Researchers develop new method for prenatal genetic testing
2023-11-22
A team of investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH), and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard have developed a non-invasive genetic test that can screen the blood of pregnant individuals to survey all genes for fetal DNA sequence variants. The team evaluated the test by examining blood samples from 51 pregnant persons, finding that the test was able to capture variants that were inherited from the mother as well as new variants that were not present in the mother and associated with prenatal diagnoses. ...
Genetic predisposition to early breast cancer in Kazakh women
2023-11-22
“Our study may reveal previously uncharacterized population-specific variants that may increase the risk of BC in the Kazakh population.”
BUFFALO, NY- November 22, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on October 4, 2023, entitled, “Determination of genetic predisposition to early breast cancer in women of Kazakh ethnicity.”
Breast cancer (BC) is the most common type of cancer among women in Kazakhstan. To date, little data are available on the spectrum of genetic variation in Kazakh women with BC.
In this new study, researchers Gulnur Zhunussova, Nazgul Omarbayeva, ...
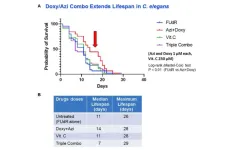
Mitochondria-targeting antibiotics extend lifespan in C. elegans
2023-11-22
“Our ultimate goal is to find existing FDA-approved drugs and dietary supplements that can not only increase lifespan but also improve healthspan.”
BUFFALO, NY- November 22, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 21, entitled, “Antibiotics that target mitochondria extend lifespan in C. elegans.”
Aging is a continuous degenerative process caused by a progressive decline of cell and tissue functions in an organism. It is induced by the accumulation of damage that affects normal cellular processes, ...
Adding a few servings of whole grains linked to slower memory decline in Black people
2023-11-22
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER 22, 2022
MINNEAPOLIS – Black people who eat more foods with whole grains, including some breads and cereals, quinoa, and popcorn, may have a slower rate of memory decline compared to Black people who eat fewer whole grain foods, according to a study published in the November 22, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The researchers did not see a similar trend in white participants.
The study does not prove that eating more whole grains slows memory decline; it only shows an association.
The study found that among Black ...
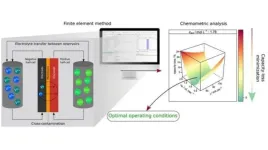
Researchers obtain promising results against capacity loss in vanadium batteries
2023-11-22
An article by researchers at the Center for Development of Functional Materials (CDMF) in Brazil describes a successful strategy to mitigate charge capacity loss in vanadium redox flow batteries, which are used by electric power utilities among other industries and can accumulate large amounts of energy. The article is published in the Chemical Engineering Journal.
CDMF is a Research, Innovation and Dissemination Center (RIDC) funded by FAPESP and hosted by the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar) in São Paulo state.
The study involved computer ...
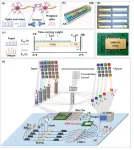
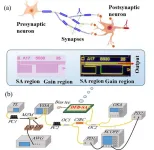
Photonic integrated neuro-synaptic core for convolutional spiking neural network
2023-11-22
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances, 10.29026/oea.2023.230140 discusses photonic integrated neuro-synaptic core for convolutional spiking neural network.
Brain science and brain-like intelligence are the cutting-edge science and technology that countries all over the world compete to seize. The rapid rise and vigorous development of emerging fields such as artificial intelligence, 5G/6G, big data, autonomous driving, and the Internet of Things has led to the explosive growth of global data. Due to the memory wall effect, the conventional von Neumann architecture performs low energy efficiency. Electronic ...
Multi-synaptic photonic SNN based on a DFB-SA chip
2023-11-22
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Science; DOI 10.29026/oes.2023.230021 overviews multi-synaptic photonic SNN based on a DFB-SA chip.
Compared with traditional artificial neural networks, spiking neural networks (SNN) are more biologically authentic, more powerful, and less power-consuming due to their spatiotemporal coding and event-driven characteristics. In recent years, optical computing has been widely considered as a hardware acceleration platform, where nonlinear computing poses a challenge. Photonic SNN provides an ultra-fast and energy-efficient platform for high-performance ...
Optical trapping of optical nanoparticles: fundamentals and applications
2023-11-22
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Science; DOI 10.29026/oes.2023.230019 overviews optical trapping of optical nanoparticles.
This article reviews the fundamentals and applications of optically trapped optical nanoparticles. Optical nanoparticles are nowadays one of the key elements of photonics. They do not only allow optical imaging of a plethora of systems (from cells to microelectronics), but also behave as highly sensitive remote sensors. In recent years, it has been demonstrated the success of optical tweezers in isolating and manipulating individual optical nanoparticles. This has opened the door to high resolution single particle scanning ...
Casas del Turuñuelo, a site of repeated animal sacrifice in Iron Age Spain
2023-11-22
The Iron Age site of Casas del Turuñuelo was used repeatedly for ritualized animal sacrifice, according to a multidisciplinary study published November 22, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Mª Pilar Iborra Eres of the Institut Valencià de Conservació, Restauració i Investigació, Spain, Sebastián Celestino Pérez of Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, Spain, and their colleagues.
Archaeological sites with evidence of major animal sacrifices are rarely ...
Earliest known European common hippopotamus fossil reveals their Middle Pleistocene dispersal
2023-11-22
Modern hippos first dispersed in Europe during the Middle Pleistocene, according to a study published November 22, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Beniamino Mecozzi of the Sapienza University of Rome and colleagues.
Modern hippos, Hippopotamus amphibius, arose from African ancestors during the Quaternary, a time when hippos were widespread in Europe. However, the details of the modern species’ origin and dispersal into Europe are unclear and highly debated. In this study, Mecozzi and colleagues provide new insights via analysis of a fossil hippo skull from the study area of Tor di Quinto in Rome.
The skull of Tor di Quinto, currently housed at the ...
Status threat - the concern that outsiders will undermine your group's status - is associated with increased age, conservatism, conspiracy mentality, and paranoia, in study of 300 US adults
2023-11-22
Status threat - the concern that outsiders will undermine your group's status - is associated with increased age, conservatism, conspiracy mentality, and paranoia, in study of 300 US adults
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0293930
Article Title: Conspiracy mentality, subclinical paranoia, and political conservatism are associated with perceived status threat
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Transplanting gut microbes from an obesity-resistant shrew can improve microbiome diversity and decrease the weight of obese mice
2023-11-22
Transplanting gut microbes from an obesity-resistant shrew can improve microbiome diversity and decrease the weight of obese mice
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0293213
Article Title: Gut microbiota of Suncus murinus, a naturally obesity-resistant animal, improves the ecological diversity of the gut microbiota in high-fat-diet-induced obese mice
Author Countries: Japan, China
Funding: This work (PONE-D-23-21281) was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the ...
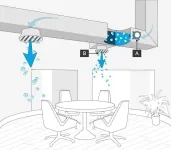
Airborne virus infectivity can be reduced by up to 99.98% by commercially available NPBI-based air purifiers, per experiment using real-world concentrations of COVID-19 strains, flu and RSV viruses
2023-11-22
Airborne virus infectivity can be reduced by up to 99.98% by commercially available NPBI-based air purifiers, per experiment using real-world concentrations of COVID-19 strains, flu and RSV viruses
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0293504
Article Title: Bipolar ionization rapidly inactivates real-world, airborne concentrations of infective respiratory viruses
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. All research and 3rd party laboratory testing was funded entirely by GPS Air. Edward Sobek is an employee of GPS Air ...
7 in 8 homicide victims in South Africa are male
2023-11-22
7 in 8 homicide victims in South Africa are male, with homicide rates peaking on weekends and holidays, and firearms and sharp items being the most common murder weapons, in analysis of almost 20,000 2017 post-mortems. END ...
In Nepalese survey, 1 in 5 men who have sex with men report having attempted suicide, with over 40 percent experiencing some suicidal ideation
2023-11-22
In Nepalese survey, 1 in 5 men who have sex with men report having attempted suicide, with over 40 percent experiencing some suicidal ideation.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/globalpublichealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pgph.0002348
Article Title: Suicidal ideation, plan, and attempt among men who have sex with men in Nepal: Findings from a cross-sectional study
Author Countries: Nepal, USA
Funding: RS received funding from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (Award Number: K01DA051346). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision ...
New tool to enable exploration of human-environment interactions
2023-11-22
Spurred by the current climate crisis, there has been a heightened attention within the scientific community in recent years to how past climate variation contributed to historic human migration and other behaviors.
Now, an international group of scientists — including archaeologists, historians, climate scientists, paleo-scientists, a volcanologist and others — are calling for a strengthened commitment to transdisciplinary collaboration to study past and present human-environmental interactions, which they say will advance our understanding of these complex, entangled histories. Their recommendations were published ...
Researchers pinpoint brain area where people who are blind recognize faces identified by sound
2023-11-22
WASHINGTON – Using a specialized device that translates images into sound, Georgetown University Medical Center neuroscientists and colleagues showed that people who are blind recognized basic faces using the part of the brain known as the fusiform face area, a region that is crucial for the processing of faces in sighted people.
The findings appeared in PLOS ONE on November 22, 2023.
“It’s been known for some time that people who are blind can compensate for their loss of vision, ...
Cognitive ability mattered in the UK’s vote for Brexit, University of Bath research shows
2023-11-22
Susceptibility to misinformation and disinformation likely to have played part in Leave vote
New research from the University of Bath’s School of Management finds that higher cognitive ability was strongly linked to voting to Remain in the 2016 UK referendum on European Union Membership.
The study shows that cognitive skills including memory, verbal fluency, fluid reasoning and numerical reasoning, were correlated with how people decided to vote.
Lead author Dr Chris Dawson, from the University of Bath’s School of Management, said: “This study adds to existing academic evidence showing that low ...
Autonomous excavator constructs a 6-meter-high dry-stone wall
2023-11-22
ETH Zurich researchers deployed an autonomous excavator, called HEAP, to build a six metre-high and sixty-five-metre-long dry-stone wall. The wall is embedded in a digitally planned and autonomously excavated landscape and park.
The team of researchers included: Gramazio Kohler Research, the Robotics Systems Lab, Vision for Robotics Lab, and the Chair of Landscape Architecture. They developed this innovative design application as part of the National Centre of Competence in Research for Digital Fabrication ...
Depression, anxiety, and stress frequently co-occur in Black pregnant individuals
2023-11-22
November 22, 2023 — Black pregnant individuals frequently experience more than one mental health concern, according to findings published by Susan Gennaro, PhD, RN, FAAN, Professor in the William F. Connell School of Nursing at Boston College, and colleagues in The Nurse Practitioner. They say prenatal screening and treatment for stress is warranted in addition to care of depression and anxiety. The Nurse Practitioner is part of the Lippincott portfolio of Wolters Kluwer.
"Prenatal interventions for Black people should aim to address mental health distress and treat high depression, anxiety, and stress," the research ...
UTA, DOE lab partner to prove new atomic cooling techniques
2023-11-22
The U.S. Department of Energy has awarded associate professor of physics Benjamin Jones a $540,000 grant to initiate a new collaborative research partnership between The University of Texas at Arlington and the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory in Richland, Washington. The project aims to prove a new atomic cooling approach required for the next generation of neutrino mass research.
Neutrinos are the most abundant particles with mass in the universe. Every time atomic nuclei come together (in the case of stars like the sun) or break apart (such as in nuclear ...
Low-pH-dependent RNA binding and oligomerization of SID-1 transmembrane family proteins: implications for their RNA transport activity
2023-11-22
In C. elegans, the protein SID1 plays a crucial role in the systemic RNA interference process by facilitating the transport of exogenous double-stranded RNA into the cytoplasm. Previously, Chen-Yu Zhang's group has already demonstrated that intact plant miRNA found in dietary sources can be absorbed through the mammalian digestive system and mediate cross-kingdom gene regulation. Mammalian SID-1 transmembrane family proteins, namely SIDT1 and SIDT2, have attracted considerable attention due to their role in facilitating the uptake of regulatory exogenous small RNAs, such as small interfering RNA (siRNA) and plant-derived ...
Nutrient found in beef and dairy improves immune response to cancer
2023-11-22
Trans-vaccenic acid (TVA), a long-chain fatty acid found in meat and dairy products from grazing animals such as cows and sheep, improves the ability of CD8+ T cells to infiltrate tumors and kill cancer cells, according to a new study by researchers from the University of Chicago.
The research, published this week in Nature, also shows that patients with higher levels of TVA circulating in the blood responded better to immunotherapy, suggesting that it could have potential as a nutritional supplement to complement clinical treatments for cancer.
“There are many studies trying to decipher ...
Overdose deaths increased in pregnant and postpartum women from early 2018 to late 2021
2023-11-22
Drug overdose deaths rose markedly between January to June 2018 and July to December 2021 among 10- to 44-year-old girls and women who were pregnant or pregnant within the previous 12 months, according to a new study by researchers at National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) at the National Institutes of Health. Overdose mortality more than tripled among those aged 35 to 44 during the study period, from 4.9 deaths per 100,000 mothers aged 35 to 44 with a live birth in the 2018 period to 15.8 in the 2021 period. Over 60% of these pregnancy-associated overdose deaths occurred outside healthcare settings, ...
Lowering a form of brain cholesterol reduces Alzheimer’s-like damage in mice
2023-11-22
In Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias, cognitive decline is driven by the overaccumulation of a normal brain protein known as tau. Wherever tau builds up, nearby brain tissue starts to degenerate and die.
Now, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have found — in mice — that Alzheimer’s-like tau deposits in the brain lead to the accumulation of a form of cholesterol known as cholesteryl esters, and that lowering cholesteryl ester levels ...
[1] ... [1538]
[1539]
[1540]
[1541]
[1542]
[1543]
[1544]
[1545]
1546
[1547]
[1548]
[1549]
[1550]
[1551]
[1552]
[1553]
[1554]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.