportion of the world’s population remains willing to get vaccinated against diseases including COVID-19, according to a new survey across 23 countries that represent more than 60% of the world’s population. The study, published in Nature Medicine, was co-led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by “la Caixa” Foundation, and the Graduate School of Public Health and Health Policy of the City University of New York (CUNY SPH).
The severe human impact of the COVID-19 pandemic led to the rapid research and development of safe and effective vaccines based on existing models, ...
Clumps of this molecule inhibit strep’s DNA-cleaving enzymes
2024-04-30
An entirely new approach to inhibiting DNA-cleaving enzymes works through the aggregation of an otherwise non-toxic molecule. This Kobe University discovery may lead to a much-needed method for curbing Streptococcus growth.
Enzymes are the body’s tools to make almost all reactions happen. But the same is true for bacteria like Streptococcus, which causes toxic shock syndrome, a rapidly progressing and deadly condition. When the body’s white blood cells try to capture the bacteria by casting nets made out ...
Cars as particles
2024-04-30
What do the flow of cars on a highway and the movement of bacteria towards a food source have in common? In both cases, annoying traffic jams can form. Especially for cars, we might want to understand how to avoid them, but perhaps we've never thought of turning to statistical physics, as Alexandre Solon, a physicist from Sorbonne Université, and Eric Bertin, from the University of Grenoble, both working for the Centre national de la recherche scientifique CNRS, have done. Their research, recently published in the Journal of Statistical Mechanics: Theory and Experiment (JSTAT), has developed a one-dimensional mathematical model ...
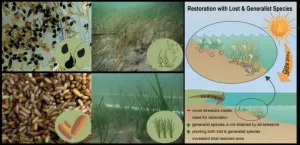
Let widgeongrass be a weed in the seagrass yard -- making seagrass restoration more resistant to rising temperatures using generalist grasses
2024-04-30
New research demonstrates that seagrass habitat restoration can be enhanced by including other grasses in addition to the declining or lost species and – ultimately – that restoration efforts must proactively select species that can withstand current and intensifying stressors driven by human activities and climate change.
Rising global temperatures combined with centuries of humans working within our seascapes has reshaped coastal ecosystems. Rebuilding or restoring coastal habitat is becoming ...
Group sales incentives boost weak brand sales, study finds
2024-04-30
New research co-authored by a UC Riverside business professor provides some sound advice for managers of retail outlets that limit their product selection to a particular brand: Managers should factor in the strength of their brand when structuring the pay incentives for their sales staff.
The study focused on what marketing scholars call “brand-managed” retail operations. These outlets include “stores within stores,” such as counters in major department stores with dedicated sales staff that offer just one brand of cosmetics such as Clinique. They can also be stores ...
The double-fanged adolescence of saber-toothed cats
2024-04-30
The fearsome, saber-like teeth of Smilodon fatalis — California's state fossil — are familiar to anyone who has ever visited Los Angeles' La Brea Tar Pits, a sticky trap from which more than 2,000 saber-toothed cat skulls have been excavated over more than a century.
Though few of the recovered skulls had sabers attached, a handful exhibited a peculiar feature: the tooth socket for the saber was occupied by two teeth, with the permanent tooth slotted into a groove in the baby tooth.
Paleontologist Jack Tseng, associate professor of integrative biology at the University of California, Berkeley, doesn't think the double fangs ...
COVID-19-induced financial hardships reveal mental health struggles
2024-04-30
When COVID-19 caused significant economic disruptions, thousands of people around the world experienced sudden shocks to their financial situation through reduced earnings or job losses.
Now economic researchers at the University of South Australia have examined the mental health effects on people who experienced immediate or expected financial setbacks during the height of the pandemic.
Data gathered from China, Japan and South Korea during the early phases of the pandemic revealed that the severe economic shocks induced by COVID-19 caused significant ...
Healthy lifestyle may offset effects of life-shortening genes by 60%+
2024-04-30
A healthy lifestyle may offset the effects of life-shortening genes by more than 60%, suggests an analysis of the findings from several large long term studies, published online in the journal BMJ Evidence Based Medicine.
While genes and lifestyle seem to have an additive effect on a person’s lifespan, an unhealthy lifestyle is independently linked to a 78% heightened risk of dying before one’s time, regardless of genetic predisposition, the research indicates.
The polygenic risk score (PRS) combines ...
Frequent teen vaping might boost risk of toxic lead and uranium exposure
2024-04-30
Frequent teen vaping might boost the risk of exposure to lead and uranium, potentially harming brain and organ development, suggests research published online in the journal Tobacco Control.
The findings underscore the need for implementation of regulations and prevention efforts targeting teens, emphasise the researchers.
Vaping is popular with teens. In 2022, an estimated 14% of US high school students—around 2.14 million—and more than 3% of middle school students—around 380,000—reported vaping in the preceding month, note the researchers.
Certain metals have been identified in e-cigarette aerosols and ...
Fentanyl inhalation may cause potentially irreversible brain damage, warn doctors
2024-04-30
Inhaling the synthetic opioid fentanyl may cause potentially irreversible brain damage (toxic leukoencephalopathy), warn doctors in the journal BMJ Case Reports, after treating a middle aged man found unresponsive in his hotel room after snorting the drug.
Leukoencephalopathy refers to inflammation and damage to the brain’s white matter—the network of nerve fibres that enable the exchange of information and communication between different areas of the brain’s grey matter.
Toxic leukoencephalopathy is a sudden or longstanding neurological syndrome, which ...
OHSU patient is world’s first documented case of brain disease from fentanyl inhalation
2024-04-30
The man arrived unconscious and near death.
Previously healthy with no known medical history, the 47-year-old arrived by ambulance to the emergency department at Oregon Health & Science University on Feb. 25, 2023. He was found collapsed in his hotel room, where he was staying during a business trip. As clinicians began administering life-saving treatment, they searched for the cause.
In a case report published online today in the journal BMJ Case Reports, clinicians laid out the surprising and unprecedented diagnosis: toxic ...
Microarray patches safe and effective for vaccinating children, trial shows
2024-04-30
EMBARGOED UNTIL 23:30 UK TIME MONDAY 29 APRIL 2024
Peer-reviewed/Randomised Control Trial/Humans
The phase 1/2 randomized trial compared results from the measles and rubella vaccine delivered by a microarray patch, a small sticking plaster-like device with an array of microscopic projections that painlessly penetrate the skin and deliver the vaccine, or by conventional injection with a needle and syringe.
The trial, which involved 45 adults (18-40 years old), 120 toddlers (15-18 months old) and 120 infants (9-10 months old) in The Gambia, ...
Montana State scientists’ research on RNA editing illuminates possible lifesaving treatments for genetic diseases
2024-04-30
BOZEMAN – A team at Montana State University published research this week that shows how RNA, the close chemical cousin to DNA, can be edited using CRISPRs. The work reveals a new process in human cells that has potential for treating a wide variety of genetic diseases.
Postdoctoral researchers Artem Nemudryi and Anna Nemudraia conducted the research alongside Blake Wiedenheft, professor in the Department of Microbiology and Cell Biology in MSU’s College of Agriculture. The paper, titled “Repair of CRISPR-guided RNA breaks enables site-specific RNA excision ...
UC Irvine astronomers’ simulations support dark matter theory
2024-04-30
Irvine, Calif., April 29, 2024 — Computer simulations by astronomers support the idea that dark matter – matter that no one has yet directly detected but which many physicists think must be there to explain several aspects of the observable universe – exists, according to the researchers, who include those at the University of California, Irvine.
The work addresses a fundamental debate in astrophysics – does invisible dark matter need to exist to explain how the universe works the way it ...
Rensselaer researcher publishes groundbreaking study on labor market discrimination against transgender people
2024-04-30
In 2020, the United States Supreme Court ruled in Bostock vs. Clayton County that transgender people are legally protected from employment discrimination. This came at a time of increased visibility, but also of legal and social challenges to the rights of transgender individuals. Meanwhile, there has been very little study of labor market discrimination against them. Rensselaer researcher Billur Aksoy, Ph.D., has recently conducted an innovative survey of Americans’ attitudes toward transgender people in the workplace.
Her paper, “Understanding Labor Market Discrimination Against Transgender ...
What's new in transportation data at PSU?
2024-04-30
Portland State University's Transportation Research and Education Center (TREC) maintains two large, public transportation data lakes: PORTAL and BikePed Portal. The latest round of funding for PORTAL, in the amount of $1.6 million, was awarded in February 2024 and will cover PORTAL's activities through the next five years. BikePed Portal, too, recently received $100K for another year of funding, and both are the focus of some exciting innovations in transportation data.
The two centralized ...
Ten-minute breath test to monitor antibiotic concentrations
2024-04-30
Test would be quicker and non-invasive but more research needed
**ECCMID has now changed name to ESCMID Global, please credit ESCMID Global Congress in all future stories**
Exhaled breath may be very promising alternative to blood for the therapeutic monitoring of antibiotics, the ESCMID Global Congress (formerly ECCMID) in Barcelona, Spain (27-30 April) will hear.
Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) is used to monitor antibiotic concentrations in patients with severe infections and in patients in intensive care units. These patients may metabolise drugs differently and so may not respond to conventional ...
Antimicrobial resistance prevalence varies by age and sex in bloodstream infections in European hospitals
2024-04-30
**ECCMID has now changed name to ESCMID Global, please credit ESCMID Global Congress in all future stories**
New research presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2024, Barcelona 27-30 April) shows that levels of resistance to antimicrobials (AMR) varies with age and sex, with age in particular showing substantial variation both between and within countries. The study is by Gwen Knight, Associate Professor at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine and co-Director of the LSHTM AMR Centre, London, UK, ...
Pathogens, including multi-drug resistant “superbugs”, found on floors, ceilings and door handles of hospital toilets, UK study finds
2024-04-30
Flushing of toilets without lids likely responsible for ceiling contamination
Put lid down before flushing at home, say the researchers
**ECCMID has now changed name to ESCMID Global, please credit ESCMID Global Congress in all future stories**
Pathogenic bacteria and fungi, including multi-drug resistant “superbugs” have been found on the floors, ceilings, door handles and other surfaces of hospital toilets in the UK, with patient toilets the worst affected, the ESCMID Global Congress (formerly ECCMID) in Barcelona, Spain (27-30 April) will ...
Sour Patch adults: 1 in 8 grown-ups love extreme tartness, study shows
2024-04-29
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — For most people, biting into a lemon would leave them puckered up and desperate to lose that sour flavor, but a new study by Penn State researchers revealed that roughly one in eight adults like intensely sour sensations. The cross-cultural study, recently published in the journal Food Quality and Preference, demonstrated there is a subset of “sour likers” who enjoy exceptionally sour foods.
“This is the first time it's been convincingly shown that there is a segment of adults who likes strongly sour things,” said John Hayes, professor ...
Vineyard Cares Business of the Year presented to Huntsman Cancer Institute
2024-04-29
Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah (the U) received the Vineyard Cares Business of the Year Award. This award, given by Vineyard as part of the Impact Vineyard Awards, honors businesses that have made significant contributions to the community.
“Receiving this award is a tremendous honor for Huntsman Cancer Institute,” says Mary Beckerle, PhD CEO of Huntsman Cancer Institute. “It underscores the incredible welcome we have received from the community as we work to expand access to world-class cancer research and care, bringing hope closer to home for our patients. I am grateful for the tireless dedication ...
[1] ... [1208]
[1209]
[1210]
[1211]
[1212]
[1213]
[1214]
[1215]
1216
[1217]
[1218]
[1219]
[1220]
[1221]
[1222]
[1223]
[1224]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.