The Paul G. Allen Frontiers Group announces Allen Discovery Center for Neuroimmune Interactions at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
2023-11-09
SEATTLE, W.A.—November 9, 2023—The Paul G. Allen Frontiers Group, a division of the Allen Institute, today announced the launch of the Allen Discovery Center (ADC) for Neuroimmune Interactions at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. The research team will comprehensively define and map the interactions between the nervous system and the immune system that take place distant from the brain, such as at the skin, lung, and gut surfaces, and analyze how these interactions relay a variety of sensations back to the brain and regulate organ physiology and tissue immune responses.
"Understanding ...
Lei Shi elected as a member of the STM Board
2023-11-09
On 16 October 2023, the newly elected STM Board Members were announced at the Annual General Meeting. Lei Shi, the Deputy Editor-in-Chief of Tsinghua University Press (TUP), and the Director of both the Journal Publishing Center and Academic Publishing Center of TUP has been elected to the designated seat representing non-Europe/US based companies. He became the first Chinese representative on the STM Board.
STM is the world’s leading association of scholarly publishers, who is committed to advance trusted research for ...
UTSA MATRIX AI Consortium receives $2 million to make AI more efficient
2023-11-09
The National Science Foundation (NSF) has awarded a $2 million grant through its Emerging Frontiers in Research Initiatives (EFRI) program to investigators at the UTSA MATRIX AI Consortium for Human Well-Being for research that will help bridge the gap between human brain processing efficiency and the limitations of current artificial intelligence (AI) models.
This endeavor seeks to create a new form of AI that rapidly learns, adapts to and operates in uncertain conditions, all while effectively addressing ...
Incheon National University researchers push the limits of gas sensing technology
2023-11-09
The world has become increasingly industrialized over the past few centuries, bringing all sorts of technology and conveniences to the masses. However, workers in industrial environments are often at the risk of exposure to many dangerous gases, such as nitrogen dioxide (NO2). Inhaling this gas can lead to serious respiratory diseases like asthma and bronchitis, and severely compromise the health of industrial workers. Constant monitoring of NO2 levels is thus needed to ensure a safe workplace.
To help with this, many types of selective gas sensors have been developed using different ...
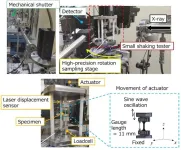
Understanding the dynamic behavior of rubber materials
2023-11-09
Rubber-like materials, commonly used in dampeners, possess a unique property known as dynamic viscoelasticity, enabling them to convert mechanical energy from vibrations into heat while exhibiting spring-like and flow-like behaviors simultaneously. Customization of these materials is possible by blending them with compounds of specific molecular structures, depending on the dynamic viscosity requirements.
However, the underlying mechanisms behind the distinct mechanical properties of these materials remain unclear. A primary reason for this knowledge gap has been the absence of a comprehensive system capable of simultaneously ...
Allergic responses to common foods could significantly increase risk of heart disease, cardiovascular death
2023-11-09
EMBARGOED UNTIL 9:05 A.M. UTC ON NOV. 9, 2023
Sensitivity to common food allergens such as dairy and peanuts could be an important and previously unappreciated cause of heart disease, new research suggests – and the increased risk for cardiovascular death includes people without obvious food allergies.
That increased risk could be comparable to – or exceed – the risks posed by smoking, as well as diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis, the researchers report.
UVA Health scientists and their collaborators looked at thousands of adults over time and found that people who produced antibodies in ...
Antibodies to cow’s milk linked to increased risk of cardiovascular death
2023-11-09
Sensitivity to common food allergens such as cow’s milk and peanuts could be an important and previously unappreciated cause of heart disease, new research suggests – and the increased risk for cardiovascular death includes people without obvious food allergies.
In a paper published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology that describes analyses led by Corinne Keet, M.D., Ph.D., pediatric allergy and immunology professor in the UNC Department of Pediatrics of two longitudinal studies, the authors show that the people who produced IgE antibodies to cow’s milk and other foods were at significantly increased risk of cardiovascular mortality. This was true even ...
Palaeo-CSI: Mosasaurs were picky eaters
2023-11-09
Joint press release Utrecht University and Natural History Museum Maastricht
The cradle of palaeontology – the study of fossil remains of animals and plants – lies in the Maastricht limestones, where the first Mosasaurus was discovered in 1766. The Dutch-Belgian border area around the Limburg capital is one of the best-explored areas in the world where Cretaceous rocks are concerned, the era that came to an abrupt end 66 million years ago. New data can now be added to all previous knowledge: the Maastricht mosasaurs turned out to be quite picky in their choice of diet. This ...
AI algorithm developed to measure muscle development, provide growth chart for children
2023-11-09
Leveraging artificial intelligence and the largest pediatric brain MRI dataset to date, researchers have now developed a growth chart for tracking muscle mass in growing children. The new study led by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, found that their artificial intelligence-based tool is the first to offer a standardized, accurate, and reliable way to assess and track indicators of muscle mass on routine MRI. Their results were published today in Nature Communications.
“Pediatric cancer patients often struggle with low ...
A breath of fresh air keeps drug-producing cells alive longer
2023-11-09
Cell-based therapies show promise for drug delivery, replacing damaged tissues, harnessing the body’s own healing mechanisms and more
But keeping cells alive to produce therapies has remained a challenge
Researchers used a smart, energy-efficient version of water splitting to produce oxygen for these cells
New approach maintains cells in vitro and in vivo, showing promise for both acute and chronic applications
EVANSTON, Ill. — In 2021, a Northwestern University-led research team received a Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) contract worth up to $33 million to develop an ...
Smartphones and smart speakers may be able to detect alcohol intoxication by analyzing voice patterns: Study
2023-11-09
By Kimberly Flynn
PISCATAWAY, NJ—Sensors in smartphones and smart speakers could help determine a person’s level of alcohol intoxication based on the changes in their voice, according to a new study in the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs.
Researchers at Stanford Medicine and the University of Toronto conducted a small study of 18 adults ages 21 and up. Participants were given a weight-based dose of alcohol and randomly assigned a series of tongue twisters—one before drinking, and one each hour up to seven hours after drinking.
The participants were asked to read the tongue twister aloud, and a smartphone was placed on a table withing ...
Forests with multiple tree species are 70% more effective as carbon sinks than monoculture forests
2023-11-09
To slow the effects of climate change, conserve biodiversity, and meet the sustainable development goals, replanting trees is vital. Restored forests store carbon within the forest’s soil, shrubs, and trees. Mixed forests are especially effective at carbon storage, as different species with complementary traits can increase overall carbon storage. Compared to single-species forests, mixed forests are also more resilient to pests, diseases, and climatic disturbances, which increases their long-term carbon storage potential. The delivery of other ecosystem services is also greater in mixed species forests, and they support higher levels of biodiversity.
Although the benefits ...
Umbilical cord milking appears to be safe in preterm infants born after 28 weeks
2023-11-09
WHAT:
A treatment to move blood from the umbilical cord into an infant’s body may provide a safe option for preterm infants born after 28 weeks who need rapid support, suggests a study supported by the National Institutes of Health. The procedure, called umbilical cord milking, involves gently squeezing the cord between the thumb and forefinger and pushing the blood into the newborn’s abdomen. The new findings suggest that concerns raised by a 2019 study of infants born before 28 weeks—which concluded that umbilical cord milking might increase the risk of bleeding inside the brain—do not apply to preterm infants born after 28 weeks. The ...
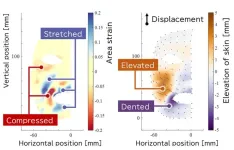
How human faces can teach androids to smile
2023-11-09
Osaka, Japan – Robots able to display human emotion have long been a mainstay of science fiction stories. Now, Japanese researchers have been studying the mechanical details of real human facial expressions to bring those stories closer to reality.
In a recent study published by the Mechanical Engineering Journal, a multi-institutional research team led by Osaka University have begun mapping out the intricacies of human facial movements. The researchers used 125 tracking markers attached to a person’s face to closely examine 44 different, singular facial actions, such as blinking or raising the corner of the mouth.
Every facial expression comes with a variety of local deformation ...
Grant helps program expand distracted driving education to online learning
2023-11-09
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) estimates there were 42,795 deaths resulting from motor vehicle crashes in 2022 in the United States. This projection is close to the previous year fatality numbers, which were the highest in 16 years.
A Herbert Wertheim School of Public Health and Human Longevity Science at University of California San Diego program aims to improve safety for all roadway users, including drivers, pedestrians and cyclists with support from a $360,000 grant from the California Office of Traffic Safety through the NHTSA.
To inform and promote safe driving, the UC San Diego Training, Research and Education for Driving Safety (TREDS) provides ...
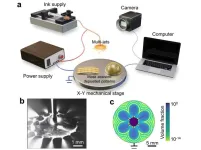
HKUST researchers develop low-cost and multifunctional microprinter for ultrafast piezoelectric material printing
2023-11-09
A research team led by The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has developed a microprinter that can print piezoelectric films 100 times faster for the production of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) for sensors, wearable or implantable medical devices, offering the possibility to lower the mass production costs.
The microprinter, built at a comparatively lower cost as compared with other printers on the market, utilizes an electrostatic field to propel streams of ink onto a platform, allowing for efficient manipulation of thin film patterns and enhanced printing speed to address the challenge of mass production ...
Oregon State to receive $6.5M for federal effort to modernize geospatial coordinate system
2023-11-09
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Oregon State University is one of four institutions selected to advance a federal effort to modernize the National Spatial Reference System, which underpins surveying, mapping, autonomous vehicle navigation, precision agriculture and the rest of the United States’ geospatial economy.
OSU will receive $6.5 million over five years from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration for research to be conducted by the new Geospatial Center for the Arctic and Pacific, or GCAP. The funding is through NOAA’s National Geodetic Survey and is part of nearly $20 million awarded overall.
The other funding ...
The Lancet: Studying medicine, Nazism, and the Holocaust crucial to strengthening medical education and ethics today
2023-11-09
Peer-reviewed/ review, analysis and opinion
The Lancet: Studying medicine, Nazism, and the Holocaust crucial to strengthening medical education and ethics today
Most comprehensive report to date on medical atrocities under Nazism and during the Holocaust – and their implications for today – details the central role health professionals played in formulating and carrying out the antisemitic, racist, and inhumane policies and practices during the Nazi regime.
The Commission challenges long-held misconceptions about medicine in the Nazi era, including the claim that medical crimes were carried out by only a ...
New study examines long term effectiveness of live shingles vaccine
2023-11-09
The effectiveness of live zoster (shingles) vaccine is highest in the first year after vaccination and then wanes substantially. But it continues to provide some protection against shingles and its complications ten years after vaccination, even in patients with a weakened immune system, finds a study published by The BMJ.
Vaccine effectiveness is a measure of how well vaccines work to protect communities in the real world.
Herpes zoster, commonly known as shingles, is a painful rash caused by reactivation of the chickenpox virus. It’s much more common among people aged 60 and older and those with a weakened ...
Latest results from PHOEBE trial show patients with advanced HER2-positive breast cancer live longer on pyrotinib
2023-11-09
Lisbon, Portugal: Patients with HER2-positive breast cancer that has started to spread to other parts of the body survive for longer if they are treated with a new drug called pyrotinib, according to results from the longest follow-up of the PHOEBE randomised clinical trial in China.
Presenting the latest results at the Advanced Breast Cancer Seventh International Consensus Conference (ABC 7), Professor Xichun Hu, of Fudan University Cancer Hospital, Shanghai, China, said the researchers had been able to analyse data on overall survival from the trial up to March 15, ...
Barnacle bends shape to fend off warm-water sea snails on the move
2023-11-09
Some barnacles are ‘morphing’ to protect themselves from predatory warm-water sea snails, which are expanding into their territory due to climate change.
Research led by the University of Southampton and published in the Journal of Biogeography shows how temperate prey species are adapting to changing water temperatures, which carry the threat of warm-water predators encroaching into their territory.
As global sea-surface temperatures rise and the number of marine heatwaves increase under global heating, coastal marine communities are changing. Warm-water predators ...
AI can map giant icebergs from satellite images 10,000 times faster than humans
2023-11-09
AI can map giant icebergs from satellite images 10,000 times faster than humans
Scientists have trained an artificial intelligence (AI) system to accurately map - in one-hundredth of a second - the surface area and outline of giant icebergs captured on satellite images.
It is a major advance on existing automated systems which struggle to distinguish icebergs from other features in the image. Manual - or human - interpretation of the image is more ...
People who contribute least in crowdsourcing can do the most to improve a public good
2023-11-08
Whether talking about the office kitchen, hiking trails or ratings on Yelp, there are always people who put in effort to leave those spaces better. There are also those who contribute nothing to that public good.
New research using large-scale online experiments suggests that rewarding people to contribute to a virtual public good, such as a simulated online rating for a ferry system, increased the accuracy of the ratings and improved the overall quality of that resource.
The multidisciplinary team, including researchers from the University of California, Davis; Hunter College, College of New York; the Max Planck Institute for ...
1 in 25 carries a genotype that is associated with a shortened lifespan
2023-11-08
1 in 25 carries a genotype that is associated with a shortened lifespan
Scientists at deCODE genetics, a subsidiary of Amgen, have published a study on actionable genotypes detected in the Icelandic population and their association with lifespan. The results of this study are among the things that have motivated the government of Iceland to announce a nationwide effort in precision medicine. As the delivery of precision medicine to a population requires considerable amount of data on genomics, transcriptomics and proteomics of the population, Icelanders are currently exceptionally well suited for ...
Zen and the art of mitochondrial maintenance: The machinery of death makes a healthier life
2023-11-08
While we all aspire for a long lifespan, what is most coveted is a long period of vigor and health, or “healthspan,” that precedes the inevitable decline of advancing age. Researchers at UC Santa Barbara have discovered that instruments of death that cells use to commit suicide when things go wrong contribute to making a longer and healthier life by revitalizing the specialized cellular compartments called mitochondria.
Mitochondria generate the energy for all of our activities, from movement to thought. These power plants inside our cells descended ...
[1] ... [1568]
[1569]
[1570]
[1571]
[1572]
[1573]
[1574]
[1575]
1576
[1577]
[1578]
[1579]
[1580]
[1581]
[1582]
[1583]
[1584]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.