Financial traders may seek better sleep by self-medicating with caffeine and alcohol to balance the effects of the stimulant and the sedative, per micro-longitudinal study
2023-11-08
Financial traders may seek better sleep by self-medicating with caffeine and alcohol to balance the effects of the stimulant and the sedative, per micro-longitudinal study
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0291675
Article Title: Sleep, alcohol, and caffeine in financial traders
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Autism brain states hold the key to unlocking childhood memories
2023-11-08
Neuroscientists have discovered a fascinating connection between the retention of early life memories and brain developmental trajectories associated with autism [Wednesday 8th November 2023].
Most of us remember little of our experiences from before two years of age. This form of memory loss, termed “infantile amnesia” refers to the seemingly complete loss of episodic and autobiographical memories formed during early life. The research team at Trinity College Dublin investigated how infantile amnesia is affected by forms of autism.
The maternal immune response, sparked into life in response to infection during pregnancy, ...
Artificial bladders shine light on bugs that cause urinary tract infections
2023-11-08
The research, published today in Science Advances, is the first to use a sophisticated human tissue model to explore the interaction between host and pathogen for six common species that cause urinary tract infections. The findings suggest that the ‘one size fits all’ approach to diagnosis and treatment currently used in most healthcare systems is inadequate.
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a growing problem, with around 400 million global cases per year and an estimated 250,000 UTI-related deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance ...
Temperature increase triggers the viral infection
2023-11-08
Researchers at Lund University, together with colleagues at the NIST Synchrotron Facility in the USA, have mapped on an atomic level what happens in a virus particle when the temperature is raised.
"When the temperature rises, the virus's genetic material changes its form and density, becoming more fluid-like, which leads to its rapid injection into the cell," says Alex Evilevitch a researcher at Lund University who led the study.
Viruses lack their own metabolism and the ability to replicate independently; they are entirely dependent on a host cell to multiply. Instead, the virus hijacks the internal machinery of the infected cell ...
Molecule tested at University of São Paulo, in Brazil, proves able to mitigate heart failure
2023-11-08
Researchers at the University of São Paulo (USP) in Brazil, partnering with Foresee Pharmaceuticals, a Taiwan and US-based biopharmaceutical company, have tested a synthetic molecule for the treatment of heart failure. The study, funded by FAPESP, was published yesterday (11/07/2023) in the European Heart Journal. The theme was also highlighted in the magazine's editorial.
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart muscle cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's needs for blood and oxygen. It causes more deaths worldwide than any other disease, in the sense that other cardiovascular disorders ...
How mice choose to eat or to drink
2023-11-08
Making decisions is hard. Even when we know what we want, our choice often leaves something else on the table. For a hungry mouse, every morsel counts. But what if the decision is more consequential than choosing between crumbs and cheese?
Stanford researchers investigated how mice resolve conflicts between basic needs in a study published in Nature on Nov. 8. They presented mice that were both hungry and thirsty with equal access to food and water and watched to see what happened next.
The behavior of the mice surprised the scientists. Some gravitated first ...
Plant lifecycle insights: Big data can predict climate change impact
2023-11-08
The study is based on a new database created by the researchers which combines, for the first time, datasets on distribution and datasets on lifecycles, making it possible to establish the prevalence of different lifecycles around the globe. It uses empirical tools and big data to examine theoretical paradigms about the way in which human disturbance is affecting annual plants and their global distribution. Among other things, it was found that annuals are expected to benefit more with the rise in human population density and due to climate change, which ...
Scientists one step closer to re-writing world’s first synthetic yeast genome, unravelling the fundamental building blocks of life
2023-11-08
Scientists have engineered a chromosome entirely from scratch that will contribute to the production of the world’s first synthetic yeast.
Researchers in the Manchester Institute of Biotechnology (MIB) at The University of Manchester have created the tRNA Neochromosome – a chromosome that is new to nature.
It forms part of a wider project (Sc2.0) that has now successfully synthesised all 16 native chromosomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, common baker’s yeast, and aims to combine ...
Scientists take major step towards completing the world’s first synthetic yeast.
2023-11-08
A UK-based team of Scientists, led by experts from the University of Nottingham and Imperial College London, have completed construction of a synthetic chromosome as part of a major international project to build the world’s first synthetic yeast genome.
The work, which is published in Cell Genomics, represents completion of one of the 16 chromosomes of the yeast genome by the UK team, which is part of the biggest project ever in synthetic biology; the international synthetic yeast genome collaboration.
The collaboration, known as 'Sc2.0' has been a 15-year project involving teams from around the world (UK, US, China, Singapore, UK, France and Australia), working together ...
New antifungal molecule kills fungi without toxicity in human cells, mice
2023-11-08
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A new antifungal molecule, devised by tweaking the structure of prominent antifungal drug Amphotericin B, has the potential to harness the drug’s power against fungal infections while doing away with its toxicity, researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and collaborators at the University of Wisconsin-Madison report in the journal Nature.
Amphotericin B, a naturally occurring small molecule produced by bacteria, is a drug used as a last resort to treat fungal infections. While AmB excels at killing fungi, it is reserved ...
Cellular “atlas” built to guide precision medicine treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
2023-11-08
Research consortium investigators analyzed over 314,000 cells from rheumatoid arthritis tissue, defining six types of inflammation involving diverse cell types and disease pathways
Understanding the disease at single-cell level may advance targeted drug development and treatment strategies
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease characterized by inflammation that leads to pain, joint damage, and disability, which affects approximately 18 million people worldwide. While RA therapies targeted to specific inflammatory pathways have emerged, only some patients’ symptoms improve with treatment, emphasizing the need for multiple ...
Estimated effectiveness of co-administration of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine with influenza vaccine
2023-11-08
About The Study: In this study that included 3.4 million adults, co-administration of the BNT162b2 BA.4/5 bivalent mRNA COVID-19 vaccine (Pfizer-BioNTech) and seasonal influenza vaccine was associated with generally similar effectiveness in the community setting against COVID-19–related and seasonal influenza vaccine-related outcomes compared with giving each vaccine alone and may help improve uptake of both vaccines.
Authors: Leah J. McGrath, Ph.D., of Pfizer Inc., in New York, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Age at diagnosis of atrial fibrillation and incident dementia
2023-11-08
About The Study: Earlier onset of atrial fibrillation was associated with an elevated risk of subsequent all-cause dementia, Alzheimer disease, and vascular dementia in this study including 433,000 UK Biobank participants, highlighting the importance of monitoring cognitive function among patients with atrial fibrillation, especially those younger than 65 years at diagnosis.
Authors: Fanfan Zheng, Ph.D., of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College in Beijing, and Wuxiang Xie, Ph.D., of the Peking University First ...
Physicists trap electrons in a 3D crystal for the first time
2023-11-08
Electrons move through a conducting material like commuters at the height of Manhattan rush hour. The charged particles may jostle and bump against each other, but for the most part they’re unconcerned with other electrons as they hurtle forward, each with their own energy.
But when a material’s electrons are trapped together, they can settle into the exact same energy state and start to behave as one. This collective, zombie-like state is what’s known in physics as an electronic “flat band,” and scientists predict that when electrons are in this state they can start to ...
Scaling up nano for sustainable manufacturing
2023-11-08
A new self-assembling nanosheet could radically accelerate the development of functional and sustainable nanomaterials for electronics, energy storage, health and safety, and more.
Developed by a team led by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), the new self-assembling nanosheet could significantly extend the shelf life of consumer products. And because the new material is recyclable, it could also enable a sustainable manufacturing approach that keeps single-use packaging and electronics out of landfills.
The ...
Validating the role of inhibitory interneurons in memory
2023-11-08
Memory, a fundamental tool for our survival, is closely linked with how we encode, recall, and respond to external stimuli. Over the past decade, extensive research has focused on memory-encoding cells, known as engram cells, and their synaptic connections. Most of this research has centered on excitatory neurons and the neurotransmitter glutamate, emphasizing their interaction between specific brain regions.
To expand the understanding of memory, a research team led by KAANG Bong-Kiun (Seoul National University, Institute ...
Scientists tame biological trigger of deadly Huntington’s disease
2023-11-08
Huntington’s disease causes involuntary movements and dementia, has no cure, and is fatal. For the first time, UC Riverside scientists have shown they can slow its progression in flies and worms, opening the door to human treatments.
Key to understanding these advancements is the way that genetic information in cells is converted from DNA into RNA, and then into proteins. DNA is composed of chemicals called nucleotides: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). The order of these nucleotides determines what biological instructions are contained in a strand of DNA.
On occasion, some DNA nucleotides repeat themselves, ...
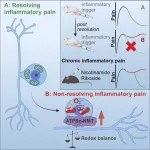
Disturbances in sensory neurons may alter transient pain into chronic pain
2023-11-08
Utrecht, November 8, 2023 - Researchers from the Center for Translational Immunology at University Medical Center Utrecht (the Netherlands) have identified that a transient inflammatory pain causes mitochondrial and redox changes in sensory neurons that persist beyond pain resolution. These changes appear to predispose to a failure in resolution of pain caused by a subsequent inflammation. Additionally, targeting the cellular redox balance prevents and treats chronic inflammatory pain in rodents.
Pain often persists in patients with an ...
SMU Lyle nanorobotics professor awarded prestigious research grant to make gene therapy safer
2023-11-08
DALLAS (SMU) – SMU nanotechnology expert MinJun Kim and his team have been awarded a $1.8 million, R01 grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) for research related to gene therapy – a technique that modifies a person’s genes to treat or cure disease.
NIH R01 (Research Program) grants are extremely competitive, with fewer than 10 percent of applicants receiving one.
The four-year grant will allow Kim, the Robert C. Womack Chair in the Lyle School of Engineering at SMU (Southern Methodist University) and principal investigator ...
$200M gift propels scientific research in the search for life beyond earth
2023-11-08
$200m Gift Propels Scientific Research in the Search for Life Beyond Earth
Legacy of Franklin Antonio represents quantum leap for The SETI Institute
November 8, 2023, Mountain View, CA – The SETI Institute, a non-profit scientific research organization, announced today a philanthropic gift of $200m from the estate of Franklin Antonio, a visionary supporter and catalyst of the work of the SETI Institute for more than 12 years. Co-founder of communications chip company, Qualcomm, Antonio passed away on May 13, 2022, leaving behind an extraordinary ...
Blood clotting risk quickly drops after stopping hormonal contraceptives
2023-11-08
(WASHINGTON, Nov. 8, 2023) – Using birth control pills and other hormone-based contraceptives is known to elevate the risk of blood clots about three-fold, but a new study suggests that this risk largely goes away within two to four weeks after one stops using these contraceptives, according to research published today in Blood.
The findings – the first to provide such confirmatory guidance on the best timing to stop contraception – can help patients and doctors weigh the benefits and risks of hormonal contraceptives and guide when to stop using them ahead of events that could further increase the risk of dangerous clots, such as major surgery, ...
New study highlights connection with strawberries, cognition and mood in middle-aged, overweight adults
2023-11-08
A new study published in Nutrients shows daily consumption of strawberries for 12 weeks reduced interference in memory and depressive symptoms among middle-aged, overweight adults with self-reported mild cognitive decline.
“Dementia is a general term that includes many different diseases, all without remedies,” says Robert Krikorian, Ph.D., principal investigator and professor in the department of psychiatry at the University of Cincinnati Academic Health Center. “It is not clear when ...
Identifying a silicon transporter to improve the yield of rice
2023-11-08
Silicon (Si) is abundant in terrestrial environments and accounts for 0.1% to 10% of a plant’s dry weight. Certain plant species show high levels of Si accumulation, and research has identified high Si accumulation as a protective mechanism against abiotic (drought, cold, heat) and biotic stressors (living organisms). Oryza sativa (rice) can store Si to the tune of 10% of the dry weight of shoots (stem, leaves, flowers), and Si is vital for stable grain production. High degree of Si deposition is believed to mitigate against damage caused ...
The American Pediatric Society selects Dr. Glenn Flores as the recipient of the 2024 David G. Nichols Health Equity Award
2023-11-08
The American Pediatric Society (APS) is pleased to announce Glenn Flores, MD, as the 2024 David G. Nichols Health Equity Award recipient.
The David G. Nichols Health Equity Award, administered by the APS and endowed by the American Board of Pediatrics (ABP) Foundation, was created to recognize demonstrated excellence in advancing child and adolescent health, well-being, and equity through quality improvement, advocacy, practice, or research. This award recognizes Dr. Flores’ outstanding contributions to advancing child and adolescent health, well-being, and equity and the ...
Device 'smells' seawater to discover, detect novel molecules
2023-11-08
Under the ocean’s surface, marine organisms are constantly releasing invisible molecules. Some of the chemical clues reveal which creatures are nearby, while others could be used someday as medications. Now, researchers in ACS Central Science report a proof-of-concept device that “sniffs” seawater, trapping dissolved compounds for analyses. The team showed that the system could easily concentrate molecules that are present in underwater caves and holds promise for drug discovery in fragile ecosystems, including coral reefs.
A ...
[1] ... [1557]
[1558]
[1559]
[1560]
[1561]
[1562]
[1563]
[1564]
1565
[1566]
[1567]
[1568]
[1569]
[1570]
[1571]
[1572]
[1573]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.