Oregon State to receive $6.5M for federal effort to modernize geospatial coordinate system
2023-11-09
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Oregon State University is one of four institutions selected to advance a federal effort to modernize the National Spatial Reference System, which underpins surveying, mapping, autonomous vehicle navigation, precision agriculture and the rest of the United States’ geospatial economy.
OSU will receive $6.5 million over five years from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration for research to be conducted by the new Geospatial Center for the Arctic and Pacific, or GCAP. The funding is through NOAA’s National Geodetic Survey and is part of nearly $20 million awarded overall.
The other funding ...
The Lancet: Studying medicine, Nazism, and the Holocaust crucial to strengthening medical education and ethics today
2023-11-09
Peer-reviewed/ review, analysis and opinion
The Lancet: Studying medicine, Nazism, and the Holocaust crucial to strengthening medical education and ethics today
Most comprehensive report to date on medical atrocities under Nazism and during the Holocaust – and their implications for today – details the central role health professionals played in formulating and carrying out the antisemitic, racist, and inhumane policies and practices during the Nazi regime.
The Commission challenges long-held misconceptions about medicine in the Nazi era, including the claim that medical crimes were carried out by only a ...
New study examines long term effectiveness of live shingles vaccine
2023-11-09
The effectiveness of live zoster (shingles) vaccine is highest in the first year after vaccination and then wanes substantially. But it continues to provide some protection against shingles and its complications ten years after vaccination, even in patients with a weakened immune system, finds a study published by The BMJ.
Vaccine effectiveness is a measure of how well vaccines work to protect communities in the real world.
Herpes zoster, commonly known as shingles, is a painful rash caused by reactivation of the chickenpox virus. It’s much more common among people aged 60 and older and those with a weakened ...
Latest results from PHOEBE trial show patients with advanced HER2-positive breast cancer live longer on pyrotinib
2023-11-09
Lisbon, Portugal: Patients with HER2-positive breast cancer that has started to spread to other parts of the body survive for longer if they are treated with a new drug called pyrotinib, according to results from the longest follow-up of the PHOEBE randomised clinical trial in China.
Presenting the latest results at the Advanced Breast Cancer Seventh International Consensus Conference (ABC 7), Professor Xichun Hu, of Fudan University Cancer Hospital, Shanghai, China, said the researchers had been able to analyse data on overall survival from the trial up to March 15, ...
Barnacle bends shape to fend off warm-water sea snails on the move
2023-11-09
Some barnacles are ‘morphing’ to protect themselves from predatory warm-water sea snails, which are expanding into their territory due to climate change.
Research led by the University of Southampton and published in the Journal of Biogeography shows how temperate prey species are adapting to changing water temperatures, which carry the threat of warm-water predators encroaching into their territory.
As global sea-surface temperatures rise and the number of marine heatwaves increase under global heating, coastal marine communities are changing. Warm-water predators ...
AI can map giant icebergs from satellite images 10,000 times faster than humans
2023-11-09
AI can map giant icebergs from satellite images 10,000 times faster than humans
Scientists have trained an artificial intelligence (AI) system to accurately map - in one-hundredth of a second - the surface area and outline of giant icebergs captured on satellite images.
It is a major advance on existing automated systems which struggle to distinguish icebergs from other features in the image. Manual - or human - interpretation of the image is more ...
People who contribute least in crowdsourcing can do the most to improve a public good
2023-11-08
Whether talking about the office kitchen, hiking trails or ratings on Yelp, there are always people who put in effort to leave those spaces better. There are also those who contribute nothing to that public good.
New research using large-scale online experiments suggests that rewarding people to contribute to a virtual public good, such as a simulated online rating for a ferry system, increased the accuracy of the ratings and improved the overall quality of that resource.
The multidisciplinary team, including researchers from the University of California, Davis; Hunter College, College of New York; the Max Planck Institute for ...
1 in 25 carries a genotype that is associated with a shortened lifespan
2023-11-08
1 in 25 carries a genotype that is associated with a shortened lifespan
Scientists at deCODE genetics, a subsidiary of Amgen, have published a study on actionable genotypes detected in the Icelandic population and their association with lifespan. The results of this study are among the things that have motivated the government of Iceland to announce a nationwide effort in precision medicine. As the delivery of precision medicine to a population requires considerable amount of data on genomics, transcriptomics and proteomics of the population, Icelanders are currently exceptionally well suited for ...
Zen and the art of mitochondrial maintenance: The machinery of death makes a healthier life
2023-11-08
While we all aspire for a long lifespan, what is most coveted is a long period of vigor and health, or “healthspan,” that precedes the inevitable decline of advancing age. Researchers at UC Santa Barbara have discovered that instruments of death that cells use to commit suicide when things go wrong contribute to making a longer and healthier life by revitalizing the specialized cellular compartments called mitochondria.
Mitochondria generate the energy for all of our activities, from movement to thought. These power plants inside our cells descended ...
MPFI researcher awarded $1.2 Million from Chan Zuckerberg Initiative
2023-11-08
Dr. Vidhya Rangaraju has been named a recipient of the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative’s “Ben Barres Early Career Acceleration Award,” which will provide her lab with $1.2 million over four years to study dysfunctions of brain energy supply.
Dr. Rangaraju is a Research Group Leader at the Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience (MPFI). With this award, her lab will investigate the causes of disrupted energy supply in neurons that lead to cognitive decline in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). ...
With new grant, RPI works to shrink microchips, expand semiconductor workforce
2023-11-08
Transistors — the tiny on-off switches inside microchips — have gotten smaller and smaller over the years, increasing computing power and enabling smaller devices. During that time, the copper wires that connect these switches have likewise shrunk.
However, smaller, thinner wires create a big problem, said Daniel Gall, professor of materials science and engineering at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute.
“The job of the wire is to conduct electrons — electricity. Imagine a wire as a crowded hallway that the electrons have to get through. The narrower the hallway, the more the electrons bump into things and scatter. We call that resistance,” Gall ...
Single gene controls Corn Belt weed's resistance to soil-applied herbicide
2023-11-08
URBANA, Ill. — Waterhemp, the aggressive weed threatening Corn Belt crop production, is throwing curveballs once again, according to researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign. The weed has famously developed resistance to not one or two, but seven herbicide sites-of-action classes, nearly exhausting the chemical tools farmers can use to defend their livelihood.
In a new Weed Science study, U. of I. researchers show that a single major gene is responsible for waterhemp’s resistance to S-metolachlor ...
Your education and income level may affect your survival, recovery from stroke
2023-11-08
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER 8, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – People with low education and income levels may have a 10% increased risk of death or being dependent on others to complete daily tasks three months after a stroke compared to people with high education and income levels, according to new research published in the November 8, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study does not prove that low education and income cause worse outcomes after stroke. It only shows an association.
“Compared ...
For epilepsy, yoga may be good for your mind
2023-11-08
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER 8, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – For people with epilepsy, doing yoga may help reduce feelings of stigma about the disease along with reducing seizure frequency and anxiety, according to new research published in the November 8, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
“People with epilepsy often face stigma that can cause them to feel different than others due to their own health condition and that can have a significant impact on their quality of life,” said study author ...
Increasing workplace flexibility associated with lower risk of cardiovascular disease
2023-11-08
Embargoed for release: Wednesday, November 8, 4:00 PM ET
Key points:
In a randomized trial of the cardiometabolic impacts of workplace interventions designed to reduce work-family conflict, older employees and those at baseline higher risk for cardiometabolic disease saw their risk of developing cardiovascular disease decrease equivalent to five to 10 years of age-related cardiometabolic changes.
The study is among the first to assess whether changes to the work environment can affect cardiometabolic risk.
Boston, MA—Increasing workplace flexibility may lower employees’ risk of cardiovascular disease, according to a new ...
New interactive evidence-based mapping tool gives policymakers more insight into highly concentrated cannabis products
2023-11-08
After conducting the first scoping review of its kind, researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have developed an evidence based interactive mapping tool to assist policymakers as they consider regulating the concentration of THC in cannabis products and as more potent products move into the marketplace.
Their review, funded by the State of Colorado, was released today in the American Journal of Public Health (AJPH).
“We looked at studies that measured adverse or beneficial effects of high concentration ...
Independent monitoring of the WHO pandemic agreement is non-negotiable, experts say
2023-11-08
An accountability framework, including independent monitoring of state compliance, is critical for the pandemic agreement's success, according to researchers at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health and affiliates at Spark Street Advisors. The paper and findings are published in BMJ Global Health.
“Countries signing up to a pandemic agreement is no guarantee of its effective implementation,” said Nina Schwalbe, adjunct assistant professor in the Department of Population and Family Health and principal visiting fellow at Columbia Mailman School. “Countries' lack of compliance with ...
NASA’s Webb findings support long-proposed process of planet formation
2023-11-08
Scientists using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope just made a breakthrough discovery in revealing how planets are made. By observing water vapor in protoplanetary disks, Webb confirmed a physical process involving the drifting of ice-coated solids from the outer regions of the disk into the rocky-planet zone.
Theories have long proposed that icy pebbles forming in the cold, outer regions of protoplanetary disks — the same area where comets originate in our solar system — should be the fundamental seeds of planet formation. The main requirement of these theories is that pebbles should drift inward toward the star due to friction in the gaseous disk, ...
UTIA faculty member serves as editor of the Journal of Food Distribution Research
2023-11-08
Carlos Trejo-Pech, an associate professor in the Department of Agricultural and Resource Economics at the University of Tennessee Institute of Agriculture, is a newly appointed editor of the Journal of Food Distribution Research.
“It is a great honor and big responsibility to serve as a journal editor of a publication outlet in the agricultural economics and agribusiness discipline,” said Trejo-Pech. “We, the editors, are committed to disseminating the results of high-quality research.”
The journal was established in 1969 under the auspices of the Food Distribution Research Society, the only body of scholars and practitioners in the United States dedicated ...
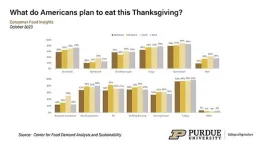
October Consumer Food Insights Report highlights thanksgiving meal plans
2023-11-08
October Consumer Food Insights Report highlights Thanksgiving meal plans
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Nearly eight in 10 Americans will celebrate the upcoming Thanksgiving holiday with a special meal, according to the October 2023 Consumer Food Insights Report.
The survey-based report out of Purdue University’s Center for Food Demand Analysis and Sustainabilityassesses food spending, consumer satisfaction and values, support of agricultural and food policies, and trust in information sources. Purdue ...
Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Small change, big effect
2023-11-08
Hodgkin’s lymphoma is one of the most common types of lymphoma in young adults. It is characterized by the presence of enlarged B lymphocytes, which are unusual in that they bear on their surface the identifying markers of many other immune cells – such as those found on phagocytes, dendritic cells, or T cells. Now, a team led by Stephan Mathas from the Experimental and Clinical Research Center (ECRC) has explained how these changes take place in the cells and what impact they have. The ECRC is a joint institution of the Max Delbrück Center and Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin.
“Many different ...
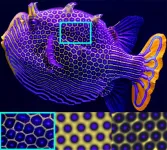
How animals get their stripes and spots
2023-11-08
Nature has no shortage of patterns, from spots on leopards to stripes on zebras and hexagons on boxfish. But a full explanation for how these patterns form has remained elusive.
Now engineers at the University of Colorado Boulder have shown that the same physical process that helps remove dirt from laundry could play a role in how tropical fish get their colorful stripes and spots. Their findings were published Nov. 8 in the journal Science Advances.
“Many biological questions are fundamentally ...
A fifth of European Red List flora and fauna species may be at risk of extinction
2023-11-08
A new analysis of 14,669 threatened species of plants and animals found in Europe reveals that about one fifth face the risk of extinction, and that agricultural land-use change poses a significant threat to these species. Axel Hochkirch of the Musée National d’Histoire Naturelle, Luxembourg, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on November 8, 2023.
The variety of species of living things—biodiversity—is declining around the world, as more and more species face the risk of extinction. Many efforts, including some by governments and nonprofit organizations, aim to reduce the loss ...
Head lice evolution mirrors human migration and colonization in the Americas
2023-11-08
A new analysis of lice genetic diversity suggests that lice came to the Americas twice – once during the first wave of human migration across the Bering Strait, and again during European colonization. Marina Ascunce, currently at the USDA-ARS, and colleagues, report these findings in a new study published November 8 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE.
The human louse is a wingless, blood-sucking parasite that lives its entire life on its host. It is one of the oldest known parasites to live on humans, and the two species have coevolved ...
A digital detox may not improve wellbeing: social media users who reduced their use for a week saw decreases in positive emotions as well as in negative ones
2023-11-08
A digital detox may not improve wellbeing: social media users who reduced their use for a week saw decreases in positive emotions as well as in negative ones
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0293467
Article Title: Restricting social networking site use for one week produces varied effects on mood but does not increase explicit or implicit desires to use SNSs: Findings from an ecological momentary assessment study
Author Countries: UK
Funding: This work was supported by the Economic and Social Research ...
[1] ... [1556]
[1557]
[1558]
[1559]
[1560]
[1561]
[1562]
[1563]
1564
[1565]
[1566]
[1567]
[1568]
[1569]
[1570]
[1571]
[1572]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.