Curiosity and pure maths
2023-11-13
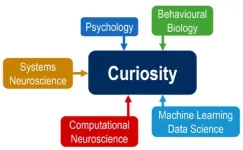
The German Research Foundation (DFG) will be funding a new Research Training Group (RTG) at the University of Göttingen from next year. The RTG "Curiosity" is based at the Faculty of Biology and Psychology. Funding is expected to total around 7.8 million euros over the following five years. In addition, the DFG has extended the funding for the RTG "Fourier Analysis and Spectral Theory" at the Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science by five years. The award for this RTG totals around 4.5 million euros over the extended funding period.
Curiosity is broadly defined ...
Limited positive childhood experiences linked to higher binge-eating risk in college
2023-11-13
New findings from the University of Houston Department of Health and Human Performance reveal a significant association between a lower number of positive childhood experiences and a higher prevalence of binge-eating disorder characteristics, as well as lower scores for intuitive eating.
Binge eating, which includes consuming a substantial amount of food within a brief timeframe and experiencing a loss of control, is linked to adverse weight-related health effects and challenges in mental well-being. Intuitive eating, ...
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Nanotechnology expert Nikhil Koratkar named American Physical Society Fellow
2023-11-13
Nikhil Koratkar, Ph.D., John A. Clark and Edward T. Crossan Professor of Engineering at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, has been named a fellow of the American Physical Society (APS). Koratkar was recognized for his pioneering contributions to the field of nanoscale science and technology and the use of nanoscale materials in composites and energy storage devices. Each year, no more than 0.05% of the society membership is recognized by their peers for election to the status of fellow of the American Physical Society.
The APS Fellowship Program recognizes members ...
Children’s National Hospital selected as member of ARPA-H Investor Catalyst Hub spoke network
2023-11-13
WASHINGTON, D.C. (Nov. 13, 2023) – Children’s National Hospital was selected as a spoke for the Investor Catalyst Hub, a regional hub of ARPANET-H, a nationwide health innovation network launched by the Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health (ARPA-H).
The Investor Catalyst Hub seeks to accelerate the commercialization of groundbreaking and accessible biomedical solutions. It uses an innovative hub-and-spoke model designed to reach a wide range of nonprofit organizations and Minority-Serving Institutions, with the aim of delivering scalable healthcare outcomes for all Americans.
“The needs of ...
Antiviral treatment is largely underused in children with influenza, study findings show
2023-11-13
Despite national medical guidelines supporting the use of antiviral medications in young children diagnosed with influenza, a new study reports an underuse of the treatment.
“Trends in Outpatient Influenza Antiviral Use Among Children and Adolescents in the United States” was published in Pediatrics, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Academy of Pediatrics.
“Antiviral treatment, when used early, improves health outcomes with influenza,” said lead author and principal investigator James Antoon, MD, PhD, MPH, assistant professor of Pediatrics and Hospital ...
Twisted magnets make brain-inspired computing more adaptable
2023-11-13
A form of brain-inspired computing that exploits the intrinsic physical properties of a material to dramatically reduce energy use is now a step closer to reality, thanks to a new study led by UCL and Imperial College London researchers.
In the new study, published in the journal Nature Materials, an international team of researchers used chiral (twisted) magnets as their computational medium and found that, by applying an external magnetic field and changing temperature, the physical properties of these materials could be adapted to suit different machine-learning tasks.
Such an approach, known as physical reservoir ...
New heat map charts unequal civic opportunity in the US
2023-11-13
People in many parts of the United States possess few chances for the robust community engagement that underpins healthy democracies, according to a new report that for the first time maps civic opportunity across the country.
The heat map created by Johns Hopkins University’s SNF Agora Institute, reveals patterns of inequality in civic opportunity tied to race, class, immigration status and education. Researchers also found that a great deal of civic engagement happens through local faith institutions and social and fraternal organizations, not D.C.-based advocacy organizations that tend to carry political clout.
The report is the initial phase ...
One step closer to Mars immigration
2023-11-13
Immigration to and living on Mars have long been depicted in science fiction works. But before dream turns into reality, there is a hurdle man has to overcome -- the lack of essential chemicals such as oxygen for long-term survival on the planet. However, hope looms up thanks to recent discovery of water activity on Mars.
Scientists are now exploring the possibility of decomposing water to produce oxygen through electrochemical water oxidation driven by solar power with the help of oxygen evolution reaction (OER) catalysts. The challenge is to find a ...
National survey indicates more young adults begin tobacco use with vaping, not cigarettes
2023-11-13
Young adults are now more likely to vape than to use traditional cigarettes. After years of public health success in decreasing the numbers of people using cigarettes, researchers are seeing striking increases in the numbers of young people who use e-cigarettes regularly – so much so that, for the first time, there are more young people who begin to use nicotine through vaping rather than through cigarettes.
“We now have a shift such that there are more ‘never smokers’ who vape than established smokers,” ...
Widening gender gap in life expectancy in the US
2023-11-13
About The Study: This analysis finds that COVID-19 and the drug overdose epidemic were major contributors to the widening gender gap in life expectancy (nearly six years) between women and men in recent years. Men experienced higher COVID-19 death rates for likely multifactorial reasons, including higher burden of comorbidities and differences in health behaviors and socioeconomic factors, such as labor force participation, incarceration, and homelessness. Differentially worsening mortality from diabetes, heart disease, homicide, and suicide suggest that chronic metabolic disease and mental illness may also contribute.
Authors: Brandon W. Yan, M.D., ...
Shift from smoking cigarettes to vaping nicotine in young adults
2023-11-13
About The Study: The data from this nationally representative survey study reveal a shift in tobacco use among young adults (ages 18-24), showing historically low cigarette use, which has positive public health significance. However, e-cigarette use is higher (14.5%) than reported previously, coinciding with the introduction of salt-based devices in 2015 to 2018. Over half of established vaping young adults never regularly smoked. Research suggests that exclusive e-cigarette users are unlikely to ...
Trends in prevalence of breastfeeding initiation and duration among US children
2023-11-13
About The Study: The findings of this study indicate an increase in the prevalence of breastfeeding initiation and breastfeeding duration at 12 months from 1999 to 2018 in the U.S. Temporal changes of breastfeeding duration at 12 months were more prevalent among male infants, older mothers, Mexican American and multiracial participants, and households with higher income.
Authors: Yongjun Zhang, Ph.D., M.D., of the Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine in Shanghai, is the corresponding author.
To access ...
Study finds melatonin use soaring among youth
2023-11-13
Nearly one in five school-aged children and preteens now take melatonin for sleep, and some parents routinely give the hormone to preschoolers, according to new research from the University of Colorado Boulder published Nov. 13 in JAMA Pediatrics.
This concerns the authors, who note that safety and efficacy data surrounding the products are slim, such dietary supplements lack full regulation by the Food and Drug Administration.
“We hope this paper raises awareness for parents and clinicians, and sounds the alarm for the scientific community,” said lead author Lauren Hartstein, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow ...
How good can overpower evil in the genetic determination of Alzheimer’s disease
2023-11-13
San Francisco—November 13, 2023—Researchers at Gladstone Institutes have discovered that a rare genetic variant known as the “Christchurch mutation” can block detrimental effects of apolipoprotein E4, the best-established risk factor for the most common form of Alzheimer’s disease.
The apolipoprotein E (APOE) gene has long been known to affect the risk of Alzheimer’s disease through its three main variants: E2 (low risk), E3 (intermediate risk), and E4 (high risk). More recently, a ...
Recreation of ancient seawater reveals which nutrients shaped the evolution of early life
2023-11-13
Scientists know very little about conditions in the ocean when life first evolved, but new research published in Nature Geoscience has revealed how geological processes controlled which nutrients were available to fuel their development.
All life uses nutrients such as zinc and copper to form proteins. The oldest lifeforms evolved in the Archean Eon, three and a half billion years before the dinosaurs first appeared. These microbes showed a preference for metals such as molybdenum and manganese compared to their more recent counterparts. This ...
Cycle of fasting and feeding is crucial for healthy ageing
2023-11-13
Fasting interventions, which involve alternating periods of fasting and refeeding, are generally thought to improve health. But these interventions don’t work as well in old animals. The question is: Why? By studying the short-lived killifish, researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Biology of Ageing in Cologne have shown that older fish deviate from a youthful fasting and refeeding cycle, and instead enter a state of perpetual fasting, even when ingesting food. However, the benefits of refeeding after fasting in old killifish can be restored by genetically activating a specific subunit of AMP kinase, an important sensor ...
How climate change could be affecting your brain
2023-11-13
A new element of the catastrophic impacts of climate change is emerging – how global warming is impacting the human brain.
In a paper published today in Nature Climate Change, an international team of academics explore the ways in which research has shown that a changing environment affects how our brains work, and how climate change could impact our brain function in the future. The paper is led by the University of Vienna with input from the universities of Geneva, New York, Chicago, Washington, Stanford, Exeter in the UK and the Max Plank Institute in Berlin. It also explores the role that neuroscientists can play in further understanding and addressing ...
Reducing systolic blood pressure to less than 120 mm Hg reduced cardiovascular event risk
2023-11-13
Research Highlights:
In a 3-year trial, intensive treatment with antihypertensive medication to reduce systolic blood pressure, the top number, to less than 120 mm Hg reduced cardiovascular disease events among people at high-risk for cardiovascular disease by 12% compared to standard treatment with a target of less than 140 mm Hg.
The effects were consistent regardless of participants’ diabetes status (Type 1, Type 2 or none) or history of stroke.
Embargoed until 8 a.m. ET, Monday, Nov. 13, 2023
PHILADELPHIA, ...
Ovarian cancer: Artificial intelligence predicts therapy responses
2023-11-13
A model based on artificial intelligence is able to predict the therapy outcome (measured by volumetric reduction of tumor lesions) in 80% of ovarian cancer patients. The AI-based model has an accuracy of 80%, significantly better than current clinical methods. The tool, named IRON (Integrated Radiogenomics for Ovarian Neoadjuvant therapy), analyzes various patient clinical features, from circulating tumor DNA in the blood (liquid biopsy) to general characteristics (age, health status, etc.), tumor markers, and disease images obtained through CT scans. ...
American Heart Association honors Gladstone President Deepak Srivastava with Distinguished Scientist Award
2023-11-13
Deepak Srivastava, MD, president of Gladstone Institutes and a renowned cardiovascular researcher, took the stage on Saturday in Philadelphia to receive the American Heart Association’s Distinguished Scientist award—joining a preeminent group of scientists and clinicians who’ve earned the association’s highest honor over the past decade.
The American Heart Association applauded Srivastava for his significant, original, and sustained scientific contributions that have advanced the association’s mission: “To be a relentless ...
Second-most distant galaxy discovered using James Webb Space Telescope
2023-11-13
The second- and fourth-most distant galaxies ever observed have been discovered in a region of space known as Pandora’s Cluster, or Abell 2744, using data from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). Following up on a deep field image of the area, an international team led by Penn State researchers confirmed the distance of these ancient galaxies and inferred their properties using new spectroscopic data — information about light emitted across the electromagnetic spectrum — from JWST. At nearly 33 billion light years away, these incredibly distant ...
Researchers explore origins of lupus, find reason for condition’s prevalence among women
2023-11-13
For years, researchers and clinicians have known that lupus, an autoimmune condition, occurs in women at a rate nine times higher than in men. Some of the factors that cause the disease’s high prevalence in women have eluded discovery, but in a new study investigating the immune system processes in lupus and the X chromosome, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers have uncovered answers about the disease’s frequency in females.
A number of dysregulated genetic and biological pathways contribute to the development of lupus and its varied symptoms of muscle and joint pain, ...
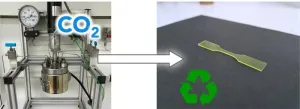
Capture or reuse CO2 as a chemical source for the production of sustainable plastics
2023-11-13
A scientific team has developed a new polyurethane production technique using CO2 to create new types of easily recyclable plastics. The study, published in the Journal of the American Chemistry Society (J.A.C.S.), could provide a solution for the development of truly sustainable plastics.
Commodity plastics have transformed global industry. Whether in construction, clothing, vehicles or food packaging, these plastics are everywhere in our daily lives, so much so that their global use has been estimated at around 460 million tons in 2019. This number is staggering, but not surprising, because plastics, also known as synthetic polymers, have met a large ...
Self-deception may seed ‘hubris balancing,’ leading to Putin’s war against Ukraine
2023-11-13
Strategy underlies the affairs of national leaders, including how they view and interact with other states — but what if such strategy is borne of self-deception? That’s the thrust of a novel international relations theory that Ryuta Ito of Hiroshima University has now expanded upon, providing psychological rationalization to explain the irrational acts of national leaders at war.
Ito penned his reasoning on Sept. 5 in the journal International Affairs.
“Why did Vladimir Putin decide to invade Ukraine in 2022?” asked Ito, assistant professor in the Graduate School of Humanities and Social Sciences at Hiroshima University. ...
Appropriate statin prescriptions increase sixfold with automated referrals
2023-11-13
PHILADELPHIA— The odds of prescribing the appropriate dose of statins—a medicine used to lower “bad” cholesterol levels—increased sixfold when automated referrals were made to pharmacy services, instead of relying on traditional prescribing methods, according to researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. More than 90 million people in the U.S. use statins, making it one of the most prescribed medications in the county. Despite their effectiveness in lowering cholesterol levels and the risk of cardiovascular ...
[1] ... [1548]
[1549]
[1550]
[1551]
[1552]
[1553]
[1554]
[1555]
1556
[1557]
[1558]
[1559]
[1560]
[1561]
[1562]
[1563]
[1564]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.