Sex differs in intestinal MCT1 function
2023-11-15
Monocarboxylate transporter 1 (MCT1) plays a crucial role in the transport of lactate, pyruvate, ketone bodies, and short-chain fatty acids (SCFA), as well as MCT1-targeted drugs in various tissues. How MCT1 and lactate in the intestine modulate the physiology and pathophysiology of the body is unclear. A recent study published in Life Metabolism reveals that intestinal MCT1 regulates intestinal inflammation and metabolism in a sex-dimorphic pattern, which further confirms that metabolic homeostasis is ...
National Climate Assessment reporting continues at AGU23 in San Francisco
2023-11-15
WASHINGTON — AGU congratulates the many members of our scientific community whose work contributed to the Fifth National Climate Assessment (NCA5), which was published today.
Climate reporting will remain essential as we close out a year of record global temperatures, wildfires in Canada, Hawaii and the U.S. Southeast, droughts in the Amazon and Mississippi river basins, and billion-dollar flooding disasters in the U.S Northeast and California, aggravated by human-driven climate change.
AGU’s upcoming 2023 Annual Meeting, convening 11-15 December, will host authors from each of the NCA’s 32 chapters and feature deep ...
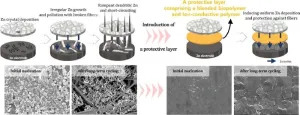
Using cosmetic ingredient for battery protection
2023-11-15
Xanthan gum, derived from plants like cabbage and known for its carbohydrate content, serves as a natural protective barrier in cosmetics to retain their benefits on the skin. In a recent development, this remarkable substance has been harnessed to create a protective shield for battery electrodes, rather than for the skin.
Professor Changshin Jo from the Graduate Institute of Ferrous & Eco Materials Technology and the Department of Chemical Engineering and Jooyoung Jang, a PhD candidate, from the Department of Chemical Engineering at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), have crafted a protective film by blending ...
SFI Press releases new editions of Murray Gell-Mann books
2023-11-15
The opening lines of Homer’s Odyssey describe its eponymous hero as polytropos, a man of many turns. It’s no coincidence that SFI co-founder Murray Gell-Mann invoked Homer’s crafty, long-voyaging hero when he envisioned the pinnacle of the scientific endeavor.
“Murray described his ideal scientist as an ‘Odyssean,’ one who lives somewhere between the analytical Apollonian and the intuitive Dionysian, one who loves to simplify yet is equally enamored of complication,” says David Krakauer, SFI President and Editor-in-Chief of the SFI Press. “Over the course of Murray’s life, he realized this ideal in his own ...
THE LANCET: Alarming new projections reveal soaring health risks of persistent global inaction over the climate emergency
2023-11-15
Peer-reviewed / Review and Analysis / People
The Lancet: Alarming new projections reveal soaring health risks of persistent global inaction over the climate emergency
New global projections in the 8th annual report of the Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change reveal the grave and mounting threat to health of further delayed action on climate change, with the world likely to experience a 4.7-fold increase in heat-related deaths by mid-century.
Report also highlights how climate inaction is costing lives and livelihoods today. In 2022, individuals were, on average, exposed to 86 days of health-threatening ...
COVID-19 showed the importance of genomic surveillance – now we need it to help fight antimicrobial resistance, say researchers
2023-11-15
During the COVID-19 pandemic, genomic surveillance proved vital in helping understand the evolution and spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Now, an international group of researchers is calling for its potential to be harnessed to tackle antimicrobial resistance (AMR), a major global challenge that could ultimately result in many more deaths than the coronavirus pandemic.
AMR already causes substantial sickness and death worldwide, responsible for approximately 1.27 million deaths in 2019. Some estimates suggest that by 2050, it could kill as many as 10 million people each year.
Professor Sharon Peacock at the University ...
UK soft drinks levy linked to fall in child hospital admissions for tooth extraction
2023-11-15
The UK soft drinks industry levy introduced in 2018 may have reduced the number of under 18s having a tooth removed due to tooth decay by 12%, suggests research published in the open access journal BMJ Nutrition, Prevention & Health.
The fall in hospital admissions may have saved more than 5,500 hospital admissions for tooth decay alone and the largest reductions were in children aged up to nine years old.
Sugar-sweetened drinks account for around 30% of the added sugars in the diets of children aged one to three years and over 50% by late ...
HIIT in water improves exercise capacity in adults with long term health conditions
2023-11-15
High-intensity interval training in water, often called aquatic HIIT (AHIIT) improves exercise capacity in adults with chronic conditions and has a similar impact as land based training (LBHIIT), suggests research published in the open access journal BMJ Open Sport & Exercise Medicine.
The researchers say AHIIT may provide a safe and valuable alternative for people with chronic conditions who are unable to perform LBHIIT.
HIIT is a type of interval training exercise that involves brief bursts of high intensity movements followed by short recovery periods of lower intensity movements.
HIIT is considered to have more health benefits than moderate-intensity ...
The Lancet: Deferred clamping of umbilical cord reduces risk of death in premature babies by at least a third, suggest two studies with the most comprehensive analysis to date
2023-11-15
Peer-reviewed / Systematic review and meta-analysis / People
The Lancet: Deferred clamping of umbilical cord reduces risk of death in premature babies by at least a third, suggest two studies with the most comprehensive analysis to date
Meta-analysis of 3,292 infants across 21 studies finds premature babies whose umbilical cord is clamped 30 seconds or more after birth are less likely to die before leaving the hospital, compared to those whose cord is clamped immediately after birth.
A second companion meta-analysis of 47 trials including 6,094 babies suggests waiting at least ...
Clustering method can better describe the pathological process in patients with traumatic brain injury
2023-11-15
Monitoring brain injury biomarkers and glucose variation in patients who have suffered an acute cranial injury during the entire first week of hospitalisation can provide a more accurate picture of the pathological process. This is according to a paper by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden published in The Lancet Neurology. It is hoped that their findings can eventually lead to more personalised treatment.
After samples of brain injury markers and glucose have been taken over the entire first week of intensive care, patients with traumatic brain injury can be divided into different groups with different disease trajectories ...
Delaying cord clamping could halve risk of death in premature babies
2023-11-15
Waiting for two minutes or longer to clamp the umbilical cord of a premature baby soon after birth could help reduce the risk of death, compared with immediately clamping the umbilical cord, or waiting a shorter time before doing so. Delaying clamping could decrease the child's risk of death by more than half relative to immediate clamping.
The new findings, published today in two companion papers in The Lancet, examined clinical trial data and outcomes of thousands of premature babies which had delayed cord clamping compared to those whose cord was clamped immediately after birth.
Delaying clamping of the umbilical cord allows ...
Richard Haynes receives Marcus Wallenberg Prize for development of forest economic model
2023-11-15
Richard Haynes, a former research forester and program manager at the USDA Forest Service Pacific Northwest Research Station, received the 2023 Marcus Wallenberg Prize at a ceremony in Stockholm, Sweden. Awarded annually, the international prize is bestowed by the King of Sweden in recognition of scientific achievements that contribute to forestry and forest industries.
Haynes was recognized for his work developing the Timber Assessment Market Model (TAMM), a spatial model that projects volumes and prices in the solidwood products and sawtimber stumpage ...
Increased threat of war enhances pup survival
2023-11-15
Animal offspring may survive better when their groups are in greater conflict with rival factions, research from the University of Bristol has shown for the first time.
Battles between competing groups can lead to serious injury or death and intergroup conflict has always been thought to have a negative effect on reproductive success.
But findings published today in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B turn that long-held belief on its head.
Using a decade of life-history data from a wild population of dwarf mongooses, University of Bristol researchers found that ...
How COVID-19 compromised U.S. gains in controlling HIV
2023-11-15
The COVID-19 pandemic slowed previous gains made in controlling HIV blood levels and worsened health disparities, according to UC Francisco researchers leading the largest U.S. evaluation of the impact of the public health crisis on people with HIV.
While the country had been making progress on its goals to reduce HIV before COVID-19, the researchers found the pandemic compromised those gains by leveling off improvements in the overall population and worsening outcomes among Black patients and people who inject illicit drugs.
“Equity in HIV outcomes likely worsened during the pandemic, with decreased ...
Texas A&M professor published in leading history journal
2023-11-15
Dr. Sonia Hernández, professor in the Department of History at Texas A&M University, has published an article in the September issue of the Journal of American History, the leading scholarly publication in the field of American history and the official academic journal of the Organization of American Historians.
Her article, titled "Gendering Transnational State Violence: Intertwined Histories of Intrigue and Injustice along the U.S.-Mexican Borderlands, 1900-1913,” ...
US men die 6 years before women, as life expectancy gap widens
2023-11-14
We’ve known for more than a century that women outlive men. But new research led by UC San Francisco and Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health shows that, at least in the United States, the gap has been widening for more than a decade. The trend is being driven by the COVID-19 pandemic and the opioid overdose epidemic, among other factors.
In a research paper, published Nov. 13, 2023, in JAMA Internal Medicine, the authors found the difference between how long American men and women live increased to 5.8 years in 2021, the largest it’s been since 1996. This ...
Microplastics come from everywhere – yes, from sex toys too
2023-11-14
As more research reveals how many microplastic particles humans are ingesting and absorbing in their bloodstreams, Duke and Appalachian State researchers led by Joana Sipe and Christine Hendren have examined a source for microplastic absorption many would not have considered: sex toys. In a study originally published in Microplastics and Nanoplastics in March 2023, researchers will discuss the risks of sex toys at the 2023 Society for Risk Analysis Annual Conference. The majority of American adults report having used sex toys, which, ...
Disrupting a single gene could improve CAR T cell immunotherapy, new study shows
2023-11-14
CAR T cell therapy, a powerful type of immunotherapy, has begun to revolutionize cancer treatment. Pioneered at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK), the therapy involves engineering a patient’s T cells so they recognize and attack cancer cells. These CAR (chimeric antigen receptor) T cells are then multiplied in a lab and given back to the patient to be a continual fighting force against the cancer.
New research from the lab of physician-scientist Michel Sadelain, MD, PhD, shows that disrupting a single ...
UIUC professors receive AFOSR grant to study detrimental defects in superconducting qubit junctions
2023-11-14
University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign professors Angela Kou (Physics), Pinshane Huang (MatSE), Wolfgang Pfaff (Physics) and Andre Schleife (MatSE) have received an Air Force Office of Scientific Research grant for their project “Identifying the origin and lossy defects in Josephson junctions”. The two-year, nearly $1 million grant aims to take a materials science approach to address the detrimental defects of Josephson junctions in superconducting qubits.
The current state of quantum computing is called the noisy intermediate-scale quantum ...
Mirvie announces completion of enrollment of 10,000 person landmark research study for pregnancy health
2023-11-14
South San Francisco, CA (November 14, 2023) – Mirvie, a company pioneering the prediction of life-threatening pregnancy complications months in advance, today announced the completion of enrollment of its landmark 10,000 person research study for pregnancy health, in collaboration with leading experts in obstetrics and maternal-fetal medicine.
“This monumental effort represents a new chapter for pregnancy health,” said Maneesh Jain, CEO and co-founder of Mirvie. “Today, we face a massive crisis in maternal health, and innovative solutions are desperately needed. The audacious scale of this generalizable study – involving over 10,000 individuals – ...
Study finds strongest evidence yet for local sources of cosmic ray electrons
2023-11-14
A new study using data from the CALorimetric Electron Telescope (CALET) instrument on the International Space Station has found evidence for nearby, young sources of cosmic ray electrons, contributing to a greater understanding of how the galaxy functions as a whole.
The study included more than seven million data points representing particles arriving at CALET’s detector since 2015, and CALET’s ability to detect electrons at the highest energies is unique. As a result, the data includes more electrons at high energies than any previous work. That makes the statistical analysis of the data more robust and lends support to the conclusion that there are one or more local ...
Special Issue of Criminology & Public Policy examines cybercrime and cybersecurity
2023-11-14
Cybercrime—computer hacking, social engineering, intellectual property theft, electronic fraud, online interpersonal violence, identity theft, and Internet-facilitated sexual victimization—is a leading threat to national security, with millions of victims in both the United States and around the world, and billions of dollars being spent to combat it.
Criminology and related disciplines are just beginning to understand cybercrime and how best to deter and prevent it—or at least reduce its harms. ...
Special issue of Medicare Care supports the need to study economic impacts on patient outcomes
2023-11-14
November 14, 2023 — A special supplemental issue of Medical Care, sponsored by the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation (ASPE) in the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, supports the growing recognition that economic factors often affect health outcomes, patient decision-making, and equity in health care. Medical Care, the official journal of the Medical Care Section of the American Public Health Association, is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
The scope of patient-centered outcomes research (PCOR) was expanded to include economic outcomes in the 2019 reauthorization ...
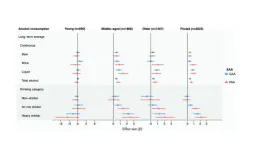
Alcohol consumption and epigenetic age acceleration across human adulthood
2023-11-14
“Our findings may help to understand the role of alcohol-associated biological aging in the development of age-related diseases such as CVD and cancer.”
BUFFALO, NY- November 14, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 20, entitled, “Alcohol consumption and epigenetic age acceleration across human adulthood.”
The alcohol-associated biological aging remains to be studied across adulthood. In their new study, ...
How one lab at MSK is working to harness the power of the immune system against cancer
2023-11-14
Investigator Ming Li, PhD, has dedicated his career to understanding the intricate workings of the immune system — both in general and for the critical role it plays in cancer.
Study by study, his lab at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) is sharing new insights into the molecular and cellular mechanisms involved in immune regulation — a type of knowledge-building that scientists call “basic science” or “discovery science.” But Dr. Li is equally focused ...
[1] ... [1542]
[1543]
[1544]
[1545]
[1546]
[1547]
[1548]
[1549]
1550
[1551]
[1552]
[1553]
[1554]
[1555]
[1556]
[1557]
[1558]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.