Pre- and post-surgical immunotherapy improves outcomes for patients with operable lung cancer
2024-05-15
Compared with pre-surgical (neoadjuvant) chemotherapy alone, adding perioperative immunotherapy – given before and after surgery – significantly improved event-free survival (EFS) in patients with resectable early-stage non-small cell lung cancer(NSCLC), according to researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Results from the Phase III CheckMate 77T study were published today in the New England Journal of Medicine. At a median follow-up of 25.4 months, the median EFS with chemotherapy alone was 18.4 months, while the median had not yet ...
'Trojan horse' weight loss drug more effective than available therapies
2024-05-15
“I consider the drugs available on the marked today as the first generation of weight-loss drugs. Now we have developed a new type of weight-loss drug that affects the plasticity of the brain and appears to be highly effective.”
So says Associate Professor and Group Leader Christoffer Clemmensen, from the Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Basic Metabolic Research at the University of Copenhagen, who is senior author of the new study, which has been published in the prestigious scientific journal Nature.
In the study, Christoffer Clemmensen and colleagues demonstrate a new use of the weight loss hormone GLP-1. GLP-1 can be used as a ‘Trojan ...
Reduced risk of breast cancer following bariatric surgery in women with hyperinsulinemia
2024-05-15
Bariatric surgery is associated with a reduced risk of breast cancer in women with obesity. These are the findings of a study conducted at the University of Gothenburg. The risk reduction is greatest for those with high blood insulin levels at the time of surgery.
The study, published in JAMA Surgery, is based on data from 2,867 women with obesity, half of whom had undergone bariatric surgery at 25 surgical departments. The remaining women, comprising the control group, received standard obesity treatment at 480 healthcare centers. The groups were otherwise comparable in terms of age and body composition.
The results show that a total of ...
Copper can't be mined fast enough to electrify the US
2024-05-15
Copper cannot be mined quickly enough to keep up with current U.S. policy guidelines to transition the country's electricity and vehicle infrastructure to renewable energy, according to a University of Michigan study.
The Inflation Reduction Act, signed into law in 2022, calls for 100% of cars manufactured to be electric vehicles by 2035. But an electric vehicle requires three to five times as much copper as an internal combustion engine vehicle—not to mention the copper required for upgrades to the electric grid.
"A ...
Guideline issued for people with epilepsy who may become pregnant
2024-05-15
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, MAY 15, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – A new guideline has been issued to help neurologists and other clinicians determine the best antiseizure medications for people with epilepsy who may become pregnant. The guideline is published in the May 15, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology (AAN), and was developed through a collaboration between the AAN, the American Epilepsy Society (AES) and the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine (SMFM). It was endorsed by the Child Neurology Society.
The guideline partially updates two 2009 AAN and AES ...
Only 20% of U.S. nonprofit hospitals invested in housing as part of the federal community benefit mandate
2024-05-15
Waltham — May 15, 2024 — A nationwide assessment of how nonprofit hospitals are addressing housing-related needs in their communities appears in the latest issue of Medical Care, the official journal of the Medical Care Section of the American Public Health Association. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Approximately 60% of hospitals in the United States are 501(c)(3) nonprofit organizations ...
The crystallization of memory: Study reveals how practice forms new memory pathways in the brain
2024-05-15
A new study led by UCLA Health has shown that repetitive practice not only is helpful in improving skills but also leads to profound changes in the brain’s memory pathways.
The research, published in the journal Nature and co-led by Rockefeller University, sought to unravel how the brain’s ability to retain and process information, known as working memory, improves through training.
To test this, researchers tasked mice with identifying and recalling a sequence of odors over the course of two weeks. Researchers then tracked neural activity in the animals as they practiced the task by using a novel, custom-built microscope that can image cellular activity ...
Dartmouth-led study provides new insights into phage therapy design
2024-05-15
Results from a new Dartmouth-led study, involving collaborators at the University of Pittsburgh and Yale University and published in the journal PLOS Biology, are providing new insights into the therapeutic potential of bacteriophage (phage) therapy for treating diseases like cystic fibrosis (CF).
A major challenge of treating people with CF—an inherited disease that causes sticky, thick mucus to build up in the lungs—are the persistent infections the disease causes which can lead to respiratory failure and death.
“Opportunistic ...
This time, it’s personal: Enhancing patient response to cancer immunotherapy
2024-05-15
LA JOLLA (May 15, 2024)—Immunotherapy has revolutionized the way we treat cancer in recent years. Instead of targeting the tumor itself, immunotherapies work by directing patients’ immune systems to attack their tumors more effectively. This has been especially impactful in improving outcomes for certain difficult-to-treat cancers. Still, fewer than half of all cancer patients respond to current immunotherapies, creating an urgent need to identify biomarkers that can predict which patients are most likely to benefit.
Recently, scientists have noticed that patients whose tumors have a mutation in a gene called ARID1A are ...
A novel multifunctional catalyst turns methane into valuable hydrocarbons
2024-05-15
Methane, a greenhouse gas that contributes significantly towards global warming, is also an important source of energy and an essential chemical resource. When used as a chemical feedstock, methane is typically converted into methanol first and then into hydrocarbons. However, this sequential conversion requires complex industrial setups. More importantly, since methane is a very stable molecule, its conversion into methanol requires tremendous amounts of energy when using conventional means, such ...
Two decades of studies suggest health benefits associated with plant-based diets
2024-05-15
Vegetarian and vegan diets are generally associated with better status on various medical factors linked to cardiovascular health and cancer risk, as well as lower risk of cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and death, according to a new review of 49 previously published papers. Angelo Capodici and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on May 15, 2024.
Prior studies have linked certain diets with increased risk of cardiovascular disease and cancer. A diet that is poor in plant products and rich in meat, refined grains, sugar, and salt is associated with higher risk of death. Reducing consumption of animal-based ...
Bluetooth tracking devices provide new look into care home quality
2024-05-15
Wearable Bluetooth devices can shed light on the care that residents of care homes are receiving and which residents are most in need of social contact, according to a new study published this week in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Carl Thompson of University of Leeds, UK.
In the UK alone, nearly half a million people reside in some form of care home, including long-term care facilities, nursing homes and residential homes. There is no single reliable method that works well to evaluate care home quality, in part because care homes are complex social systems with diverse interacting groups.
In the new study, researchers tested the feasibility of collecting social network ...
Scientists want to know how the smells of nature benefit our health
2024-05-15
Spending time in nature is good for us. Studies have shown that contact with nature can lift our well-being by affecting emotions, influencing thoughts, reducing stress and improving physical health. Even brief exposure to nature can help. One well-known study found that hospital patients recovered faster if their room included a window view of a natural setting.
Knowing more about nature’s effects on our bodies could not only help our well-being, but could also improve how we care for land, preserve ecosystems and design cities, homes and parks. Yet studies on the benefits of contact with nature have typically focused primarily ...
Singing researchers find cross-cultural patterns in music and language
2024-05-15
Language and music may share evolutionary functions. Both speech and song have features such as rhythm and pitch. But are similarities and differences between speech and song shared across cultures?
To investigate this question, 75 researchers—speaking 55 languages—were recruited across Asia, Africa, the Americas, Europe and the Pacific. Among them were experts in ethnomusicology, music psychology, linguistics, and evolutionary biology. The researchers were asked to sing, perform instrumentals, ...
Killer whales breathe just once between dives, study confirms
2024-05-15
A new study has confirmed a long-held assumption: that orcas take just one breath between dives.
The researchers used drone footage and biological data from tags suction-cupped to 11 northern and southern resident killer whales off the coast of B.C. to gather information on the animals’ habits.
Whaley fun facts
Published in PLOS ONE, the study found that residents spend most of their time making shallow dives, with the majority of dives less than one minute. The longest dive recorded was 8.5 minutes, for an adult male. “Killer whales are like sprinters who don’t have the marathon endurance of blue and humpback whales to make deep and prolonged dives,” ...
Bees and butterflies on the decline in western and southern North America
2024-05-15
Bee and butterfly populations are in decline in major regions of North America due to ongoing environmental change, and significant gaps in pollinator research limit our ability to protect these species, according to a study published May 15, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Sara Souther of Northern Arizona University, US, and colleagues.
Recent research has detected declines in populations of pollinator species, sparking alarm from scientists and policymakers concerned about negative impacts on ecosystems and agriculture. These declines have been linked to various factors including climate change, habitat loss, and invasive species, but ...
Singing researchers investigate cross-cultural patterns in music, language
2024-05-15
Seventy-five researchers from 46 countries recorded themselves performing traditional music and speaking in their own languages in a novel experiment investigating cross-cultural differences and similarities.
With rare exceptions, the rhythms of songs and instrumental melodies were slower than for speech, while the pitches were higher and more stable, according to the study published in Science Advances.
Unique for the number of languages represented – 55 – and the diversity of the researchers, the study provides “strong evidence for cross-cultural regularities,” according to senior author Dr Patrick ...
Animal brain inspired AI game changer for autonomous robots
2024-05-15
A team of researchers at Delft University of Technology has developed a drone that flies autonomously using neuromorphic image processing and control based on the workings of animal brains. Animal brains use less data and energy compared to current deep neural networks running on GPUs (graphic chips). Neuromorphic processors are therefore very suitable for small drones because they don’t need heavy and large hardware and batteries. The results are extraordinary: during flight the drone’s deep neural network processes data up to 64 times faster and consumes three times less energy than when running on a GPU. Further developments of this technology may ...
Summers warm up faster than winters, fossil shells from Antwerp show
2024-05-15
Niels de Winter, affiliated with the Department of Earth Sciences at Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam and the AMGC research group at Vrije Universiteit Brussel, measured alongside colleagues from institutions such as the Institute for Natural Sciences in Brussels the chemical composition of fossil shells from Antwerp, Belgium. Those shells originate from molluscs such as oysters, cockles, and scallops found during the construction works of the Kieldrecht Lock. The molluscs lived lived during the Pliocene, approximately ...
Wearing face masks did not reduce risk of COVID infection after first Omicron wave, research shows
2024-05-15
After the first Omicron wave, research shows that many of the risks of Covid infection changed
Before February 2022, always wearing face masks and being retired were associated with reduced risk, but not after
Overseas travel was not associated with increased risk prior to February 2022, but then became a significant risk
Peer reviewed – meta-regression- humans
New research from the University of East Anglia has found that wearing face masks did not lower the risk of Covid infection following the initial surge of the Omicron variant.
The analysis of official data found that several risk ...
SF State receives $14M from the Genentech Foundation to support underrepresented students in STEM
2024-05-15
SAN FRANCISCO – May 15, 2024 – San Francisco State University announced today that it received $14 million from the Genentech Foundation to support two University programs that are training the next generation of life sciences leaders. The new five-year grant is the latest in the Genentech Foundation’s transformational support for University programs, which has totaled more than $33 million during their long-lasting partnership. This partnership has impacted more than 700 students since 2008, and an additional 350 students are projected to be supported by the new funding.
The new funds will continue sponsoring San Francisco State’s Genentech ...
Penalties for dropping out of ecosystem services incentive programs should equal lost environmental benefits
2024-05-15
Payment for Ecosystem Services programs (PES) are important tools that governments around the world use to improve water quality, protect forests and wildlife habitat, and sequester carbon. Under these programs, landowners - usually farmers - are paid to use their land in ways that protect or restore the environment, such as replacing row crops with trees or grassy zones adjacent to waterways. Many PES program contracts last 5 to 20 years, but participant drop out rates have consistently risen over the years.
A recent study by University of Maryland economists showed that PES programs ...
Lithuanian researchers’ new development in solar cell technology – a promise of a significant advancement in the field
2024-05-15
Researchers from Kaunas University of Technology (KTU), Lithuania, who contributed to the development of record-breaking solar cells a few years ago, expanded their invention. The self-assembled monolayers can now be applied not only in inverted but also in regular structure perovskite solar cells.
Self-assembling molecules arrange themselves into a single-molecule-thick layer and in this case, they act as an electron-transporting layer in solar cells.
“The molecules that make up these monolayers, like a clever glue, ...
A simple internet with significant possibilities
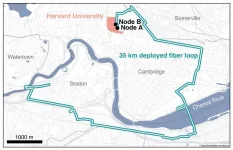
2024-05-15
It’s one thing to dream up a quantum internet that could send hacker-proof information around the world via photons superimposed in different quantum states. It’s quite another to physically show it’s possible.
That’s exactly what Harvard physicists have done, using existing Boston-area telecommunication fiber, in a demonstration of the world’s longest fiber distance between two quantum memory nodes to date. Think of it as a simple, closed internet between point A and B, carrying a signal encoded not by classical ...
Unwrapping the origin story of the baobab
2024-05-15
The baobab (Adansonia) is a genus of trees with eight extant (in existence currently) species and a long history of humans marveling at them. For as much admiration the baobabs get, there is an equal amount of mystery surrounding their origin.
Genomic and ecological analyses recently done by a global research team led by Sino-Africa Joint Research Center, CAS (hosted by Wuhan Botanical Garden of the Chinese Academy of Sciences), suggest that Madagascar, is the origin from where all other baobab species hail. With a deeper understanding of the baobabs' genetics, researchers are hoping to uncover some clues on what ...
[1] ... [1172]
[1173]
[1174]
[1175]
[1176]
[1177]
[1178]
[1179]
1180
[1181]
[1182]
[1183]
[1184]
[1185]
[1186]
[1187]
[1188]
... [8822]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.