From disorder to order: flocking birds and “spinning” particles
2024-04-26
Researchers Kazuaki Takasan and Kyogo Kawaguchi of the University of Tokyo with Kyosuke Adachi of RIKEN, Japan's largest comprehensive research institution, have demonstrated that ferromagnetism, an ordered state of atoms, can be induced by increasing particle motility and that repulsive forces between atoms are sufficient to maintain it. The discovery not only extends the concept of active matter to quantum systems but also contributes to the development of novel technologies that rely on the magnetic ...
Cardiovascular risk associated with social determinants of health at individual and area levels
2024-04-26
About The Study: The findings of this study of 26,000 participants from four large U.S. studies suggest that both individual- and area-level social determinants of health may be considered in future development of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk assessment tools, particularly among Black individuals.
Authors: Yiyi Zhang, Ph.D., of Columbia University Medical Center in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.8584)
Editor’s ...
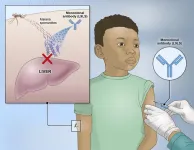
Experimental NIH malaria monoclonal antibody protective in Malian children
2024-04-26
One injected dose of an experimental malaria monoclonal antibody was 77% effective against malaria disease in children in Mali during the country’s six-month malaria season, according to the results of a mid-stage clinical trial. The trial assessed an investigational monoclonal antibody developed by scientists at the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and results appear in The New England Journal of Medicine.
“A long-acting monoclonal antibody delivered at a single health care visit that rapidly provides high-level protection against malaria in these vulnerable populations would fulfill an unmet public health need,” said Dr. Jeanne ...
Energy trades could help resolve Nile conflict
2024-04-26
Scientists have shed light on a new, transformative approach that could help resolve a dispute over the Nile river’s water resources.
The Nile is one of the longest rivers globally and spreads over 11 countries in East Africa, supplying water, energy production, environmental quality and cultural wealth. However, the use of Nile resources has been a long-standing source of tension, often overshadowing opportunities for cooperation and mutual benefit.
But as the demand for energy, water, and food in Africa is steadily increasing, the study, led by The University of Manchester in collaboration with regional organisations, offers a glimmer of hope at a resolution.
The research, ...
Homelessness a major issue for many patients in the emergency department
2024-04-26
Housing insecurity is an issue for 1 in 20 patients who go to emergency departments at major medical centers in the Southeast, according to a Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) study published in JAMA Network Open.
These patients were more likely to present with a chief complaint of suicide, to be uninsured, and to have multiple visits during the study period from Jan. 5 to May 16, 2023.
“This points to the importance of prioritizing mental health care and homeless ...
Undocumented Latinx patients got COVID-19 vaccine at same rate as US citizens
2024-04-26
For undocumented Latinx patients who sought care in the emergency room during the pandemic, the reported rate of having received the COVID-19 vaccine was found to be the same as U.S. citizens, a new UCLA Health study found. These findings surprised researchers, given that COVID-19 disproportionately affected the Latinx community in infections, hospitalizations, and death.
Dr. Jesus R. Torres, lead study author and emergency medicine physician at UCLA Health, aimed to study undocumented people because they tend not to be identified in existing research even though they comprise approximately 3% of the ...
ETRI develops an automated benchmark for labguage-based task planners
2024-04-26
If instructed to “Place a cooled apple into the microwave,” how would a robot respond?
Initially, the robot would need to locate an apple, pick it up, find the refrigerator, open its door, and place the apple inside. Subsequently, it would close the refrigerator door, reopen it to retrieve the cooled apple, pick up the apple again, and close the door. Following this, the robot would need to locate the microwave, open its door, place the apple inside, and then close the microwave door. Evaluating how well these steps are executed exemplifies the essence of ...
Revolutionizing memory technology: multiferroic nanodots for low-power magnetic storage
2024-04-26
Traditional memory devices are volatile and the current non-volatile ones rely on either ferromagnetic or ferroelectric materials for data storage. In ferromagnetic devices, data is written or stored by aligning magnetic moments, while in ferroelectric devices, data storage relies on the alignment of electric dipoles. However, generating and manipulating magnetic fields is energy-intensive, and in ferroelectric memory devices, reading data destroys the polarized state, requiring the memory cell to be re-writing.
Multiferroic materials, which contain both ferroelectric and ferromagnetic orders, offer a promising solution for more efficient ...
Researchers propose groundbreaking framework for future network systems
2024-04-26
In a new study published in Engineering, Academician Wu Jiangxing’s research team unveils a theoretical framework that could revolutionize the landscape of network systems and architectures. The paper titled “Theoretical Framework for a Polymorphic Network Environment,” addresses a fundamental challenge in network design—achieving global scalability while accommodating the diverse needs of evolving services.
For decades, the quest for an ideal network capable of seamlessly scaling across various dimensions has remained elusive. The team, however, has identified a critical barrier known as the “impossible service-level ...
New favorite—smart electric wheel drive tractor: realizes efficient drive with ingenious structure and intelligent control
2024-04-26
Electric tractors are intended to be used in the field instead of traditional fuel tractors and can be used in greenhouse planting, indoor farming, mountainous operations, and other special operating scenarios. Unlike traditional fuel tractors, electric tractors have no exhaust emissions, rapid drive system response, flexible power output, or other advantages. These scenarios require electric tractors to be able to adapt to complex drive and operating environments, putting higher requirements on the design of electric tractors and their control systems. Therefore, ...
Using stem cell-derived heart muscle cells to advance heart regenerative therapy
2024-04-26
Regenerative heart therapies involve transplanting cardiac muscle cells into damaged areas of the heart to recover lost function. However, the risk of arrhythmias following this procedure is reportedly high. In a recent study, researchers from Japan tested a novel approach that involves injecting ‘cardiac spheroids,’ cultured from human stem cells, directly into damaged ventricles. The highly positive outcomes observed in primate models highlight the potential of this strategy.
Cardiovascular diseases are still among the top causes of death worldwide, and especially prevalent ...
Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation awards Quantitative Biology Fellowships to four cutting-edge scientists
2024-04-26
Damon Runyon has announced its 2024 Quantitative Biology Fellows, four exceptional early-career scientists who are bringing cutting-edge computational tools to bear on some of the most important questions in cancer biology. From the packaging of DNA to mechanisms of chemotherapy resistance, their projects aim to shed light on these fundamental questions through large-scale data collection, mathematical modeling, and quantitative analysis.
“In the five years since we named the first class of Quantitative Biology Fellows, it has only become more evident that these scientists bring fresh perspectives and creative ...
Climb stairs to live longer
2024-04-26
Athens, Greece – 26 April 2024: Climbing stairs is associated with a longer life, according to research presented today at ESC Preventive Cardiology 2024, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
“If you have the choice of taking the stairs or the lift, go for the stairs as it will help your heart,” said study author Dr. Sophie Paddock of the University of East Anglia and Norfolk and Norwich University Hospital Foundation Trust, Norwich, UK. “Even brief bursts of physical activity have beneficial health impacts, and short bouts of stair climbing should be an achievable target to integrate into ...
Scientists capture X-rays from upward positive lightning
2024-04-26
Globally, lightning is responsible for over 4,000 fatalities and billions of dollars in damage every year; Switzerland itself weathers up to 150,000 strikes annually. Understanding exactly how lightning forms is key for reducing risk, but because lightning phenomena occur on sub-millisecond timescales, direct measurements are extremely difficult to obtain.
Now, researchers from the Electromagnetic Compatibility Lab, led by Farhad Rachidi, in EPFL’s School of Engineering have for the first time directly measured an elusive phenomenon that explains a lot about the birth of a lightning bolt: X-ray radiation. In a collaborative study with the University of Applied Sciences of Western ...
AMS Science Preview: Hawaiian climates; chronic pain; lightning-caused wildfires
2024-04-26
The American Meteorological Society continuously publishes research on climate, weather, and water in its 12 journals. Many of these articles are available for early online access–they are peer-reviewed, but not yet in their final published form.
Below is a selection of articles published early online recently. Some articles are open-access; to view others, members of the media can contact kpflaumer@ametsoc.org for press login credentials.
Routine Climate Monitoring in the State of Hawai‘i: Establishment of State Climate Divisions
Bulletin of the American Meteorological ...
Researchers advance detection of gravitational waves to study collisions of neutron stars and black holes
2024-04-26
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (04/26/2024) — Researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities College of Science and Engineering co-led a new study by an international team that will improve the detection of gravitational waves—ripples in space and time.
The research aims to send alerts to astronomers and astrophysicists within 30 seconds after the detection, helping to improve the understanding of neutron stars and black holes and how heavy elements, including gold and uranium, are produced.
The findings were recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS), a peer-reviewed, open access, scientific journal.
Gravitational ...
Automated machine learning robot unlocks new potential for genetics research
2024-04-26
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (04/26/2024) — University of Minnesota Twin Cities researchers have constructed a robot that uses machine learning to fully automate a complicated microinjection process used in genetic research.
In their experiments, the researchers were able to use this automated robot to manipulate the genetics of multicellular organisms, including fruit fly and zebrafish embryos. The technology will save labs time and money while enabling them to more easily conduct new, large-scale genetic experiments that were not possible previously using manual techniques
The research is featured on the cover of the ...
University of Toronto scientists appointed as GSK chairs will advance drug delivery research and vaccine education tools for healthcare professionals
2024-04-26
The University of Toronto’s Leslie Dan Faculty of Pharmacy has announced the appointments of two leading scientists as endowed GSK research chairs. These appointments represent the collaborative efforts between the two organizations to advance the field of pharmacy and drive positive change in patient care.
Anna Tadio, professor at the Leslie Dan Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Toronto, and senior associate scientist at The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) is the inaugural holder of the GSK Chair in Vaccine Education and Practice-Oriented Tools.
Bowen Li, ...
Air pollution and depression linked with heart disease deaths in middle-aged adults
2024-04-26
Athens, Greece – 26 April 2024: A study in more than 3,000 US counties, with 315 million residents, has suggested that air pollution is linked with stress and depression, putting under-65-year-olds at increased risk of dying from cardiovascular disease. The research is presented today at ESC Preventive Cardiology 2024, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
“Our study indicates that the air we breathe affects our mental well-being, which in turn impacts heart health,” ...
More efficient molecular motor widens potential applications
2024-04-26
Light-driven molecular motors were first developed nearly 25 years ago at the University of Groningen, the Netherlands. This resulted in a shared Nobel Prize for Chemistry for Professor Ben Feringa in 2016. However, making these motors do actual work proved to be a challenge. A new paper from the Feringa lab, published in Nature Chemistry on 26 April, describes a combination of improvements that brings real-life applications closer.
First author Jinyu Sheng, now a postdoctoral researcher at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA), adapted a ‘first generation’ light-driven molecular ...
Robotic nerve ‘cuffs’ could help treat a range of neurological conditions
2024-04-26
Researchers have developed tiny, flexible devices that can wrap around individual nerve fibres without damaging them.
The researchers, from the University of Cambridge, combined flexible electronics and soft robotics techniques to develop the devices, which could be used for the diagnosis and treatment of a range of disorders, including epilepsy and chronic pain, or the control of prosthetic limbs.
Current tools for interfacing with the peripheral nerves – the 43 pairs of motor and sensory nerves that connect the brain and the spinal cord – are outdated, bulky and carry a high risk of nerve injury. However, the robotic nerve ‘cuffs’ ...
Researchers identify targets in the brain to modulate heart rate and treat depressive disorders
2024-04-26
Study led by Brigham investigators suggests heart rate may be a useful tool to determine where to stimulate the brains of individuals with depressive disorders when brain scans aren’t available
A new study by researchers at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, suggests a common brain network exists between heart rate deceleration and depression. By evaluating data from 14 people with no depression symptoms, the team found stimulating some parts of the brain linked to depression with transcranial magnetic stimulation ...
Findings of large-scale study on 572 Asian families supports gene-directed management of BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene carriers in Singapore
2024-04-26
Singapore, 26 April 2024 – A team of clinician-scientists and scientists from the University of Nottingham (Malaysia campus), National Cancer Centre Singapore (NCCS), Cancer Research Malaysia, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore), University of Malaya, University of Cambridge, A*STAR’s Genome Institute of Singapore (GIS) and other institutions, have conducted the largest study done to date of BRCA1 and BRCA2 (BReast CAncer Gene 1 and 2) carriers in an Asian population and refined breast and ovarian cancer risk estimates for this population. The findings, ...
Many children with symptoms of brain injuries and concussions are missing out on vital checks, national US study finds
2024-04-26
Almost a quarter of US children with symptoms of a brain injury or concussion are not checked for the condition, with younger children particularly likely to be overlooked, a new national study finds.
The peer-reviewed US research, which is published in the journal Brain Injury, also shows that children with symptoms or a diagnosis of a brain injury or concussion were more likely to have symptoms of depression than other youngsters. They also found it harder to make friends.
Routine checks would help ensure such children receive the care that they need, says ...
Genetic hope in fight against devastating wheat disease
2024-04-26
Fungal disease Fusarium head blight (FHB) is on the rise due to increasingly humid conditions induced by climate change during the wheat growing season, but a fundamental discovery by University of Adelaide researchers could help reduce its economic harm.
While some types of wheat are resistant to FHB thanks to the action of the TaHRC gene at the Fhb1 locus, how this gene functions in wheat cells was unknown until now.
Collaborating with Nanjing Agriculture University, the University of Adelaide research team has shown TaHRC works in the nucleus of wheat cells, ...
[1] ... [1213]
[1214]
[1215]
[1216]
[1217]
[1218]
[1219]
[1220]
1221
[1222]
[1223]
[1224]
[1225]
[1226]
[1227]
[1228]
[1229]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.