Lowering a form of brain cholesterol reduces Alzheimer’s-like damage in mice
2023-11-22
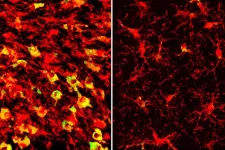
In Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias, cognitive decline is driven by the overaccumulation of a normal brain protein known as tau. Wherever tau builds up, nearby brain tissue starts to degenerate and die.
Now, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have found — in mice — that Alzheimer’s-like tau deposits in the brain lead to the accumulation of a form of cholesterol known as cholesteryl esters, and that lowering cholesteryl ester levels ...
Segregated patterns of hospital care delivery and health outcomes
2023-11-22
About The Study: This study of Medicare claims data for 4,386 hospitals found that higher segregation of hospital care was associated with poorer health outcomes for both Black and white patients, with significantly greater negative health outcomes for Black populations, supporting racial segregation as a root cause of health disparities. Policymakers and clinical leaders could address this important public health issue through payment reform efforts and expansion of health insurance coverage, in addition to supporting upstream efforts to reduce racial segregation in hospital ...
Mortality and hospitalization risks in patients with cancer and the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant
2023-11-22
About The Study: This study showed that during the Omicron-dominant period, patients with solid cancer and COVID-19 had higher mortality and hospitalization risks following COVID-19 infection versus patients without solid cancer with COVID-19, and that COVID-19 vaccination in the patients with cancer mitigated this risk.
Authors: Salomon M. Stemmer, M.D., of Beilinson Hospital in Petah Tikva, Israel, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2023.5042)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional ...
ADHD medications and long-term risk of cardiovascular diseases
2023-11-22
About The Study: Longer cumulative duration of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) medication use was associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, particularly hypertension and arterial disease, compared with nonuse in this study of 278,000 individuals in Sweden ages 6 to 64 who had an incident ADHD diagnosis or ADHD medication dispensation. These findings highlight the importance of carefully weighing potential benefits and risks when making treatment decisions about ...
Racial and ethnic disparity in preoperative chemosensitivity and survival in patients with early-stage breast cancer
2023-11-22
About The Study: In this study of 103,000 individuals with early-stage breast cancer, Black patients had a higher mortality risk compared with white patients among those with residual disease after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. This highlights the need for personalized treatment strategies for Black patients to help them attain pathologic complete response.
Authors: Shipra Gandhi, M.D., of Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center in Buffalo, New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed ...
From the first bite, our sense of taste helps pace our eating
2023-11-22
When you eagerly dig into a long-awaited dinner, signals from your stomach to your brain keep you from eating so much you’ll regret it – or so it’s been thought. That theory had never really been directly tested until a team of scientists at UC San Francisco recently took up the question.
The picture, it turns out, is a little different.
The team, led by Zachary Knight, PhD, a UCSF professor of physiology in the Kavli Institute for Fundamental ...
Team discovers rules for breaking into Pseudomonas
2023-11-22
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Researchers report in the journal Nature that they have found a way to get antibacterial drugs through the nearly impenetrable outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a bacterium that – once it infects a person – is notoriously difficult to treat.
By bombarding P. aeruginosa with hundreds of compounds and using machine learning to determine the physical and chemical traits of those molecules that accumulated inside it, the team discovered how to penetrate the bacterium’s defenses. They used this information ...
Camouflaging stem cell-derived transplants avoids immune rejection
2023-11-22
Cell and organ transplants can be lifesaving, but patients often encounter long waiting lists due to the shortage of suitable donors. According to donatelife.net, in 2021 6,000 people died in the U.S. alone while waiting for a transplant. One day, transplants generated from stem cells may alleviate the constant organ donor shortage, making transplants available to a larger group of patients.
An issue with donation, whether it’s with solid tissues or cells from deceased or living donors, is immune rejection. Unless the donor material is carefully matched to the recipient’s immune system, the transplant will be rejected. However, stem cell research ...
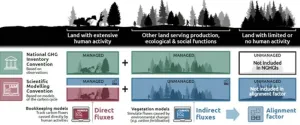
Mind the gap: Caution needed when assessing land emissions in the COP28 Global Stocktake
2023-11-22
Effective management of land, whether for agriculture, forests, or settlements, plays a crucial role in addressing climate change and achieving future climate targets. Land use strategies to mitigate climate change include stopping deforestation, along with enhancing forest management efforts. Countries have recognized the importance of the land use, land-use change, and forestry (LULUCF) sector, with 118 of 143 countries including land-based emissions reductions and removals in their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), which are at the heart of the Paris Agreement and the achievement of its long-term goals.
A new study, published in Nature, demonstrates that estimates of current land-based ...
Developing a new perspective for the EU beekeeping sector: B-GOOD legacy booklet
2023-11-22
The aim of the B-GOOD project (Giving Beekeeping Guidance By Computational-Assisted Decision Making) was to pave the way towards healthy and sustainable beekeeping within the European Union by following a collaborative and interdisciplinary approach. By merging data from within and around beehives, as well as wider socioeconomic conditions and by developing and testing innovative tools to perform risk assessments, B-GOOD provided guidance for beekeepers and helped them make better and more informed decisions.
The communication of scientific information and the transformation of scientific ...
How do temperature extremes influence the distribution of species?
2023-11-22
As the planet gets hotter, animal and plant species around the world will be faced with new, potentially unpredictable living conditions, which could alter ecosystems in unprecedented ways. A new study from McGill University researchers, in collaboration with researchers in Spain, Mexico, Portugal, Denmark, Australia, South Africa and other universities in Canada, investigates the importance of temperature in determining where animal species are currently found to better understand how a warming climate ...
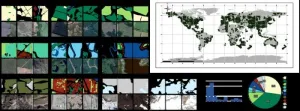
New remote sensing dataset improves global land change tracking
2023-11-22
Tracking unprecedented changes in land use over the past century, global land cover maps provide key insights into the impact of human settlement on the environment. Researchers from Sun Yat-sen University created a large-scale remote sensing annotation dataset to support Earth observation research and provide new insight into the dynamic monitoring of global land cover.
In their study, published Oct 16 in the Journal of Remote Sensing, the team examined how global land use/landcover (LULC) has undergone dramatic changes with the advancement of industrialization and urbanization, including deforestation and flooding.
“We ...
A Special Collection collaboration between SLAS and SBI2
2023-11-22
Oak Brook, IL – The latest issue of SLAS Discovery is a joint Special Collection between SLAS and the Society of Biomolecular Imaging and Informatics (SBI2) to celebrate the 10th Annual SBI2 High-Content Imaging and Informatics meeting. This collaboration features a curated special collection of articles that highlight the significant impact of high-content imaging in basic and translational research. Volume 28, Issue 7 features one perspective, four original research articles and one short communication.
Perspective
Evolution and Impact of High Content Imaging
This ...
A new diagnostic tool to identify and treat pathological social withdrawal, Hikikomori
2023-11-22
Fukuoka, Japan—Researchers at Kyushu University have developed a new tool to help clinicians and researchers assess individuals for pathological social withdrawal, known as Hikikomori. The tool, called Hikikomori Diagnostic Evaluation, or HiDE, can be a practical guide on collecting information on this globally growing pathology.
Hikikomori is a condition characterized by sustained physical isolation or social withdrawal for a period exceeding six months. It was first defined in Japan in 1998, ...
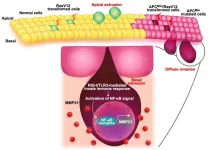
Survival of the fittest? New study shows how cancer cells use cell competition to evade the body’s defenses
2023-11-22
Living cells compete with each other and try to adapt to the local environment. Cells that are unable to do so are eliminated eventually. This cellular competition is crucial as the surrounding normal epithelial cells use it to identify and eliminate mutant cancer cells. Studies have reported that when activating mutants of “Ras” proteins are expressed in mammalian epithelial cells, they are pushed toward the lumen, excreted along with other bodily waste, and eliminated by competition. Epithelial cells containing Ras mutants have been reported to be removed in this manner in several organs, including the small intestine, stomach, pancreas, and lungs. ...
Danish researchers puncture 100-year-old theory of odd little 'water balloons'
2023-11-22
Quinoa and many other extremely resilient plants are covered with strange balloon-like 'bladders' that for 127 years were believed to be responsible for protecting them from drought and salt. Research results from the University of Copenhagen reveal this not to be the case. These so-called bladder cells serve a completely different though important function. The finding makes it likely that even more resilient quinoa plants will now be able to be bred, which could lead to the much wider cultivation of this sustainable ...
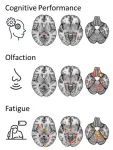
Novel MRI reveals brain changes in long-COVID patients
2023-11-22
CHICAGO – People with long COVID exhibit patterns of changes in the brain that are different from fully recovered COVID-19 patients, according to research being presented next week at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
“To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study comparing patients with long COVID to both a group without history of COVID-19 and a group that went through a COVID-19 infection but is subjectively unimpaired,” said one of the study’s lead authors, Alexander Rau, M.D., resident in the Departments of Neuroradiology and Diagnostic and ...
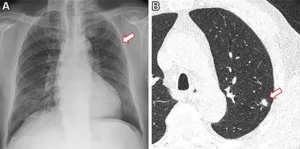
AI identifies non-smokers at high risk for lung cancer
2023-11-22
CHICAGO – Using a routine chest X-ray image, an artificial intelligence (AI) tool can identify non-smokers who are at high risk for lung cancer, according to a study being presented next week at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Lung cancer is the most common cause of cancer death. The American Cancer Society estimates about 238,340 new cases of lung cancer in the United States this year and 127,070 lung cancer deaths. Approximately 10-20% of lung cancers occur in “never-smokers” – people who have never smoked cigarettes ...
This sea worm’s butt swims away, and now scientists know how
2023-11-22
A research team, led by Professor Toru Miura from the University of Tokyo, shows how the expression of developmental genes in the Japanese green syllid worms, Megasyllis nipponica, helps form their swimming reproductive unit called stolon.
Life always finds ways to surprise us. The presence of a unique reproductive mechanism of some annelid worms or segmented worms is one such surprise. In a process called stolonization, the posterior body part with gonads of the syllid worm detaches from its original body. The detached part is called the stolon, and it is full of gametes (eggs or sperms). The stolon swims around by itself and spawns when it ...
New study on experience of adopted people as they become parents
2023-11-22
Becoming a parent is a key turning point for adopted people
Parenting is always challenging, but for adopted people becoming a mum or dad can be extra demanding, as well as extra special – according to research from the University of East Anglia.
A new study is the first in to investigate the lived experiences of adopted people in the UK as they become parents.
It finds that they are affected by issues that link back to their adoption and to difficult experiences in their past – related to loss, rejection, abuse and neglect.
Because of these ...
Anti-rheumatic drugs could prevent thyroid disease
2023-11-22
Anti-rheumatic drugs used for rheumatoid arthritis might prevent the development of autoimmune thyroid disease, according to a new observational study by researchers from Karolinska Institutet published in the Journal of Internal Medicine.
It is well known that patients with rheumatoid arthritis are at increased risk of autoimmune thyroid diseases such as Hashimoto's disease and Graves' disease. While patients with RA are usually treated with immunomodulatory drugs that affect the immune system, such drugs are rarely used in autoimmune thyroid diseases. Instead, such patients are treated with thyroid hormone to compensate for the changes in normal ...
Does spaceflight increase men’s risk of erectile dysfunction?
2023-11-22
During missions into space, astronauts are exposed to high levels of galactic cosmic radiation and weightlessness. Simulation experiments in male rats indicated that these aspects of spaceflight can negatively affect vascular tissues relevant to erectile dysfunction, even after a period of long-term recovery.
The research, which is published in The FASEB Journal, indicated that vascular alterations are induced by relatively low doses of galactic cosmic radiation and to a lesser extent simulated weightlessness, primarily through increases in oxidative stress. Treatment with different antioxidants could counter some of these ...
What are the effects of workforce automation across race and gender in the United States?
2023-11-22
Advances in areas such as robotics and artificial intelligence enable the automation of a range of occupational tasks, leading to fundamental changes in the nature of work. New research published in The American Journal of Economics and Sociology indicates that the effects of job automation vary across race and gender, and without targeted interventions, will likely result in increasing inequality.
The research analyzes two distinct measures of automation job displacement risk for more than 1.4 million Americans across 385 occupations. The findings show that the intersection of race and gender has a significant effect on automation risks. For example, ...
Has the COVID-19 pandemic compromised bone health?
2023-11-22
Results from a study published in the American Journal of Human Biology suggest that the COVID-19 pandemic has had negative effects on bone tissue—including both bone mineral density in the forearm and total bone mineral content.
The study by investigators at Comenius University, in Slovakia, included 387 young adults whose bone health measurements were taken prior to the COVID-19 pandemic and 386 whose measurements were taken from September 2020 to November 2022 during the pandemic. Individuals participated in the study only once, either before or during the pandemic.
Certain lifestyle changes during the pandemic may have contributed ...
Does stem cell transplantation benefit patients with knee osteoarthritis?
2023-11-22
Cell therapy represents a potential regenerative treatment for osteoarthritis. A recent analysis of all relevant published studies indicates that stem cell transplantation from different sources is effective for treating knee osteoarthritis, the most prevalent chronic joint disease.
The review and meta-analysis, which is published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research, included 16 studies involving 875 patients with knee osteoarthritis (441 in the stem cell transplantation group and 434 in the control group). Stem cell treatment was associated with significant reductions in patient-reported pain from the third month onwards. The most significant pain relief at different postoperative months ...
[1] ... [1539]
[1540]
[1541]
[1542]
[1543]
[1544]
[1545]
[1546]
1547
[1548]
[1549]
[1550]
[1551]
[1552]
[1553]
[1554]
[1555]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.