(Press-News.org) Calm body, calm mind, say the practitioners of mindfulness. A new study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis indicates that the idea that the body and mind are inextricably intertwined is more than just an abstraction. The study shows that parts of the brain area that control movement are plugged into networks involved in thinking and planning, and in control of involuntary bodily functions such as blood pressure and heartbeat. The findings represent a literal linkage of body and mind in the very structure of the brain.
The research, published April 19 in the journal Nature, could help explain some baffling phenomena, such as why anxiety makes some people want to pace back and forth; why stimulating the vagus nerve, which regulates internal organ functions such as digestion and heart rate, may alleviate depression; and why people who exercise regularly report a more positive outlook on life.
“People who meditate say that by calming your body with, say, breathing exercises, you also calm your mind,” said first author Evan M. Gordon, PhD, an assistant professor of radiology at the School of Medicine’s Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology. “Those sorts of practices can be really helpful for people with anxiety, for example, but so far, there hasn’t been much scientific evidence for how it works. But now we’ve found a connection. We’ve found the place where the highly active, goal-oriented ‘go, go, go’ part of your mind connects to the parts of the brain that control breathing and heart rate. If you calm one down, it absolutely should have feedback effects on the other.”
Gordon and senior author Nico Dosenbach, MD, PhD, an associate professor of neurology, did not set out to answer age-old philosophical questions about the relationship between the body and the mind. They set out to verify the long-established map of the areas of the brain that control movement, using modern brain-imaging techniques.
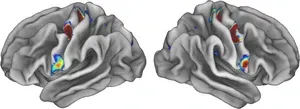
In the 1930s, neurosurgeon Wilder Penfield, MD, mapped such motor areas of the brain by applying small jolts of electricity to the exposed brains of people undergoing brain surgery, and noting their responses. He discovered that stimulating a narrow strip of tissue on each half of the brain causes specific body parts to twitch. Moreover, the control areas in the brain are arranged in the same order as the body parts they direct, with the toes at one end of each strip and the face at the other. Penfield’s map of the motor regions of the brain — depicted as a homunculus, or “little man” — has become a staple of neuroscience textbooks.
Gordon, Dosenbach and colleagues set about replicating Penfield’s work with functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). They recruited seven healthy adults to undergo hours of fMRI brain scanning while resting or performing tasks. From this high-density dataset, they built individualized brain maps for each participant. Then, they validated their results using three large, publicly available fMRI datasets — the Human Connectome Project, the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development Study and the UK Biobank — which together contain brain scans from about 50,000 people.
To their surprise, they discovered that Penfield’s map wasn’t quite right. Control of the feet was in the spot Penfield had identified. Same for the hands and the face. But interspersed with those three key areas were another three areas that did not seem to be directly involved in movement at all, even though they lay in the brain’s motor area.
Moreover, the nonmovement areas looked different than the movement areas. They appeared thinner and were strongly connected to each other and to other parts of the brain involved in thinking, planning, mental arousal, pain, and control of internal organs and functions such as blood pressure and heart rate. Further imaging experiments showed that while the nonmovement areas did not become active during movement, they did become active when the person thought about moving.
“All of these connections make sense if you think about what the brain is really for,” Dosenbach said. “The brain is for successfully behaving in the environment so you can achieve your goals without hurting or killing yourself. You move your body for a reason. Of course, the motor areas must be connected to executive function and control of basic bodily processes, like blood pressure and pain. Pain is the most powerful feedback, right? You do something, and it hurts, and you think, ‘I’m not doing that again.’”
Dosenbach and Gordon named their newly identified network the Somato (body)-Cognitive (mind) Action Network, or SCAN. To understand how the network developed and evolved, they
scanned the brains of a newborn, a 1-year-old and a 9-year-old. They also analyzed data that had been previously collected on nine monkeys. The network was not detectable in the newborn, but it was clearly evident in the 1-year-old and nearly adult-like in the 9-year-old. The monkeys had a smaller, more rudimentary system without the extensive connections seen in humans.
“This may have started as a simpler system to integrate movement with physiology so that we don’t pass out, for example, when we stand up,” Gordon said. “But as we evolved into organisms that do much more complex thinking and planning, the system has been upgraded to plug in a lot of very complex cognitive elements.”
Clues to the existence of a mind-body network have been around for a long time, scattered in isolated papers and inexplicable observations.
“Penfield was brilliant, and his ideas have been dominant for 90 years, and it created a blind spot in the field,” said Dosenbach, who is also an associate professor of biomedical engineering, of pediatrics, of occupational therapy, of radiology, and of psychological & brain sciences. “Once we started looking for it, we found lots of published data that didn’t quite jibe with his ideas, and alternative interpretations that had been ignored. We pulled together a lot of different data in addition to our own observations, and zoomed out and synthesized it, and came up with a new way of thinking about how the body and the mind are tied together.”
END
Mind-body connection is built into brain, study suggests
Findings point to brain areas that integrate planning, purpose, physiology, behavior, movement
2023-04-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Race, ethnicity–adjusted age recommendation for initiating breast cancer screening
2023-04-19
About The Study: This study of 415,000 breast cancer deaths in female patients in the U.S. from 2011 to 2020 provides evidence-based race-adapted starting ages for breast cancer screening. The findings suggest that health policy makers and clinicians could consider an alternative, race and ethnicity–adapted approach in which Black female patients start screening earlier.
Authors: Mahdi Fallah, M.D., Ph.D., of the German Cancer Research Center in Heidelberg, Germany, and Tianhui Chen, M.D., Ph.D., of the Zhejiang Cancer Hospital in Hangzhou, China, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Cognitive function in people with familial risk of depression
2023-04-19
About The Study: Depression in prior generations was associated with lower cognitive performance in offspring, whether assessed by family history or genetic data. There are opportunities to generate hypotheses about how this arises through genetic and environmental determinants, moderators of brain development and brain aging, and potentially modifiable social and lifestyle factors across the life span.
Authors: Breda Cullen, Ph.D., of the University of Glasgow in Glasgow, United Kingdom, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Nature publication on loops, flags and tension in DNA
2023-04-19
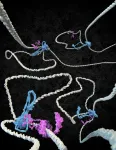
1 Cohesin loops DNA
It has been known for more than a century that the long DNA strands in cell nuclei are neatly folded into the characteristic shape of chromosomes, resembling bottlebrushes , in preparation for cell division. And also between divisions, chromosomes are organised into loops that are important for regulating the processing genetic information. In 2018, Dekker and his group were the first to visualise how SMC protein complexes such as condensin and cohesin extrude loops in DNA.
#2 CTCF flags have a direction and determine where a ...
Nature-study reveals new mechanism for DNA folding
2023-04-19
A hitherto unknown mechanism for DNA folding is described in a study in Nature published by researchers from Karolinska Institutet and the Max Planck Institute for Biophysics. Their findings provide new insights into chromosomal processes that are vital to both normal development and to prevent disease.
The DNA in our cells is organised into chromosomes, which are highly dynamic structures that are altered when genes are transcribed, when DNA damage is repaired or when chromosomes are compacte in preparation for cell division. These processes are affected by so called SMC protein complexes (SMC, Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes), which by mediating chromosomal interactions ...
New findings pave the way for stable organic solar cells that may enable cheap and renewable electricity generation
2023-04-19
Due to the recent improvements in the efficiency with which solar cells made from organic (carbon-based) semiconductors can convert sunlight into electricity, improving the long-term stability of these photovoltaic devices is becoming an increasingly important topic. Real-world applications of the technology demand that the efficiency of the photovoltaic device be maintained for many years. To address this key problem, researchers have studied the degradation mechanisms for the two components used in the light-absorbing layer of organic solar cells: the ‘electron donor’ and ‘electron ...
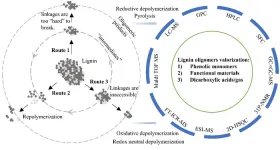
Perspective on oligomeric products from lignin depolymerization: their generation, identification, and further valorization
2023-04-19
Lignin depolymerization is playing a pivotal role in transforming the second most abundant biopolymers in nature into many valuable chemicals/fuels. This route could directly replace their petrol-based equivalents and therefore a great pathway to fight climate change and contribute to future sustainability. Interpretation of the reaction pathways is always desired to gain an insightful mechanic view in understanding the depolymerization chemistry and also paving new paths for lignin valorization at the industrial scale. However, such interpretation heavily relies on the state-of-art analytical capability since ...
UVA launches ambitious effort to reduce health disparities
2023-04-19
The University of Virginia School of Medicine has launched a new Center for Health Equity and Precision Public Health to improve the health and well-being of rural residents, the economically challenged and minority groups across Virginia and beyond.
The center will bring to bear expertise from across UVA to tackle many of today’s greatest public health issues. The goal: reduce health disparities and promote health equity to help people live longer, healthier lives.
“The pandemic has really taught us that, one, our public health infrastructure is not nearly as strong as it should be. And, two, we can't ...
Wonder drug-capsule may one day replace insulin injection for diabetics
2023-04-19
Scientists in Melbourne have designed a new type of oral capsule that could mean pain-free delivery of insulin and other protein drugs.
Co-lead researcher Professor Charlotte Conn, a biophysical chemist from RMIT University, said protein drugs had proven challenging to deliver orally as the drugs degrade very quickly in the stomach – until now.
“These types of drugs are typically administered with an injection – thousands of diabetics in Australia need insulin injections up to several times a day, which can be unpleasant for the patient and results in high healthcare costs,” said Conn, from RMIT’s School of Science.
She said the new technology could also be ...
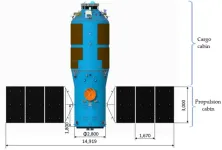
Scientists reviewed the research and development of Tianzhou cargo spacecraft
2023-04-19
Cargo spacecraft is robotic spacecraft designed to support space station operation by transporting food, propellant and other supplies. Tianzhou cargo spacecraft (The abbreviation is TZ) is a Chinese automated cargo spacecraft developed by the China Academy of Space Technology, as part of China's manned space Station program. The China Academy of Space Technology began to design TZ in 2010. Its main tasks are transporting and storing supplies for the space station, storing and descending waste materials for the space ...
SwRI launches the Global Decarbonized Mobility Summit Nov. 13-17
2023-04-19
SAN ANTONIO – 4.19.23 —Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) will host the inaugural Global Decarbonized Mobility Summit (GDMS) on Nov. 13-17. The multi-day summit will bring together key stakeholders in the transportation industry to discuss technology challenges associated with sustainable decarbonized mobility solutions for on-and-off-road applications.
The GDMS will assemble industry members from SwRI’s many automotive-related consortia and joint industry projects at its San Antonio headquarters. Throughout the summit, SwRI staff experts will hold sessions on the latest research and development advancements, pathways ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
[Press-News.org] Mind-body connection is built into brain, study suggestsFindings point to brain areas that integrate planning, purpose, physiology, behavior, movement