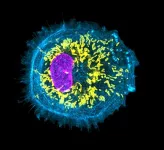
Colliding ribosomes activate RNA repair
2023-11-15
Aldehydes are toxic compounds that are produced in the body by metabolic processes, especially upon alcohol consumption. They are dangerous because they bind to cellular macromolecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins, and crosslink them.
Crosslinking damage to DNA must be repaired by the cell to prevent premature aging and cancer. However, it was previously unknown whether and how cells sense and resolve crosslinking damage to single-stranded RNA. A team led by Professor Julian Stingele from ...
On two small islands in the Indian Ocean, an endangered palm with the world’s largest seed sows a lesson about landscape restoration
2023-11-15
Every tree species has its story. Unraveling all 73,000 of them is a significant undertaking for science, in no small part because a considerable proportion of tree biodiversity is tropical, rare, remote and subject to the ravages of deforestation. And an estimated 9,200 tree species have yet to be discovered.
Even trees well-known to science have mysteries. One is the Seychelles’ endangered coco de mer, or sea coconut palm tree, which is now relegated to parts of two small Indian Ocean islands and in decline. Only some 8,200 individuals remain.
What Lodoicea madivica lacks in range it makes ...
New scientific study reveals the crucial role of herbivorous fishes and sea urchins in restoring Caribbean coral reefs
2023-11-15
A new study by Dr. Lindsay Spiers (Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission) and Professor Thomas Frazer (College of Marine Science at the University of South Florida), published in PeerJ Life & Environment, presents crucial findings on the feeding preferences of herbivorous fishes and the sea urchin Diadema antillarum in Little Cayman. The study, titled "Comparison of feeding preferences of herbivorous fishes and the sea urchin Diadema antillarum in Little Cayman," sheds new light on the dynamics of these herbivores and their impact on the resilience of Caribbean coral reefs.
Caribbean coral reefs face significant challenges, ...
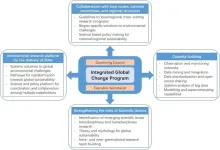
The Future of Future Earth: How global science programs can navigate the complex, shifting challenges in sustainability science
2023-11-15
The global change program Future Earth is an international alliance of organizations and agencies that was launched by the UN in June 2012. The Future Earth 2025 Vision identified eight global challenges for scientific research to accelerate progress in sustainability, improve collaboration, and mobilize resources.
After more than a decade of this global change program, researchers are analyzing the challenges Future Earth has faced and the path forward. Discussion presented in a recently published paper reviews these challenges faced by the coalition and proposes solutions to help these programs meet the many needs of the global community.
The paper was published on ...
Georgetown Global Health Center launches first open-access wildlife disease database
2023-11-15
WASHINGTON (November 15, 2023) – Georgetown University Medical Center’s Center for Global Health Science and Security (GHSS) today announces the launch of a first-of-its-kind wildlife disease database -- a system for collecting records of viruses, bacteria, fungi, parasites, etc. -- designed to support an early warning system for potential viral emergence. The Pathogen Harmonized Observatory, or PHAROS, is open to the global community and free to access.
Scientists in GHSS’ Verena program, a collaborative ...
University of Basel delivers first biological implants for treatment of cartilage lesions and osteoarthritis in humans
2023-11-15
The Department of Biomedicine at the University of Basel and the University Hospital Basel, today announced that it delivered the first surgical procedure to treat Osteoarthritis (OA) in humans. The procedure called Nasal Chondrocyte Tissue-Engineered Cartilage, or N-TEC, provides an innovative alternative to cure confined knee cartilage lesions as well as to address degenerative OA cases that have to date required knee joint replacements – prosthetics that routinely need replacing after 15-20 years.
The team at Basel is spearheading the next-generation human clinical trials that will ...
From 2018 to 2022, eating disorder claim lines increased 65 percent nationally as a percentage of all medical claim lines
2023-11-15
NEW YORK, NY—November 15, 2023—From 2018 to 2022, eating disorder claim lines increased 65 percent nationally as a percentage of all medical claim lines.[1] All eating disorders studied increased during this period, but at different rates: avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID) by 305 percent,[2] binge-eating disorder by 81 percent, anorexia nervosa (anorexia) by 73 percent and bulimia nervosa (bulimia) by 3 percent. These and other findings on eating disorders are reported in a FAIR Health white paper released today: Spotlight on Eating Disorders: An Analysis of Private Healthcare Claims.
Eating ...
NTU Singapore’s strength in research excellence sees it ranked 22nd globally and first in Singapore with most number of highly cited researchers
2023-11-15
Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) is up one spot to 22nd globally in this year’s Highly Cited Researchers list by Clarivate, a United Kingdom-based data company.
For the sixth year running, the University has the largest number of influential scientists among Singapore institutions recognised, with 42 NTU researchers that have significant and broad influence in their fields of research named.
These 42 scientists account for 44 mentions in the list, with two individuals recognised more ...
New study finds association between insecticide exposure and lower sperm concentration in adult men
2023-11-15
EMBARGOED until November 15, 2023
Contact: Michelle Thompson
George Mason University
mthomp7@gmu.edu
703-993-3485
New study finds association between insecticide exposure and lower sperm concentration in adult men
Comprehensive systematic review of 25 studies over nearly 50 years reveals consistent evidence of associations between insecticide exposure and lower sperm concentration
FAIRFAX, Va – Melissa J. Perry, Sc.D., MHS, dean of the George Mason University ...
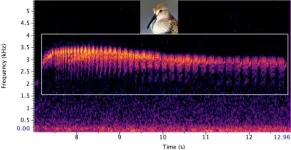
New deep learning AI tool helps ecologists monitor rare birds through their songs
2023-11-15
Researchers have developed a new deep learning AI tool that generates life-like birdsongs to train bird identification tools, helping ecologists to monitor rare species in the wild. The findings are presented in the British Ecological Society journal, Methods in Ecology and Evolution.
Identifying common bird species through their song has never been easier, with numerous phone apps and software available to both ecologists and the public. But what if the identification software has never heard a particular bird before, or only has a small sample of recordings to reference? This is a problem facing ...
Study finds increasingly popular oral nicotine pouches do little to curb smokers’ cravings
2023-11-15
Oral nicotine pouches, a tobacco-leaf-free product marketed as an alternative to cigarettes, do little to curb current smokers’ nicotine cravings, according to a new study. Public health scientists with The Center for Tobacco Research at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute report these findings in the medical journal Addiction.
Nicotine pouches are small pre-portioned bags filled with nicotine powder, flavorings, artificial sweeteners and other chemicals that extend shelf life. Marketed ...
More than 10% of samples from a stool-based colorectal cancer test may be unsatisfactory
2023-11-15
Bottom Line: Over 10% of fecal immunochemical tests (FIT) used for routine colorectal cancer (CRC) screening in a safety-net health system contained unsatisfactory samples that could not be processed.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR)
Authors: Rasmi Nair, MBBS, PhD, an assistant professor at the Peter O’Donnell Jr. School of Public Health of UT Southwestern Medical Center, and Po-Hong Liu, MD, a gastroenterology fellow at UT Southwestern Medical Center
Background: ...
Underworld marketplace exposed: Fake IDs for sale on the dark web
2023-11-15
Counterfeit Australian identity documents, especially driver’s licences, rank among some of the most frequently listed and sold identity documents on anonymous dark web marketplaces, according to new research from the Centre of Forensic Science at the University of Technology Sydney (UTS).
These documents are used by crime rings, terrorist organisations and other criminals for a wide range of illicit activities, including identity crime, money laundering, human and drug trafficking, illegal immigration, scams and ...
Shark fear: Just when you thought it was safe to get back in the water…
2023-11-15
It’s one of the most famous taglines in film history, immortalising sharks as ruthless predators. But beyond the horror generated by Spielberg’s Jaws series, a persistent fear of sharks remains, with consequences that extend into reality.
Following human-shark interactions in South Australia, this fear has prompted the Education Department’s ban on school-based sea activities for at least the remainder of the term. And while safety is at the core of such decisions, we should be cautious of scaremongering, says UniSA shark ...
The role of iron in blindness caused by ocular toxoplasmosis
2023-11-15
Researchers from Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine have identified the role of iron in ocular toxoplasmosis (OT), a form of toxoplasmosis that causes blindness. They found reduced iron concentration in the clear gel part of the eye of human patients and iron accumulation in the retina of mice. Treatment of mice with a compound that decreases iron was successful in reducing their symptoms. Their findings show the important role of iron in the disease and that controlling it may lead to a successful treatment. Their ...
New study reveals the critical role of microglia in human brain development
2023-11-15
An international team of scientists has uncovered the vital role of microglia, the immune cells in the brain that acts as its dedicated defense team, in early human brain development. By incorporating microglia into lab-grown brain organoids, scientists were able mimic the complex environment within the developing human brain to understand how microglia influence brain cell growth and development. This research represents a significant leap forward in the development of human brain organoids and has the potential to significantly impact ...
Sex differs in intestinal MCT1 function
2023-11-15
Monocarboxylate transporter 1 (MCT1) plays a crucial role in the transport of lactate, pyruvate, ketone bodies, and short-chain fatty acids (SCFA), as well as MCT1-targeted drugs in various tissues. How MCT1 and lactate in the intestine modulate the physiology and pathophysiology of the body is unclear. A recent study published in Life Metabolism reveals that intestinal MCT1 regulates intestinal inflammation and metabolism in a sex-dimorphic pattern, which further confirms that metabolic homeostasis is ...
National Climate Assessment reporting continues at AGU23 in San Francisco
2023-11-15
WASHINGTON — AGU congratulates the many members of our scientific community whose work contributed to the Fifth National Climate Assessment (NCA5), which was published today.
Climate reporting will remain essential as we close out a year of record global temperatures, wildfires in Canada, Hawaii and the U.S. Southeast, droughts in the Amazon and Mississippi river basins, and billion-dollar flooding disasters in the U.S Northeast and California, aggravated by human-driven climate change.
AGU’s upcoming 2023 Annual Meeting, convening 11-15 December, will host authors from each of the NCA’s 32 chapters and feature deep ...
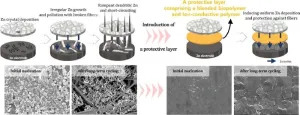
Using cosmetic ingredient for battery protection
2023-11-15
Xanthan gum, derived from plants like cabbage and known for its carbohydrate content, serves as a natural protective barrier in cosmetics to retain their benefits on the skin. In a recent development, this remarkable substance has been harnessed to create a protective shield for battery electrodes, rather than for the skin.
Professor Changshin Jo from the Graduate Institute of Ferrous & Eco Materials Technology and the Department of Chemical Engineering and Jooyoung Jang, a PhD candidate, from the Department of Chemical Engineering at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), have crafted a protective film by blending ...
SFI Press releases new editions of Murray Gell-Mann books
2023-11-15
The opening lines of Homer’s Odyssey describe its eponymous hero as polytropos, a man of many turns. It’s no coincidence that SFI co-founder Murray Gell-Mann invoked Homer’s crafty, long-voyaging hero when he envisioned the pinnacle of the scientific endeavor.
“Murray described his ideal scientist as an ‘Odyssean,’ one who lives somewhere between the analytical Apollonian and the intuitive Dionysian, one who loves to simplify yet is equally enamored of complication,” says David Krakauer, SFI President and Editor-in-Chief of the SFI Press. “Over the course of Murray’s life, he realized this ideal in his own ...
THE LANCET: Alarming new projections reveal soaring health risks of persistent global inaction over the climate emergency
2023-11-15
Peer-reviewed / Review and Analysis / People
The Lancet: Alarming new projections reveal soaring health risks of persistent global inaction over the climate emergency
New global projections in the 8th annual report of the Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change reveal the grave and mounting threat to health of further delayed action on climate change, with the world likely to experience a 4.7-fold increase in heat-related deaths by mid-century.
Report also highlights how climate inaction is costing lives and livelihoods today. In 2022, individuals were, on average, exposed to 86 days of health-threatening ...
COVID-19 showed the importance of genomic surveillance – now we need it to help fight antimicrobial resistance, say researchers
2023-11-15
During the COVID-19 pandemic, genomic surveillance proved vital in helping understand the evolution and spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Now, an international group of researchers is calling for its potential to be harnessed to tackle antimicrobial resistance (AMR), a major global challenge that could ultimately result in many more deaths than the coronavirus pandemic.
AMR already causes substantial sickness and death worldwide, responsible for approximately 1.27 million deaths in 2019. Some estimates suggest that by 2050, it could kill as many as 10 million people each year.
Professor Sharon Peacock at the University ...
UK soft drinks levy linked to fall in child hospital admissions for tooth extraction
2023-11-15
The UK soft drinks industry levy introduced in 2018 may have reduced the number of under 18s having a tooth removed due to tooth decay by 12%, suggests research published in the open access journal BMJ Nutrition, Prevention & Health.
The fall in hospital admissions may have saved more than 5,500 hospital admissions for tooth decay alone and the largest reductions were in children aged up to nine years old.
Sugar-sweetened drinks account for around 30% of the added sugars in the diets of children aged one to three years and over 50% by late ...
HIIT in water improves exercise capacity in adults with long term health conditions
2023-11-15
High-intensity interval training in water, often called aquatic HIIT (AHIIT) improves exercise capacity in adults with chronic conditions and has a similar impact as land based training (LBHIIT), suggests research published in the open access journal BMJ Open Sport & Exercise Medicine.
The researchers say AHIIT may provide a safe and valuable alternative for people with chronic conditions who are unable to perform LBHIIT.
HIIT is a type of interval training exercise that involves brief bursts of high intensity movements followed by short recovery periods of lower intensity movements.
HIIT is considered to have more health benefits than moderate-intensity ...
The Lancet: Deferred clamping of umbilical cord reduces risk of death in premature babies by at least a third, suggest two studies with the most comprehensive analysis to date
2023-11-15
Peer-reviewed / Systematic review and meta-analysis / People
The Lancet: Deferred clamping of umbilical cord reduces risk of death in premature babies by at least a third, suggest two studies with the most comprehensive analysis to date
Meta-analysis of 3,292 infants across 21 studies finds premature babies whose umbilical cord is clamped 30 seconds or more after birth are less likely to die before leaving the hospital, compared to those whose cord is clamped immediately after birth.
A second companion meta-analysis of 47 trials including 6,094 babies suggests waiting at least ...
[1] ... [1554]
[1555]
[1556]
[1557]
[1558]
[1559]
[1560]
[1561]
1562
[1563]
[1564]
[1565]
[1566]
[1567]
[1568]
[1569]
[1570]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.