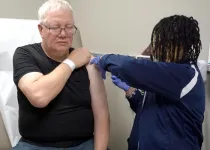
Survey finds many Americans are letting their guard down during respiratory illness season
2023-11-13
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Despite the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention warning this year will be potentially dangerous for respiratory illnesses, a third of Americans are not concerned about the threat, according to a new national survey by The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center.
The survey found that while the majority of those polled (87%) said they do everything they can to avoid spreading seasonal viruses, one-third think their vaccine decision doesn’t affect others and that they don’t need ...
New research maps 14 potential evolutionary dead ends for humanity and ways to avoid them
2023-11-13
For the first time, scientists have used the concept of evolutionary traps on human societies at large. They find that humankind risks getting stuck in 14 evolutionary dead ends, ranging from global climate tipping points to misaligned artificial intelligence, chemical pollution, and accelerating infectious diseases.
The evolution of humankind has been an extraordinary success story. But the Anthropocene — the proposed geological epoch shaped by us humans — is showing more and more cracks. Multiple global crises, such as the Covid-19 pandemic, climate change, food insecurity, financial crises, and conflicts have started to occur simultaneously ...
Lepodisiran, an extended-duration short interfering RNA targeting lipoprotein(a)
2023-11-12
About The Study: In this phase 1 study of 48 participants with elevated lipoprotein(a) levels, lepodisiran was well tolerated and produced dose-dependent, long-duration reductions in serum lipoprotein(a) concentrations. The findings support further study of lepodisiran, which is a short interfering RNA directed at hepatic synthesis of apolipoprotein(a), an essential component necessary for assembly of lipoprotein(a) particles.
Authors: Steven E. Nissen, M.D., of the Cleveland Clinic Center for Clinical Research in Cleveland, is the ...
Trial shows a single dose of an experimental therapy reduces lipoprotein(a), an important heart disease risk factor, more than 94% for nearly a year
2023-11-12
Cleveland: Findings from a phase 1 trial reported by a Cleveland Clinic physician show that a single dose of an experimental therapy produced greater than 94% reductions in blood levels of lipoprotein(a), a key driver of heart disease risk, with the results lasting for nearly a year.
Results from the “Efficacy and Safety of Lepodisiran: An Extended Duration Short-Interfering RNA Targeting Lipoprotein(a) Study” were presented today during a late-breaking science session at the American Heart ...
Gailen Marshall installed as ACAAI President
2023-11-12
ANAHEIM, Calif. (November 12, 2023) – Allergist Gailen Marshall, MD, PhD, of Jackson, MS, was installed as president of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI) at the ACAAI Annual Scientific Meeting on November 12 in Anaheim, Calif. Allergist James Tracy, DO, of Omaha, NE, was elected ACAAI president-elect.
Other newly elected ACAAI officers are Cherie Zachary, MD, Eagan, MN as vice president and Kelly Maples, MD, Norfolk, VA as treasurer. Regents elected for three-year terms include Aikaterini Anagnostou, MD, MSc, PhD, Houston, Texas, Brian T. Kelly, MD, MA, Omaha, Nebraska and Mervat Nassef, MD, New York, New ...
Decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate after dapagliflozin in heart failure with mildly reduced or preserved ejection fraction
2023-11-12
About The Study: Among patients with heart failure with mildly reduced ejection fraction or heart failure with preserved ejection fraction treated with dapagliflozin in this randomized clinical trial, an initial estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) decline was frequent but not associated with subsequent risk of cardiovascular or kidney events. These data reinforce clinical guidance that sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors should not be interrupted or discontinued in response to an initial eGFR decline.
Authors: Finnian R. Mc Causland, ...
2023 Joseph A. Johnson Award goes to Yale University professor of physics
2023-11-12
AIP and the National Society of Black Physicists congratulate Charles D. Brown II as the winner of the 2023 Joseph A. Johnson Award for Excellence. Dante O’Hara and Danielle Speller are also being recognized with Honorable Mentions.
The Johnson Award, now in its fourth year, is given by AIP and NSBP to recognize early-career scientists who demonstrate scientific ingenuity and impactful mentorship and service – the core values of NSBP founder Joseph A. Johnson.
“We are excited to recognize Dr. Brown’s impact on the physics community,” said Michael Moloney, CEO of AIP. ...
A high-risk antiphospholipid antibody profile matters in pediatric patients with antiphospholipid syndrome
2023-11-12
San Diego, CA, November 12, 2023 - A new study by Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) investigators has found that an initial high-risk antibody profile for antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) tended to remain high in pediatric patients. The results were presented today in a poster session at American College of Rheumatology (ACR) Convergence 2023, the ACR’s annual meeting.1
“There are a lot of unanswered questions about how APS affects pediatric patients since evidence to date has been very limited,” said Jheel Pandya, MD, a pediatric rheumatology fellow at HSS and lead author of the research. “Our study reveals that an initial high-risk ...
Hormonal contraceptives in teens may alter risk assessment
2023-11-12
[Embargoed until 1 p.m. (ET) Sunday, Nov. 12]
WASHINGTON – Hormonal contraceptives taken by adolescents may influence development of the brain in a way that alters the recognition of risks, a new study in rats suggests.
Scientists at The Ohio State University are exploring how common synthetic hormones used for birth control affect the prefrontal cortex, an area of the brain that continues to develop throughout adolescence.
The researchers found that myelination, the formation of protective coating on axons projecting from the main body of brain cells, increased in rats given hormonal birth control compared to untreated rats, while the number ...
Early-life stress changes more genes in brain than a head injury
2023-11-12
WASHINGTON – A surprising thing happened when researchers began exploring whether early-life stress compounds the effects of a childhood head injury on health and behavior later in life: In an animal study, stress changed the activation level of many more genes in the brain than were changed by a bump to the head.
It’s already known that head injuries are common in young kids, especially from falling, and can be linked to mood disorders and social difficulties that emerge later in life. Adverse childhood experiences are also very ...
Summer wildfire and winter air pollution and particulates linked to different risks of heart attack and severe chest pain, new study finds
2023-11-12
Short-term increases in air pollution can cause problems for a lot of people, but especially to those with diagnosed or undiagnosed heart disease. But it’s not just a potential issue for pollution coming from cars and industrial processes.
New research from Intermountain Health in Salt Lake City shows that pollutants trapped in lower, colder layers of air in mountain-region communities present sometimes higher risk for this population, while wildfire smoke from often distant locales may also impact risk.
“We’re finding that air pollution is affecting ...
New study finds current dosing recommendations may not help patients achieve optimal vitamin D levels
2023-11-12
Low levels of Vitamin D have been shown to be associated with a higher risk of having a cardiac event, like a heart attack or stroke. For this reason, treatment by Vitamin D pills or injections are being investigated as a possible preventative method in these patients.
However, two new studies from Intermountain Health in Salt Lake City have found that current dosing recommendations are not helping patients achieve optimal Vitamin D levels, suggesting that trials looking into the effectiveness of Vitamin D treatment to prevent cardiac events were not using appropriately sufficient doses, leading to inaccurate results.
In their studies, Intermountain ...
Study finds poor ventilation use during CPR for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest
2023-11-12
The ventilation technique, also known as rescue breathing, commonly used during cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) for people with cardiac arrest is often performed poorly by professional emergency responders, and this ineffective strategy is linked to significantly worse patient survival rates, according to a study supported by the National Institutes of Health. Ventilation involves administering breaths to a patient to provide life-sustaining oxygen and inflate the lungs when they stop breathing or during cardiac arrest, when the heart suddenly stops pumping blood. Among the nearly 2,000 ...
Blood thinner apixaban prevents strokes in patients with device-detected atrial fibrillation
2023-11-12
The widely available blood thinner apixaban substantially reduced stroke in at-risk patients with a type of atrial fibrillation only detectable by a pacemaker or other implanted cardiac electronic device, a global study has found.
The oral anticoagulant medication, which helps to prevent dangerous blood clots by thinning the blood, reduced the risk of stroke and blood clotting by 37% and reduced fatal or disabling stroke by 49% in individuals with device-detected atrial fibrillation, also known as sub-clinical atrial ...
New study finds genetic testing can effectively identify patients with family history of high cholesterol to prevent heart attack, stroke, and death
2023-11-12
Familial hypercholesteremia (FH) is an inherited condition that affects about 1 in 250 people, and often shows no signs until they have a heart attack. For individuals with FH the lowering of “bad” cholesterol levels can’t be done by dietary or behavioral changes, the problem is in their genes, and targeted medications therapy is needed.
Now, new research from the Intermountain Health in Salt Lake City has found that genetic screening can identify these patients and make them candidates for treatment that could prevent heart attack, stroke, and death.
“Most of these patients already had tests that ...
New study finds genetic testing is effective in identifying patients with inherited risk of cardiomyopathy to improve quality of life and reduce deaths
2023-11-12
New research from Intermountain Health in Salt Lake City finds that genetic screening is effective in identifying patients who have a heart condition known as cardiomyopathy to improve their quality of life and reduce deaths.
By undergoing genetic screening to identity those with the potentially-fatal heart condition, clinicians can more closely monitor them and use medical interventions, when necessary, that could improve the quality of these patients’ lives, and potentially save them, researchers say in a new study of more than 30,000 heart patients.
“Our findings show that we’re ...
HSS research shows obesity is associated with worse flare symptoms and quality of life in people with early rheumatoid arthritis
2023-11-12
SAN DIEGO, CA, NOVEMBER 12, 2023 — A recent study from Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) and others has found a correlation between obesity and more severe disease flare symptoms that negatively affect quality of life in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (RA), a systemic, autoimmune, inflammatory disorder affecting multiple joints in the body. The study will be presented at ACR Convergence 2023, the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
RA is usually treated with a combination of medications to relieve swelling and pain while regulating the immune ...
Long-term blood pressure control after hypertensive pregnancy following physician-optimized self-management
2023-11-11
About The Study: Self-monitoring and physician-guided titration of antihypertensive medications was associated with lower blood pressure during the first nine months postpartum than usual postnatal outpatient care in this randomized clinical trial involving 220 participants in the United Kingdom.
Authors: Paul Leeson, Ph.D., of the University of Oxford in Oxford, United Kingdom, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.21523)
Editor’s ...
Cut salt, cut blood pressure
2023-11-11
· High blood pressure is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality
· Losing one teaspoon of salt a day results in systolic blood pressure decline comparable to effect achieved with drugs
· First study to show people already on blood pressure medication could further lower their blood pressure by reducing sodium
Chicago --- Nearly everyone can lower their blood pressure, even people currently on blood pressure-reducing drugs, by lowering their sodium intake, reports a new study from Northwestern Medicine, Vanderbilt University Medical Center and the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
“In the study, ...
Effect of dietary sodium on blood pressure
2023-11-11
About The Study: Dietary sodium reduction significantly lowered blood pressure in the majority of middle-aged to elderly adults in this study including 213 participants. The decline in blood pressure from a high- to low-sodium diet was independent of hypertension status and antihypertensive medication use, was generally consistent across subgroups, and did not result in excess adverse events.
Authors: Deepak K. Gupta, M.D., M.S.C.I., of the Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.23651)
Editor’s ...
Aspirin and hemocompatibility events with a left ventricular assist device in advanced heart failure
2023-11-11
About The Study: This randomized clinical trial found that in patients with advanced heart failure treated with a fully magnetically levitated left ventricular assist device, avoidance of aspirin as part of an antithrombotic regimen, which includes a vitamin K antagonist, is not inferior to a regimen containing aspirin, does not increase thromboembolism risk, and is associated with a reduction in bleeding events.
Authors: Mandeep R. Mehra, M.D., M.Sc., of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
New AHA Center for Telehealth™ will increase access to quality health care and improve delivery
2023-11-11
According to the American Medical Association, approximately 25% of all patients used telehealth services during the last year, exceeding the 5% who accessed their care this way before the pandemic.[1] The American Heart Association (AHA) Center for Telehealth, unveiled today, recognizes the critical role telehealth can play as a solution to close gaps in health care access, particularly in rural and underserved areas, and deliver quality care to populations that have little to no access to traditional ...
New study finds coronary calcium scores highly effective in identifying heart disease in people without any known risk factors
2023-11-11
While high cholesterol, high blood pressure, diabetes and smoking are well known heart disease risks, not everyone who has a heart attack has them. In fact, previous research has shown that 14% to 27% of heart attack patients have none of these risk factors.
Now, a new study from researchers at Intermountain Health in Salt Lake City finds that these patients had one thing in common: they all tended to have high levels of coronary calcium.
Results of the new Intermountain study show that scans that detect this kind of plaque buildup should be considered as ...
Understanding the stressed, depressed, adolescent brain
2023-11-11
WASHINGTON — Advanced brain imaging techniques reveal how adolescent brain development influences, and is influenced by, factors including chronic stress and mood disorders. The findings will be presented on Monday, November 13, 11:15 a.m. – 12:15 p.m. EST at Neuroscience 2023, the annual meeting of the Society for Neuroscience and the world’s largest source of emerging news about brain science and health.
Adolescence is a time of social, biological, and emotional changes, as well as continued brain development. Mental health among teenagers was already declining before the COVID-19 pandemic, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control ...
The brain’s response to a changing environment
2023-11-11
WASHINGTON — Changes in a person’s environment can have long-term, significant effects on the brain, whether it’s the inhalation of wildfire smoke or the experience of childhood trauma. The findings will be presented on Tuesday, November 14, 11:15 a.m. – 12:15 p.m. at Neuroscience 2023, the annual meeting of the Society for Neuroscience and the world’s largest source of emerging news about brain science and health.
The environment plays an important role in a person’s brain health and cognitive function. Previous research has established that both one’s physical and social environment effect the brain and nervous system. Next, researchers ...
[1] ... [1562]
[1563]
[1564]
[1565]
[1566]
[1567]
[1568]
[1569]
1570
[1571]
[1572]
[1573]
[1574]
[1575]
[1576]
[1577]
[1578]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.