Scientists regenerate neural pathways in mice with cells from rats
2024-04-25
Two independent research teams have successfully regenerated mouse brain circuits in mice using neurons grown from rat stem cells. Both studies, published April 25 in the journal Cell, offer valuable insights into how brain tissue forms and present new opportunities for restoring lost brain function due to disease and aging.
“This research helps to show the brain’s potential flexibility in using synthetic neural circuits to restore brain functions,” says Kristin Baldwin (@kkbaldwin238), a professor at Columbia University in New York and corresponding author ...
Publicly funded fertility program linked to a decrease in rate of multifetal pregnancy
2024-04-25
Kingston, ON, March 27, 2024 – In the era after the introduction of publicly funded in vitro fertilization (IVF) mandating elective single embryo transfer, the multifetal pregnancy rate decreased significantly for IVF, but the contribution of ovulation induction and intrauterine insemination (OI/IUI) to multifetal pregnancy still needs attention, according to a new study from ICES and Queen’s University.
Twins, triplets, and higher multifetal pregnancies are associated with some adverse outcomes ...
Cancer survivors reporting loneliness experience higher mortality risk, new study shows
2024-04-25
A new study led by researchers at the American Cancer Society (ACS) showed people surviving cancer who reported feeling more lonely experienced a higher mortality risk compared to survivors reporting low or no loneliness. Researchers observed the highest mortality risk among the group reporting the highest levels of loneliness, even after adjusting for sociodemographic characteristics. The findings are published today in the Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (JNCCN).
“Loneliness, ...
Psychiatric symptoms, treatment uptake, and barriers to mental health care among US adults with post–COVID-19 condition
2024-04-25
About The Study: In this nationally representative cross-sectional study of 25,000 participants, those experiencing post–COVID-19 condition (PCC) were approximately twice as likely to report depression and anxiety symptoms than other U.S. adults. Among individuals with these symptoms, adults with PCC were just as likely to have received mental health treatment but more likely to report cost-related barriers to accessing therapy. Care pathways for PCC should consider prioritizing mental health screening and affordable treatment.
Authors: Hiten Naik, M.D., ...
Disparities in mortality by sexual orientation in a large, prospective cohort of female nurses
2024-04-25
About The Study: In an otherwise largely homogeneous sample of female nurses, participants identifying as lesbian or bisexual had markedly earlier mortality during the study period compared with heterosexual women. These differences in mortality timing highlight the urgency of addressing modifiable risks and upstream social forces that propagate and perpetuate disparities.
Authors: Sarah McKetta, M.D., Ph.D., of Harvard University in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed ...
National trial safely scaled back prescribing of a powerful antipsychotic for the elderly
2024-04-25
Warning letters from Medicare can safely cut prescribing of a powerful but risky antipsychotic, according to a new study at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health. Researchers used Medicare data to study the effects of the letters on hundreds of thousands of older adults with dementia. They found a significant and lasting reduction in prescribing but no signs of adverse effects on patient health. The findings are published in JAMA Network Open.
“Our study shows that low-cost letter interventions can safely reduce antipsychotic prescribing to patients with dementia,” said Adam Sacarny, PhD, assistant professor of Health Policy and Management at Columbia Mailman School. ...
Premature mortality higher among sexual minority women, study finds
2024-04-25
Key takeaways:
A new study led by the Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute examined differences in premature mortality by sexual orientation among a large group of women followed for three decades.
Findings show that sexual minority women died much sooner than heterosexual women, with bisexual women having the most pronounced differences.
This work highlights the urgent need to address sexual orientation-related inequities in preventable illness, including a focus on the systems and laws that ...
Extreme long-term research shows: Herring arrives earlier in the Wadden Sea due to climate change
2024-04-25
Due to the changing climate, young herring arrive in the Wadden Sea earlier and earlier in spring. That is shown in a new publication by NIOZ ecologists Mark Rademaker, Myron Peck and Anieke van Leeuwen, in this month's journal Global Change Biology. "The fact that we were able to demonstrate this, was only due to very consistently, for more than 60 years, and continuously sampling the fish every spring and every fall with exactly the same fyke every time", Rademaker says. "Recognizing this kind of change requires extreme precision ...
With hybrid brains, these mice smell like a rat
2024-04-25
NEW YORK, NY--If mice ever wonder what it’s like to experience the world as a rat, some are now able to live that dream, at least when it comes to the sense of smell.
Researchers led by Columbia University's Kristin Baldwin have created mice with hybrid brains – part mouse, part rat – that sense the odors of the world with their rat neurons.
It is the first time that an animal has been able to use the sensory apparatus of another to sense and respond accurately to the world ...
Philippines' counter-terrorism strategy still stalled after 7 years since the ‘ISIS siege’ on Marawi
2024-04-25
Following the 2017 siege of Marawi, the Philippines' counter-terrorism efforts have faced an increasingly complex and unpredictable landscape. While authorities have claimed victory, one which garnered global media attention during the peak of ISIS reign in Syria and Iraq, the aftermath of Marawi highlights the urgent need for a comprehensive reassessment of the country's counter-terrorism strategy.
A new study, led by experts in security and terrorism studies at the University of Portsmouth, provides a thorough examination of the terrorist ...
BU doc honored by the American College of Surgeons
2024-04-25
(Boston)—Dane Scantling, DO, MPH, FACS, assistant professor of surgery at Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, has been awarded the C. James Carrico, MD, FACS, Faculty Research Fellowship for the Study of Trauma and Critical Care from the American College of Surgeons. The two-year, $80,000 award will support his project, "Improving Equity and Access to Trauma Care for Victims of Firearm Violence."
Firearm violence (FV) rates have risen to levels not seen ...
Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
2024-04-25
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D images with a low-power laser. This advance could make single-photon lidar practical for air and space applications such as environmental monitoring, 3D terrain mapping and object identification.
Single-photon lidar uses single-photon detection techniques to measure the time it takes laser pulses to travel to objects and back. It is particularly useful for airborne applications because it enables highly accurate 3D mapping of terrain and objects even in challenging environments such as dense vegetation or urban areas.
“Using single-photon ...
Stem cell transplants and survival rates on the rise across all racial and ethnic groups
2024-04-25
(WASHINGTON, April 25, 2024) – The volume of hematopoietic cell transplants rose among all racial/ethnic groups, but grew faster among African Americans and Hispanics compared with Non-Hispanic white individuals, mirroring changes in population growth rates. Survival after both autologous hematopoietic cell transplant (autoHCT) and allogeneic hematopoietic transplant (alloHCT) improved over time across racial/ethnic groups, though non-Hispanic African Americans still have worse outcomes, according ...
Study reports chlamydia and gonorrhea more likely to be treated per CDC guidelines in males, younger patients and individuals identifying as Black or multiracial
2024-04-25
INDIANAPOLIS – Chlamydia and gonorrhea are the two most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in the United States, impacting 2.4 million in 2021, and the number is rising. A recent study of individuals ages 15 to 60 measuring and comparing treatment rates for these STIs has found that nearly one-in-five patients with chlamydia and one-in-four patients with gonorrhea did not receive Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommended treatment for their infection.
Individuals seen by clinicians in a private healthcare setting were less likely to receive CDC recommended treatment than those seen ...
Plastic food packaging contains harmful substances
2024-04-25
Plastic is a very complex material that can contain many different chemicals, some of which can be harmful. This is also true for plastic food packaging.
“We found as many as 9936 different chemicals in a single plastic product used as food packaging,” said Martin Wagner, a professor at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU’s) Department of Biology.
Wagner has been working with chemicals in plastic products for several years. He is part of a research group at NTNU that ...
Spring snow, sparkling in the sun, can reveal more than just good skiing conditions
2024-04-25
One might think that snow, of all things, is easy to describe: it is cold, white and covers the landscape like a blanket. What else is there to say about it?
A lot, according to Mathieu Nguyen. He has just defended his doctoral thesis on the optical properties of snow at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) in Gjøvik.
“Snow reflects all wavelengths of light and can have very different colours depending on the conditions and the angle at which light hits it. The age and density ...
Using AI to improve diagnosis of rare genetic disorders
2024-04-25
HOUSTON – (April 25, 2024) – Diagnosing rare Mendelian disorders is a labor-intensive task, even for experienced geneticists. Investigators at Baylor College of Medicine are trying to make the process more efficient using artificial intelligence. The team developed a machine learning system called AI-MARRVEL (AIM) to help prioritize potentially causative variants for Mendelian disorders. The study is published today in NEJM AI.
Researchers from the Baylor Genetics clinical diagnostic laboratory noted that AIM's module can contribute to predictions ...
Study unveils balance of AI and preserving humanity in health care
2024-04-25
Cross Country Healthcare, Inc. (NASDAQ: CCRN), a pioneering force in tech-driven workforce solutions and advisory services, in collaboration with Florida Atlantic University's Christine E. Lynn College of Nursing, released its latest research findings in the fourth annual installment of the Future of Nursing Survey: “Embracing Technology While Preserving Humanity.” Drawing insights from more than 1,100 nursing professionals and students, the study illuminates the intricate interplay between cutting-edge health care technologies and the enduring essence of compassionate care.
Survey results reveal a nuanced perspective among nurses toward the integration of Artificial ...
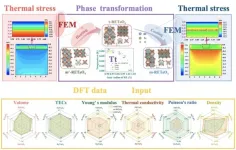
Capturing and visualizing the phase transition mediated thermal stress of thermal barrier coating materials via a cross-scale integrated computational approach
2024-04-25
Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) are widely used in gas turbine engines to obtain elevated working temperatures and improve engine efficiency. The phase transition of the ceramic layer is accompanied by a large volume difference, causing the concentration of thermal stress, eventually leading to TBCs to fall off and fail. Therefore, it is necessary to quantitatively evaluate the magnitude and distribution of thermal stress induced by phase transition in the ceramic layer.
A team of material scientists led ...
Study reveals emotional turmoil experienced after dog-theft is like that of a caregiver losing a child
2024-04-25
A new study published in the journal Animal-Human Interactions reveals that emotional turmoil experienced by dog owners after their pet has been stolen is like that of losing a loved one such as a caregiver losing their child.
The findings empirically support the notions that the ‘owner’ or guardian roles and relationships equate to familial relationships and, when faced with the theft of their pet, owners feel a similar sense of disenfranchised grief and ambiguous loss.
In the study, some participants felt the loss was more intense ...
PhRMA Foundation awards $1M for equity-focused research on digital health tools
2024-04-25
The PhRMA Foundation (PhF) awarded $500,000 grants to David G. Armstrong, DPM, MD, PhD, of the University of Southern California and Nino Isakadze, MD, MHS, of Johns Hopkins University to conduct research using digital health technologies (DHTs) to improve health equity and health outcomes for patients.
Armstrong and Isakadze were selected out of a group of seven researchers awarded $25,000 planning grants in 2023 by the Foundation to develop comprehensive research proposals to study the use of DHTs for advancing patient health, especially in underserved populations.
“Digital ...
Women with heart disease are less likely to receive life-saving drugs than men
2024-04-25
Athens, Greece – 25 April 2024: Women with heart disease are less often treated with cholesterol-lowering drugs than men, according to research presented today at ESC Preventive Cardiology 2024, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
“Cholesterol-lowering drugs save lives and prevent heart attacks, and should be prescribed to all patients with coronary artery disease,” said study author Dr. Nina Johnston of Uppsala University, Sweden. “Unfortunately, our study shows that women are missing out on these essential medications.”
Patients with ...
How electric vehicle drivers can escape range anxiety
2024-04-25
Two of the biggest challenges faced by new and potential electric vehicle (EV) drivers are range anxiety and speed of charging, but these shouldn’t have to be challenges at all. That is according to a study by Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, and the University of Delaware, USA. Researchers discovered that a change in refuelling mindset, rather than improving the size or performance of the battery, could be the answer to these concerns.
The transition from filling up at a petrol station to recharging your electric vehicle in the most convenient location for you, requires a whole new way ...
How do birds flock? Researchers do the math to reveal previously unknown aerodynamic phenomenon
2024-04-25
In looking up at the sky during these early weeks of spring, you may very well see a flock of birds moving in unison as they migrate north. But how do these creatures fly in such a coordinated and seemingly effortless fashion?
Part of the answer lies in precise, and previously unknown, aerodynamic interactions, reports a team of mathematicians in a newly published study. Its breakthrough broadens our understanding of wildlife, including fish, who move in schools, and could have applications in transportation and energy.
“This area of research is important since animals are known to take advantage of the flows, such as of air or water, left by other members of ...
Experts call for global genetic warning system to combat the next pandemic and antimicrobial resistance
2024-04-25
The Covid-19 pandemic turned the world upside down. In fighting it, one of our most important weapons was genomic surveillance, based on whole genome sequencing, which collects all the genetic data of a given microorganism. This powerful technology tracked the spread and evolution of the virus, helping to guide public health responses and the development of vaccines and treatments.
But genomic surveillance could do much more to reduce the toll of disease and death worldwide than just protect us from Covid-19. Writing in Frontiers in Science, an international collective of clinical and public health microbiologists ...
[1] ... [1216]
[1217]
[1218]
[1219]
[1220]
[1221]
[1222]
[1223]
1224
[1225]
[1226]
[1227]
[1228]
[1229]
[1230]
[1231]
[1232]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.